https://doi.org/10.59459/1859-1655/JMM.522
ĐẶCĐIỂMLOẠNTHẦNVÀMỐILIÊNQUANVỚIMỘTSỐ
CHỈSỐSINHHÓAMÁUỞ62BỆNHNHÂNHỘICHỨNG
CAIRƯỢU,ĐIỀUTRỊTẠIBỆNHVIỆNQUÂNY103
TốngThọThắng
1
,ĐoànKimCúc
1
LêVănQuân
1
,NguyễnVănLinh
1
,ĐỗXuânTĩnh
1
TÓMTẮT
Mụctiêu:Môtảđặcđiểmloạnthầnvàtìmhiểumốiliênquangiữaloạnthầnvớimộtsốchỉsốsinhhóa
máuởcácbệnhnhânhộichứngcairượu.
Đốitượngvàphươngphp:Nghiêncứuhồicứukếthợptiếncứumôtảcắtngangvềđặcđiểmloạnthần
vàmốiliênquanvớimộtsốchỉsốsinhhóamáutrên62bệnhnhânhộichứngcairượu,điềutrịnộitrútại
KhoaTâmthần,BệnhviệnQuâny103,từtháng6/2023đếntháng4/2024.
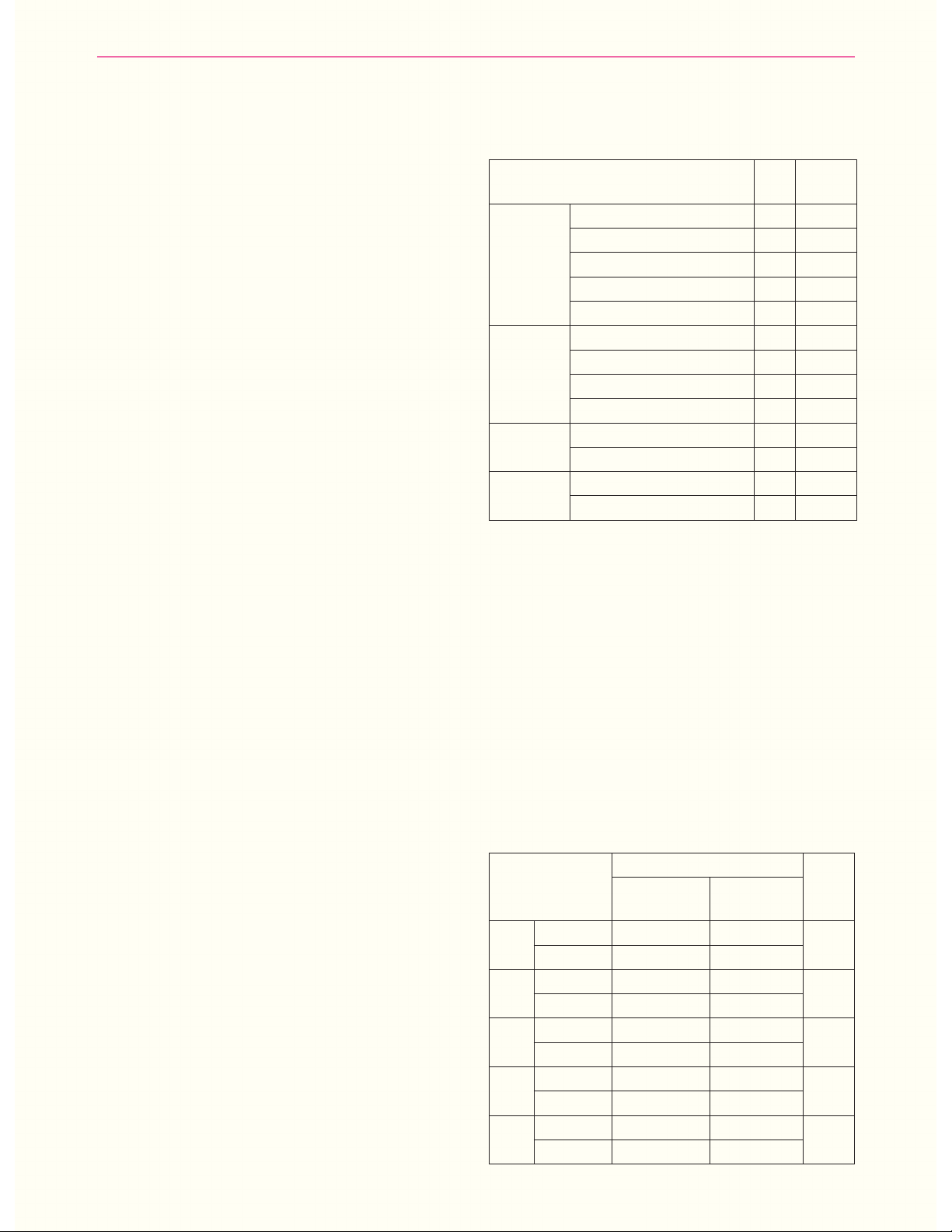
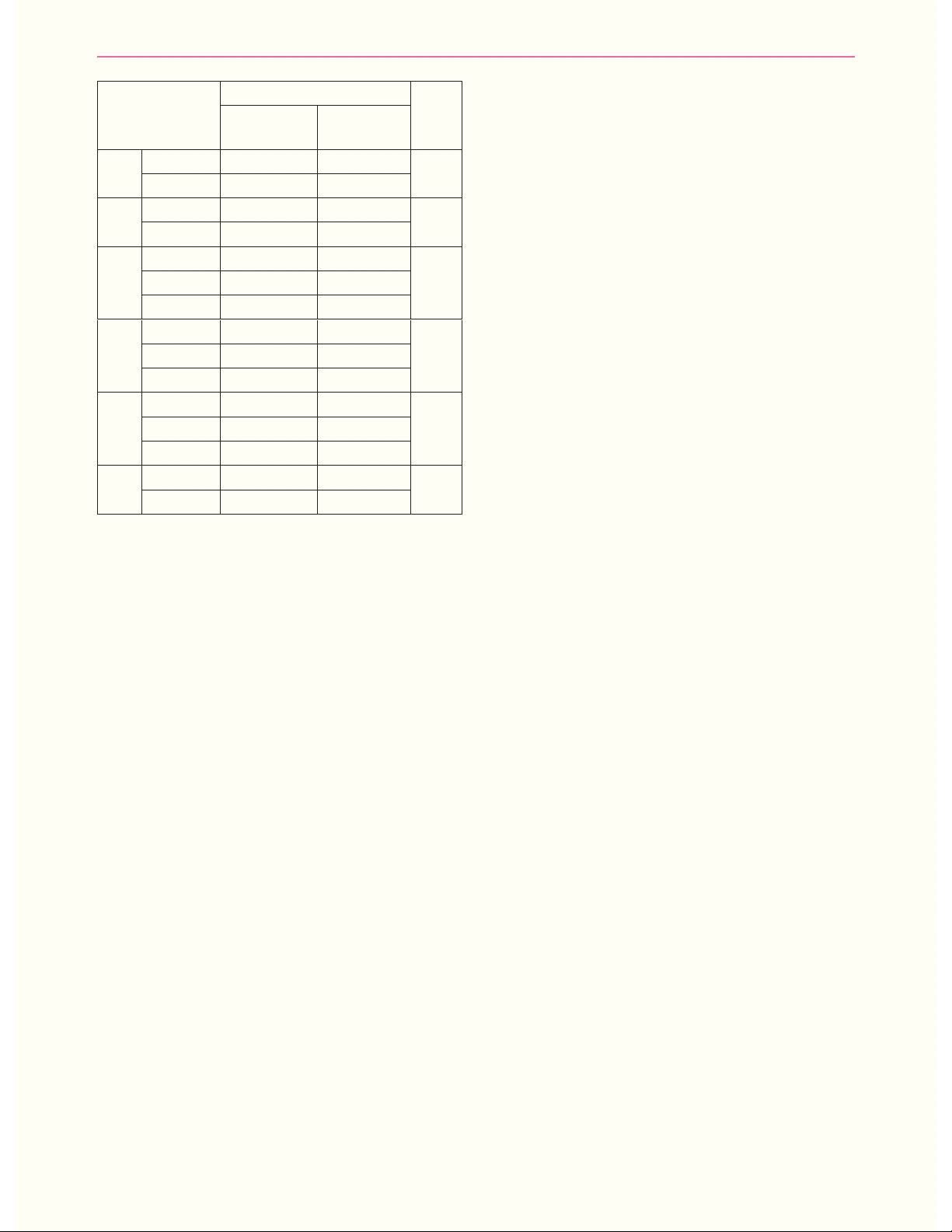
Kếtquả:Tỉlệbệnhnhânloạnthầnchỉcóảogiácchiếm24,19%;chỉcóhoangtưởngchiếm8,06%;cócả
hoangtưởngvàảogiácchiếm16,13%.Trongsốcácbệnhnhâncóảogiác,tỉlệảothịđộngvậtvàcôn
trùngnhỏchiếm32,26%;ảothịmaquỷvàảothanhbìnhphẩmcùngchiếm19,35%.Trongsốbệnhnhân
cóhoangtưởng,tỉlệhoangtưởngbịhạichiếm16,13%;hoangtưởngghentuôngchiếm9,68%.Cótỉlệ
lớnbệnhnhânloạnthầnkèmtheotăngnồngđộmộtsốchỉsốsinhhóamáu,nhưngsosánhkhôngkhác
biệtgiữanhómcóloạnthầnvànhómkhôngloạnthần,vớip>0,05.
Từkhóa:Hộichứngcairượu,đặcđiểmloạnthần,chỉsốsinhhoámáu.
ABSTRACT
Objectives:Tostudythecharacteristicsofpsychosisandanalyzetherelationshipbetweenpsychosisand
certainbiochemicalindicesinpatientswithalcoholwithdrawalsyndrome.
Subjectsandmethods:Across-sectionaldescriptivestudyexaminingtherateofpsychoticfeaturesand
biochemicalindicesin62patientswithalcoholwithdrawalsyndrometreatedasinpatientsatthePsychiatry
Department,MilitaryHospital103,fromJune2023toApril2024.
Results:Thegroupofpatientswithonlyhallucinationsaccountedforthelargestproportion,with24.19%
ofpatients;8.06%ofpatientshadonlydelusions,and16.13%hadbothdelusionsandhallucinations.The
mostcommonhallucinationswerevisualhallucinationsofsmallanimals,accountingfor32.26%,followed
byvisualhallucinationsofghostsandauditoryhallucinationswitharateof19.35%each.Themostcommon
delusionswereparanoiddelusionsat16.13%,followedbyjealousydelusionsat9.68%.Mostpatientswith
psychosishadelevatedbiochemicalbloodindices,buttherewasnosignicantdifferencebetweenthe
groupswithandwithoutpsychosis(p>0.05).
Keywords:Alcoholwithdrawalsyndrome,psychoticsymptoms,bloodbiochemicalindex.
Chịutráchnhiệmnộidung:ĐỗXuânTĩnh,Email:doxuantinhbv103@gmail.com
Ngàynhậnbài:26/8/2024;mờiphảnbiệnkhoahọc:08/2024;chấpnhậnđăng:30/8/2024.
BệnhviệnQuâny103.
1.ĐẶTVẤNĐỀ
ViệtNamlàquốcgiacólượngtiêuthụrượubialớn
trênthếgiới.TạiViệtNam,khảosáttrên5.200người
dânnăm2018,thấy60%đãtừngsửdụngrượubia
vàlượngtiêuthụtrungbìnhmộtngàycủamộtngười
tươngđương14,7gcồnnguyênchất;lượngrượubia
khôngnhãnmácsửdụngtrungbìnhởđốitượngnam
giớicaoxấpxỉgấp12lầnsovớiởnữgiới[1].
Rượulànguyênnhânđứngthứbảytrongsốcác
nguyênnhânhàngđầugâytửvongvàtàntậttrên
toàncầu.Sửdụng rượu lâungàysẽdẫnđếntình
trạngnghiệnrượu-mộttìnhtrạngbệnhlímạntính
ảnhhưởngđếnsứckhỏethểchấtvàtâmthần,gây
ảnhhưởngxấuđếnhiệusuấtcôngtácvàcácmối
quanhệgiađình,cộngđồng,xãhội[2].Tuynhiên,
khi người nghiệnrượu ngừng hoặc giảm độtngột
lượngrượutiêuthụsẽxuấthiệnhộichứngcairượu
(HCCR),gâyảnhhưởnglớntớisứckhỏethểchất
vàtâmthầncủangườibệnh,đặcbiệtlàtìnhtrạng
loạnthầndorượu.Mộtsốnghiêncứuchorằng,bệnh
nhân(BN)mắcHCCRdođãsửdụngrượutrongthời
52 TạpchíYHỌCQUÂNSỰ,SỐ374(01-02/2025)
NGHIÊNCỨU-TRAOĐỔI