http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 1 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 9, Issue 5, September–October 2018, pp. 1–9, Article ID: IJM_09_05_001
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=5
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
PUBLIC EXPENDITURE AND NATIONAL
INCOME OF INDIA: INVESTIGATING
WAGNERIAN LAW
Dhyani Mehta
Assistant Professor, Economics and Finance,
Institute of Management, Nirma University, India
ABSTRACT
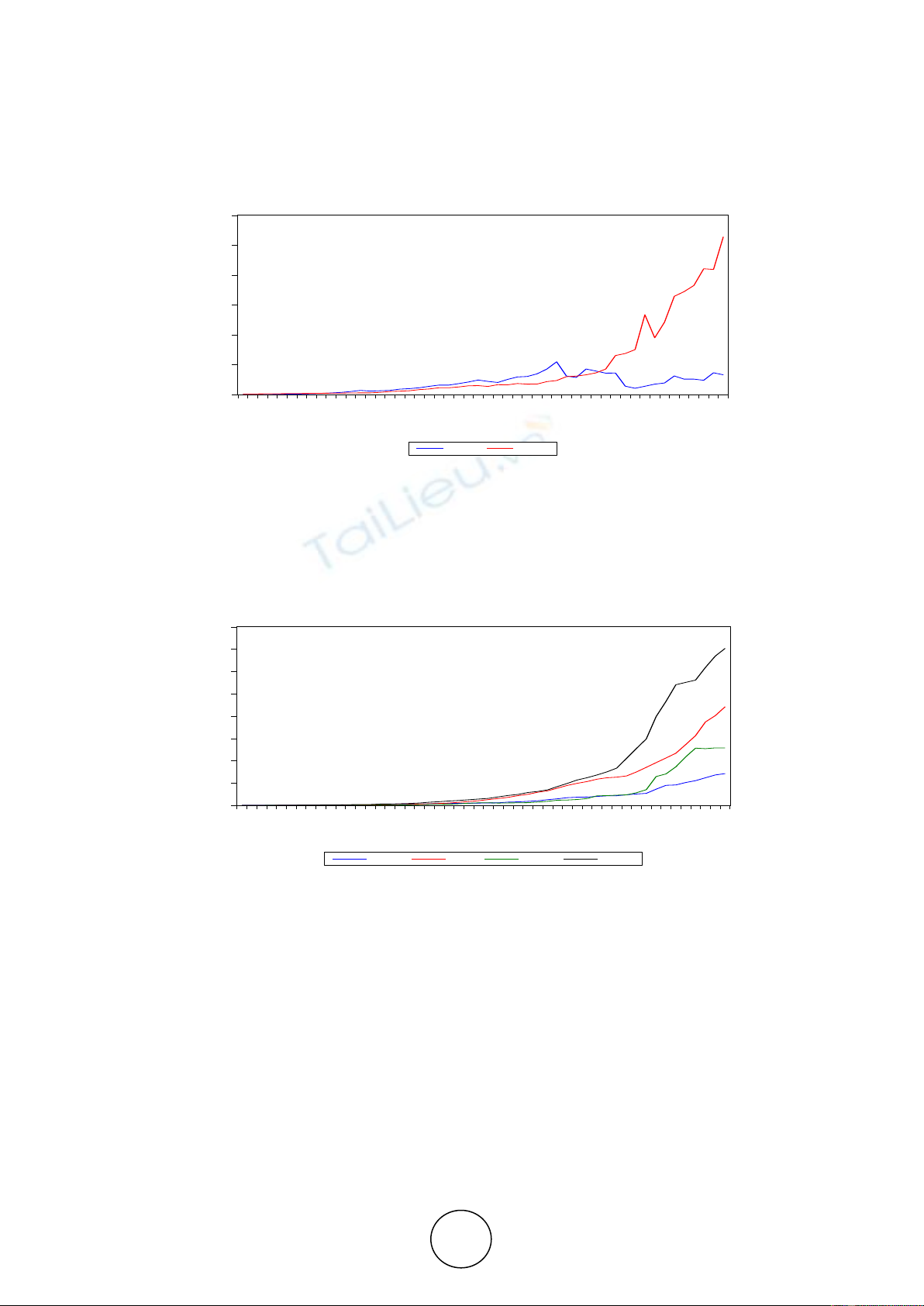
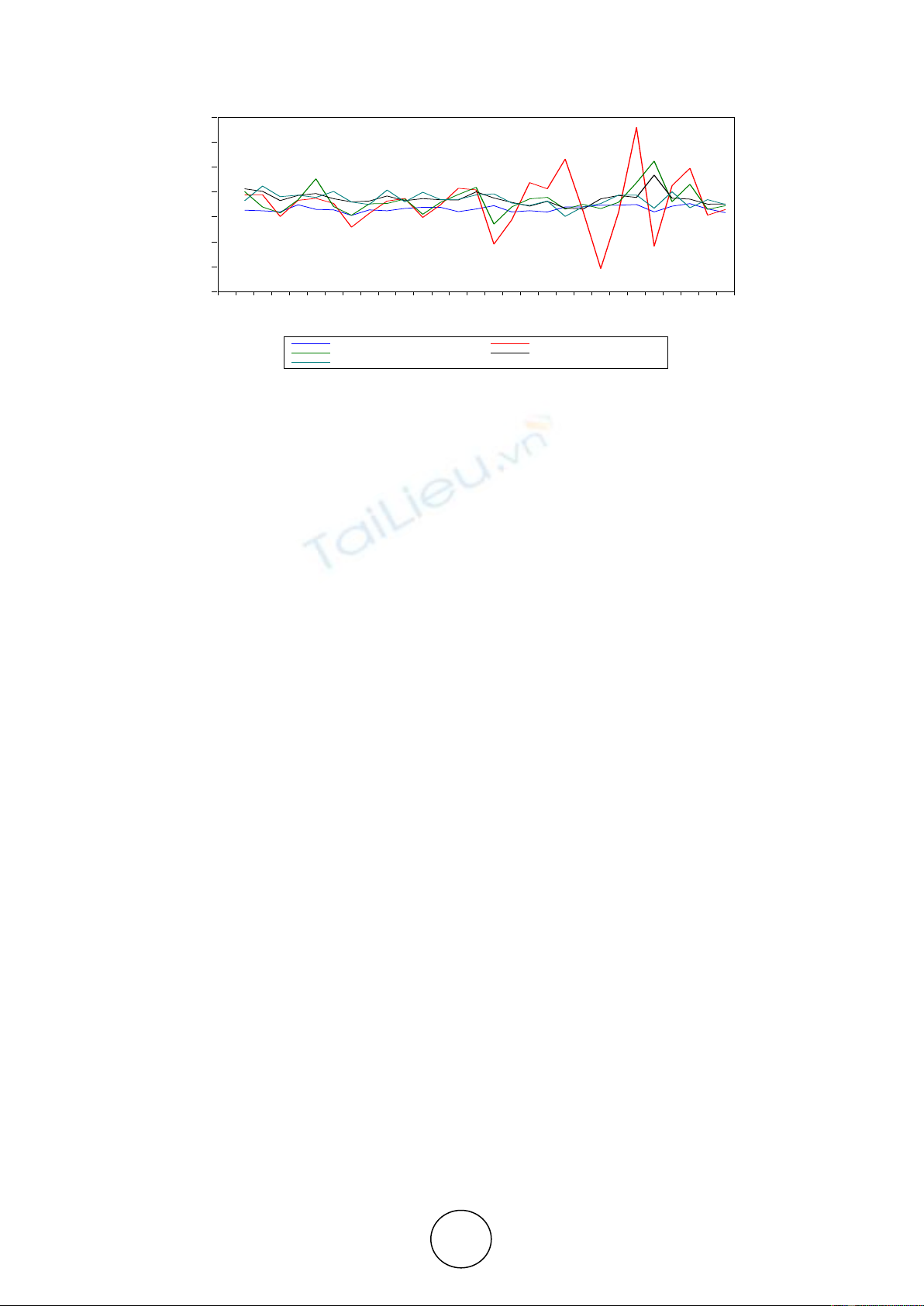
This study tried to empirically test the causal relationship and the direction of
causality between public expenditure and GDP in India, using annual data from 1966-
67 to 2015-16. The methodology employed was econometric model of the
cointegration and the Granger Causality test. The estimates shows that the variables
are stationary at first difference and follows I(1) order of integrations. Causality test
estimates shows bidirectional causal relationship running from GDP to Revenue
Expenditure and from Capital Expenditure to GDP. The estimates do not support the
existence of Keynesian hypothesis and Wagner’s Law at the disaggregate level in
India.
Key words: Public Expenditure, Wagner’s law, Keynesian hypothesis, Cointegration,
Granger Causality.
Cite this Article: Dhyani Mehta, Public Expenditure and National Income of India:
Investigating Wagnerian Law. International Journal of Management, 9 (5), 2018, pp.
1–9. http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=5
1. INTRODUCTION
Can increase in public expenditure influence economic growth? What evidence exists on the
direct relationship between public expenditure and economic growth? There is lot of debate in
public finance literatures based on views of different school of thoughts in economics. There
are both theoretical and empirical evidence on the relationship between public expenditure
and Gross domestic product (GDP) growth (Blanchard, 2008). If public expenditure
negatively influences economic growth then policymakers need to be aware of these
relationships when formulating and implementing macroeconomic policy; and if public
expenditure enhances economic growth, or at a minimum does not present obstacles to
growth. However, it is important for policy makers to manage the debt, which arises due to
increased public expenditure and its impact on economy.
Public Expenditure is one of the important growth driver of any economy; GDP growth
should be sustained for a developing economy to address issues like unemployment, poverty,
inflation etc. Public expenditure plays a very crucial role in economic growth and stability.