Franz H. Messerli; Sripal Bangalore .
Eur Heart J. 2017;38(44):3321-3323.
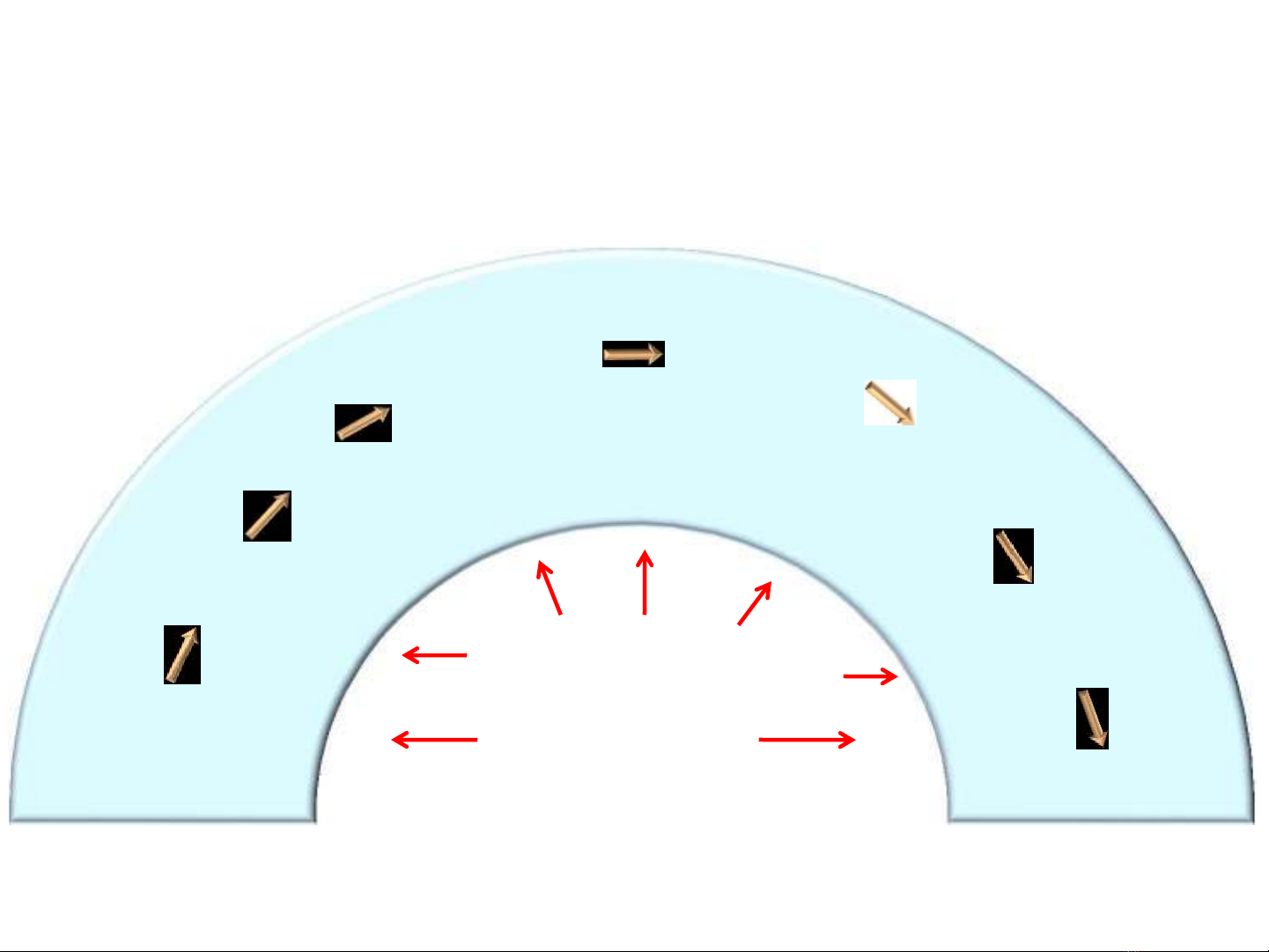
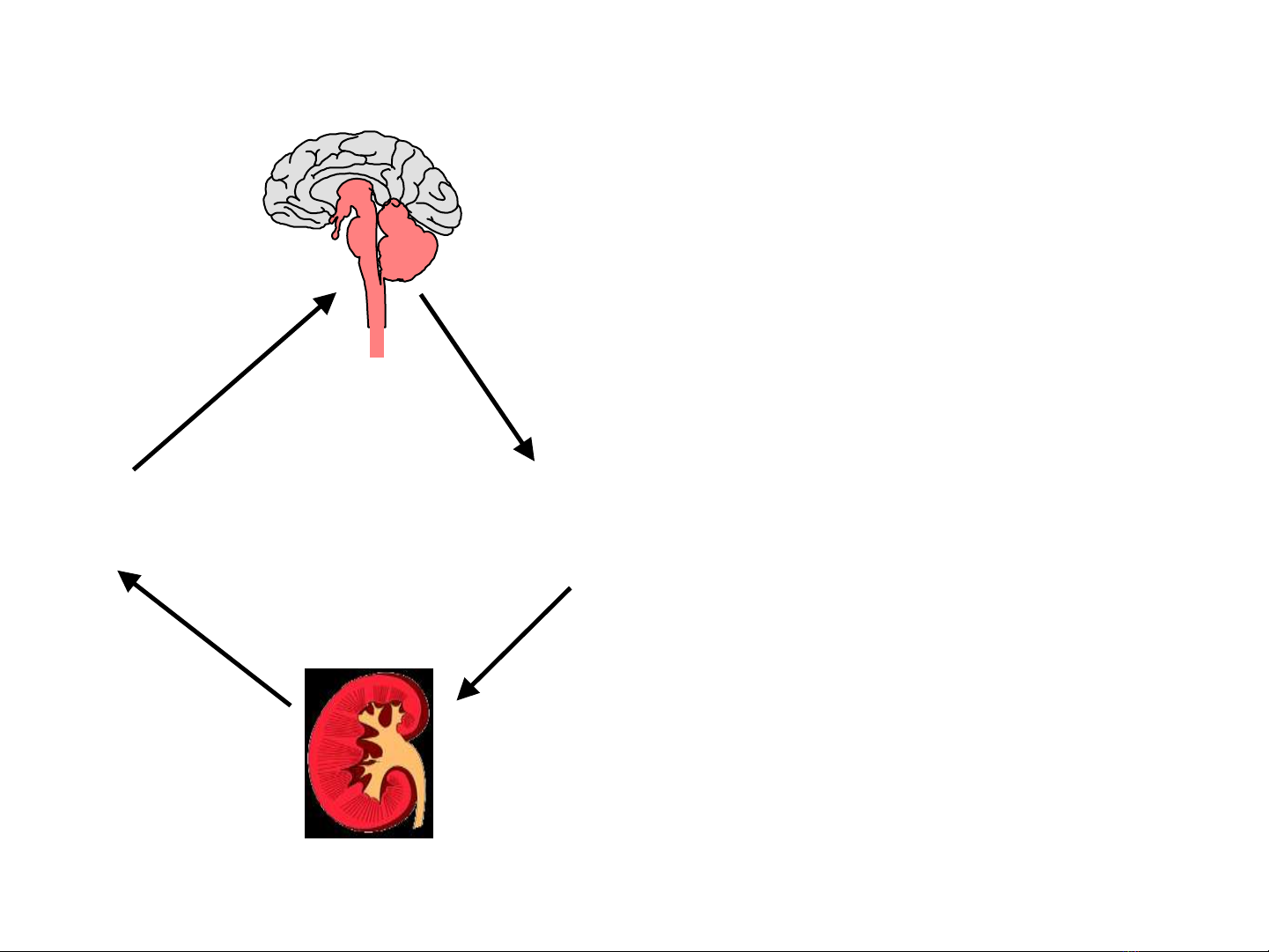
• Sympathetic overactivity has been
documented to occur in the early phases of
hypertension[6,7] as well as in the advanced
stages with hypertensive heart disease.[8]
6. Esler M et al. Mild high-renin essential hypertension. Neurogenic human hypertension? N Engl J Med 1977;296:405–411.
7. Esler M,et al. Noradrenaline release and the pathophysiology of primary human hypertension. Am J
Hypertens 1989;2:140S–146S.
8. Smith PA et al. Relation between central sympathic activity and stages of human hypertension. Am
J.Hypertens.2004.17;217-222
VNM/NONCMCGM/0518/0017