MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING
MINISTRY OF DEFENCE
108 IN STITU TE OF C LINI C AL MEDI CA L AN D P HA RMAC EU TI CA L SCI EN CES
BUI QUANG BIEU
RESEARCH ON
18
F-FDG PET/CT IMAGES IN
POSTSURGICAL DIFFERENTIATED THYROID CANCER
PATIENTS WITH HIGH SERUM THYROGLOBULIN AND
NEGATIVE
131
I WHOLE BODY SCAN
Speciality: Diagnostic Imaging
Code: 62.72.01.66
ABSTRACT OF MEDICAL PHD THESIS
Ha Noi – 2020

THE THESIS WAS DONE IN:108 INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL
MEDICA L AND PHA RMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
Supervisors:
1. Ass.Prof. PhD. Le Ngoc Ha
2. Ass.Prof. PhD. Lam Khanh
Reviewers:
1.
2.
3.
This thesis will be presented at Institute Council at: 108 Institute of
Clinical Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences
Day Month Year
The thesis can be found at:
1. National Library of Vietnam
2. Library of 108 Institute of Clinica l Medica l and
Pharmaceutical Sciences
3. Central Institute for Medical Science Infomation and
Tecnology

1
ĐẶT VẤN ĐỀ
The incidence of thyroid cancers has been increasing in recent
years. In Vietnam, thyroid carcinomas ranks the ranks the
6
th
common cancers in female. Differentiated thyroid cancers (DTC)
including papillary carcinoma, folicullar carcinoma and Hurthle cell
carcinima account for more than 90% of all thyroid cancers.
After thyroidectomy and radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy,
thyroglobulin (Tg) is considered the tumor markerand iodine-131 (
131
I)
whole body scan (WBS) is the specific image in follow-upand
detection of recurrent/metastatic DTC. However, in clinical practice,
there were 2 – 15% postsurgical DTC patients withhigh serum Tg (> 10
ng/ml)which suggested recurrence/metastasis but negative
131
I WBS.
Several studies in the world have demonstrated the diagnostic values
of
18
F-FDG PET/CT in detecting recurrence/metastasis in postoperative
DTC patients withhigh serum Tg and negative
131
I WBS
withsensitivity and specificity ranged from 82 to 95%.
In Vietnam, there still have been few researches on this issue.
Therefore, weperformed the study“Research of
18
F-FDG PET/CT
images
in postsurgical differentiated thyroid cancer patients with high serum
thyroglobulin and negative
131
I whole body scan”with two objectives:
1. To investigate clinical, paraclinical and
18
F-FDG-
PET/CTimaging characteristics of postsurgical differentiated
thyroid cancerpatients post RAI therapy with high serum
thyroglobulin and negative
131
I whole body scan.
2.
To determine the diagnostic values of
18
F-FDG-PET/CT in
postsurgical differentiated thyroid cancer patients post RAI therapy
with high serum thyroglobulin and negative
131
I whole body scan.
2
Chapter 1
OVERVIEW
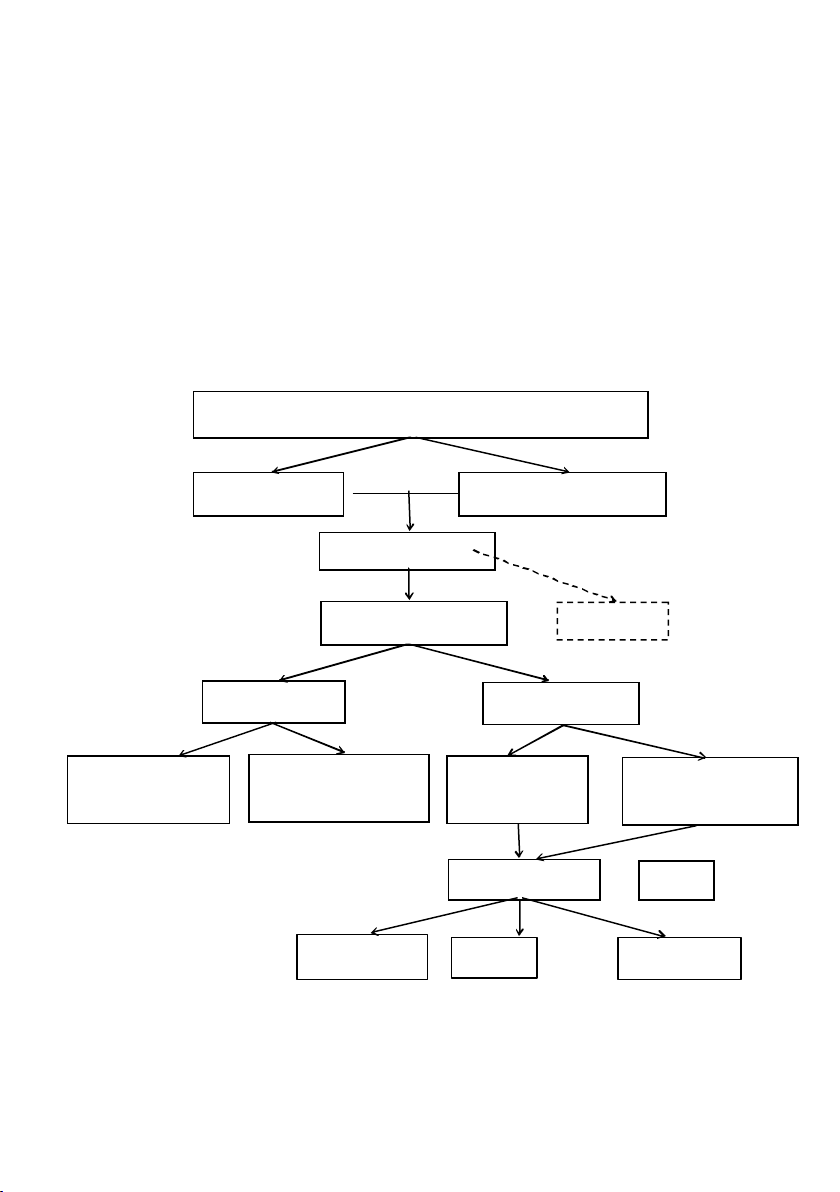
1.1. Management of postsugical DTC patients post RAI therrapy
with high Tg and negative
131
I WBS
According to NCCN and ATA Guidelines, strategies for
management of DTC patients with high Tg and negative
131
I WBS are
summarised in the diagram below.
Management of DTC patients with high Tg and negative
131
IWBS
Postsurgical and post RAI therapy DTC patients
Negative
131
IWBS
Tg> 10 ng/ml
Neck ultrasound
18
F-FDG PET/CT
Emirica lRAI
therapy
TSH suppression
Follow-up
Negative Positive
No
symptoms
With symptoms,
progression
Local therapy
TKIs
EBRT
Surgery
RFA, PEI
TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors; EBRT: external beam radiotherap y;
RFA: radiofrequency abla tion; PEI: percutaneous ethanol injection)
CT, MRI
*To evaluate invassive lesions
or if PET/CT is not available

3
1.2.
18
F-FDG PET/CT in postsurgical DTC patients with high Tg
and negative
131
I WBS
The applications of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) have
been developed for more than 40 years since it’s invention.From
1970’s, PET had been used for studies in cardiac and neuro diseases.
One decade later, the researchers also noted that PET was a valuable
diagnostic tool in oncology. Not likeother structure and anatomy
based diagnostic methods such as computed tomography (CT) or
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), PET records qualitative and
quantitative images of physiopathological and metabolic process of
diseases via labelled pharmaceutical isotopes. The combination of
PET and CT in one system PET/CT allowed optimal exploitationof
the advantages of both PET (metabolic informations of tissues) and
CT (structural changes and localization of lesions).
Currently, the most common pharmaceutical isotope used in PET
scan was
18
F-FDG (18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose), an analogue
of glucose(replacement of the 2nd hydrogen atom in the glucose
moleculewith fluor-18(
18
F).
18
F-FDG is transfered into cells via
glucose transpoters in membrane.
18
F-FDG is phosphorylated to
become
18
F-FDG-6-phosphate and is accumulated inside cells
because it cannot be metabolised or deposited in the form of
glycogen like glucose.
18
F-FDG uptake in malignant cells is mainly
due to the increase of glucose transporter (especially GluT-1) in cell
membrane and hexokinase such as HK-II...
Due to the decreasing of natri/iodine symmporter (NIS) and
increase of glucose transpoter (GLUT) in cell membrane,
18
F-FDG
PET/CT plays an important role in diagnosis of recurrence,


























