
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 1 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 9, Issue 6, November–December 2018, pp.1-12, Article ID: IJM_09_06_001
Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=6
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
INNOVATION AND ECONOMIC
DIVERSIFICATION INDICATORS – A
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS AMONG GCC
COUNTRIES WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON
SULTANATE OF OMAN
Dr. Kabaly P Subramanian
Assistant Professor, Arab Open University, Oman Branch
Rengarajan,
Lecturer, Faculty of Business Studies, Arab Open University, Oman Branch
ABSTRACT
Many empirical studies in developing economies suggest that economic
diversification is indispensable for sustained economic growth. It is also suggested by
studies that economic diversification of a country can be influenced by upgrading the
capabilities of companies, scientists, regions which will empower them to innovate
and create new products, processes and organizational structures. Hence, innovation
and economic diversification are inter-related. It is observed that long run economic
development is driven by creative processes. More diversified economy is capable of
handling economic shocks or decline of a sector. Economies with a varied set of
sectors leads to become more democratic, as different economic groups gain in
creative, economic and political power. If the growth of an economy is merely driven
by efficiency, not innovation, it leads to reduction of employment due to routines and
replacement of humans by machines
GCC countries are oil dependent economies working hard to diversify their
economies. Sultanate of Oman is one among GCC countries working with same
principle and approach. GCC countries have been investing heavily in infrastructure
and human development in order to make their economic diversification and
innovation strategies to get implemented better. Access to finance is one of the key
areas that must be focused well in order to realize the economic diversification and
innovation goals of an economy. This has been well perceived by GCC countries.
Overall, GCC countries have been move ahead in economic diversification and
innovation through its policies and prioritization, which economic indicators clearly
vouch. In this context, this paper intends to investigate the status of Innovation and
Economic diversification across GCC countries with a special focus on Sultanate of
Oman
Keyword: Innovation and economic diversification are inter-related.

Innovation and Economic Diversification Indicators – A Comparative Analysis among Gcc
Countries with a Special Focus on Sultanate of Oman
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 2 editor@iaeme.com
Cite this Article: Dr. Kabaly P Subramanian and Rengarajan, Innovation and
Economic Diversification Indicators – A Comparative Analysis among Gcc Countries
with A Special Focus On Sultanate of Oman, International Journal of Management, 9
(6), 2018, pp. 1-12.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=6
1. INTRODUCTION
Economic diversification is closely linked to innovation capabilities. Only through
introduction of creative and innovative products and production systems, diversification is
difficult to achieve. Therefore, it is imperative for nations to develop innovation ecosystems
to achieve competitive and diversified economies. This will help Universities, Public and
Private Institutions, companies and civil societies to develop deploy and disseminate new
technologies.
To realize the ambition of economic diversification, innovation needs to be given top
priority in economic, social and technology policies across GCC countries including Sultanate
of Oman. An International Monetary Fund (IMF) study on Economic Diversification in GCC
observes greater diversification would help countries sail through the VUCA world (Volatile,
Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous) of Oil Market, help create more jobs in the private
sector, increase productivity and sustainable growth and establishing a non-oil economy
which is very much essential when oil revenues start to reduce. Thus, focus on non-oil sectors
and improving the human capital to get absorbed in these sectors are key challenges for GCC
countries. Their national priorities have always been intensive industrialization and
developing abilities and skills of human resources which are essential for achieving
sustainable economic growth and diversification and to practice innovation accordingly.
2. OBJECTIVES OF THIS STUDY
Following are the objectives of this study:
1. To identify and analyze some of the determinants of innovation and economic
diversification across GCC Countries and Sultanate of Oman
2. To highlight a few plans of government in implementing innovation and economic
diversification in Sultanate of Oman.
3. To analyze certain macro-economic indicators that reflect innovation and economic
diversification happening across GCC countries and to determine closeness of
Sultanate of Oman to other GCC countries
3. LITERATURE REVIEW
Hartmann et.al. (2013)
1
presents that the major goal of economics is to understand and
promote economic development to contribute to social welfare. They have also pointed out
that innovation and welfare creation are achievable by focusing attention on the need for a
better understanding of the mutual relation between human capabilities and systems of
innovation (Johnson et al., 2003; Arocena and Sutz, 2005)
2
.
Asheim (2015)
3
points out that innovation capacity of a country comprises the
competitiveness of companies and countries and represents a dynamic view on competition.
He further states that a dynamic view on competition implies that the innovation capacity of a
country and competitiveness can very well be promoted by national research and innovation
policies prioritizing increased investments in education, research. Hartmann (2013)
4
mentions that economic diversification has a variety of positive effects i.e. economic growth,
systemic stability and a more even distribution of political power. He argues that economic
diversification is bringing about various changes in an economy like positive economic

Dr. Kabaly P Subramanian and Rengarajan
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 3 editor@iaeme.com
growth rate, bringing systemic stability etc. It is evident that economic diversification must be
the core objective of a fastest developing economy like Oman. Economy should not be
viewed as merely dynamical processes. Situngkir (2004)
5
states that economy is an open
system which large variations of point of view should be put into account be it to produce in
the microeconomic level of firms and industry and even larger macroeconomic horizon.
Entrepreneurs are passionate about the products and services their businesses sell, but their
efforts benefit the economy in other ways as well.
Hornaday (1982)
6
argues that entrepreneurship and innovation target at previously
untapped opportunity to make substantial profits (either by lowering the costs of producing
existing good/services or by creating brand new ways for people to satisfy their wants through
new products) and then takes the initiative in bringing together the necessary factors of
production to exploit this opportunity. Economic diversification of a nation will have to
attract entrepreneurs who are looking for opportunities to explore something new in the
market and make substantial profits. Amable (2016)
7
presents that organizations should attain
and maintain continuity of competitive advantage at an international level through
improvements, innovations and upgrading on a continuous basis and this includes renewal of
production methods, usage of technology, creation of new products and methods of
production.
Porter, M (1990)
8
, the competitive advantage of the nation cannot be achieved without
having ability of its industry to innovate & promotion. Economic of countries should
consider several of polices that enable firms to contribute in creating and sustaining the
competitive advantage of nation Economic diversification policies of nations will have to help
industries and companies to make necessary changes which are the outcomes of product and
process innovation and reap the necessary benefits. Anderson et al., (2011)
9
argues that the
structural strategies played vital role gain competitive advantage of the nation’s companies
that leads effectiveness in firms’ performance and that lead for growth. The effective
structures can support the economy to get worthy results.
4. METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
The study aims at presenting the innovation and economic diversification practices being
adhered to across GCC Countries and presenting the effectiveness of those policies through
economic indicators, date pertaining to such information been collected through internet
sources. Secondary data been collected from published sources (websites) such as the global
economy, World Bank database, trading economics etc.
The techniques used for analyzing data include
a) Descriptive Statistics
b) Correlation Analysis
c) Graphs
d) Comparative Economy Analysis
Since economic diversification must be substantiated, basic tools are used, and this study
provides a big space for further study and analysis.
5. DETERMINANTS OF INNOVATION IN GCC COUNTRIES
Innovation is essential for ensuring economic diversification of a nation. Economic growth is
substantially achieved by nations through its diversified policies and procedures being
adopted. Thus, innovation is the result of need for economic diversification and economic
growth is substantially achieved through innovation favoured through economic
Innovation and Economic Diversification Indicators – A Comparative Analysis among Gcc
Countries with a Special Focus on Sultanate of Oman
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 4 editor@iaeme.com
diversification policies. Some of the factors that are essential for promoting innovation and
achieving economic diversification for Oman have been analyze here.
5.1. Single Sector dependency and economic growth
Carlos et al., (2011)
10
present that changes happening in global economy directly are affecting
the performance of domestic economy, explaining the essence of economic diversification for
achieving acceptable economic growth rate. Economic diversification is achieved through
policies that promote entrepreneurship, privatization, globalization and industrialization
policies being followed at the respective nation. No country wants to depend upon one sector
since the growth rate achieved in that sector in that country is remarkable over the years.
Since this is posing a big challenge for the nation in a way that a small undesirable change in
that sector would produce adverse impact on its GDP. In GCC countries, oil and gas is a
natural essential source of revenue and that forms the major part of their total revenue, GCC
countries would like to move slowly from oil dependency to industry diversification through
innovation and entrepreneurship. In the same context, the industrial and economic policies of
Sultanate of Oman highlight clearly that the nation does not want to depend on one sector and
wants to instigate economic diversification. It has been observed that through economic
diversification and industrialization policies, GCC countries could achieve a substantial
economic growth rate if they could diversify their economic concentration. The growth rate at
which GCC economies are growing been presented below:
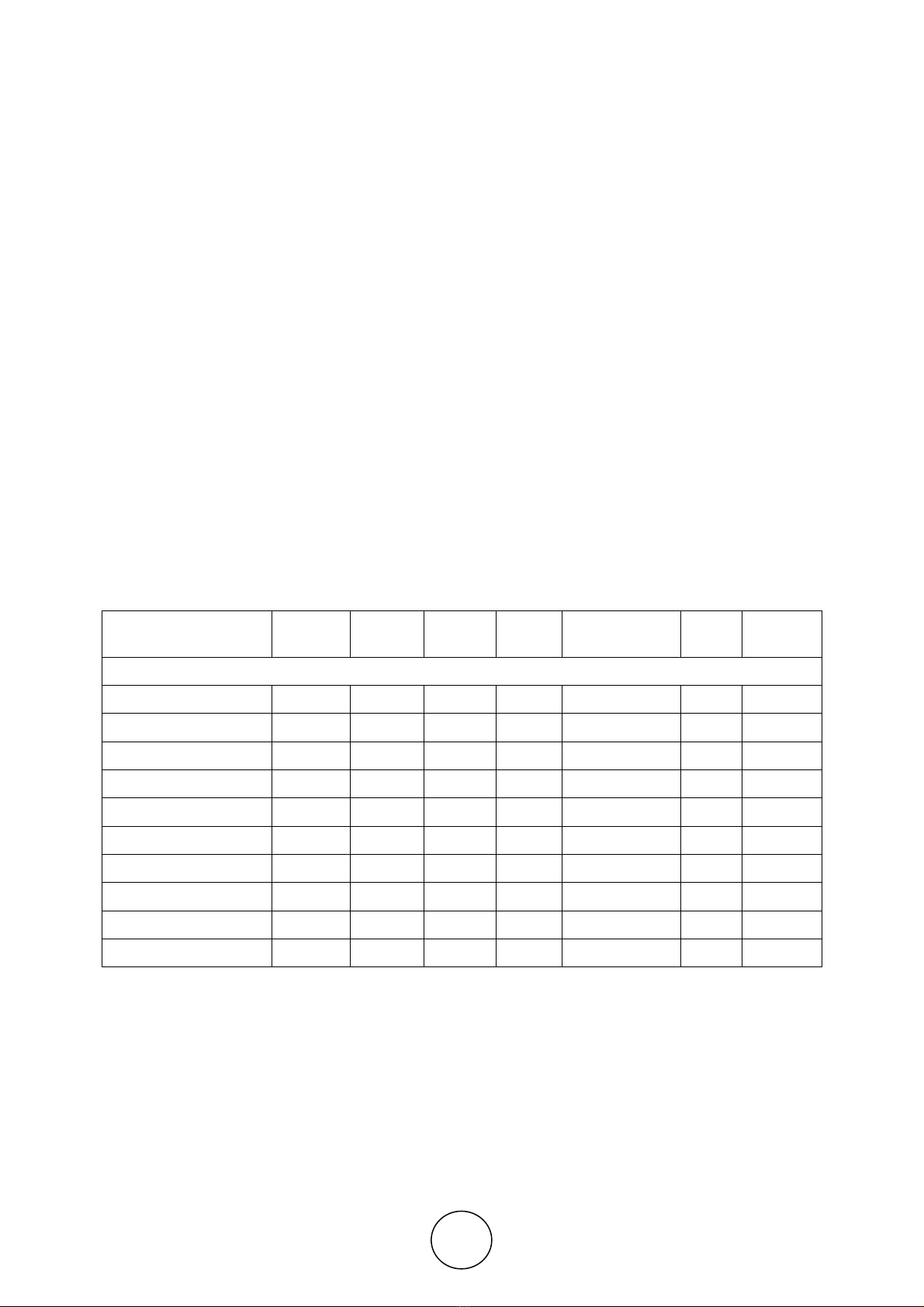
Table 1 Economic Growth: the rate of change of real GDP in GCC countries over the periods 2000 –
2017
Descriptive Statistics Bahrain Kuwait Oman Qatar Saudi Arabia UAE GCC
Average
(% of change of real GDP over the periods 2000 – 2017)
Mean 4.69 4.02 3.56 9.92 3.72 4.45 5.06
Standard Error 0.43 1.37 0.77 1.85 0.93 0.92 1.04
Median 4.34 3.28 4.47 7.18 3.88 4.44 4.60
Standard Deviation 1.82 5.80 3.26 7.65 3.93 3.88 4.39
Sample Variance 3.30 33.66 10.62 58.46 15.42 15.08 22.76
Kurtosis -0.92 0.49 -0.38 -0.74 -0.40 1.10 -0.14
Skewness 0.30 0.35 -0.34 0.75 0.09 -0.43 0.12
Range 6.31 24.40 12.00 24.57 14.06 16.09 16.24
Minimum 1.98 -7.08 -2.67 1.60 -2.82 -5.24 -2.37
Maximum 8.29 17.32 9.33 26.17 11.24 10.85 13.87
(Source: the global economy, 2018 & computed)
The table.1 illustrates how GCC Countries have been progressing over the years. The
average growth rate of GCC countries is very close to the average of GCC (5.06), which
reflects countries move in the same direction and their industrialization and economic
diversification have been clearly been addressed in their economic policies. Sultanate of
Oman has also been progressing well in implementing innovations effectively and sustaining
economic diversification (mean growth rate 3.56). Further to this, the correlation between
economic growth achieved in Sultanate of Oman and average rate achieved in GCC countries
is 0.991, which reflects Sultanate of Oman’s economy is growing at a rate comparable to the
other GCC Countries. This illustrates that economic policies and procedures governing GCC
Dr. Kabaly P Subramanian and Rengarajan
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 5 editor@iaeme.com
Countries are all directed towards achieving sustainable economic growth rate. Despite, oil
dependency predominantly prevailing in GCC countries, through economic diversification
and innovation practices; they could achieve this growth rate, which clearly shows up their
directions to achieve sustainability in the future.
5.2. Government Plans on reducing Oil Dependency in Sultanate of Oman (2016 –
2020 Plan)
Reuters (2016)
11
highlights the government’s policies of Sultanate of Oman concerning
reducing oil dependency for the next 5 years have been summarized below:
1. Cut the oil industry's contribution to gross domestic product to 22% from 44%; the
contribution of natural gas would drop to 2.4% from 3.6%.
2. Over 500 programmes and policies would seek to diversify the Omani economy into
sectors such as manufacturing, mining, transport and tourism. Cumulative investment
over the five years is expected to be OMR 41bn, against OMR 38bn envisaged in the
previous five-year plan.
3. The plan is to significantly use public-private partnerships, with 52% of total
investment to come from the private sector vs. 42% in the last plan. The plan assumes
an average oil price of USD 45/ barrel in 2016, USD 55 in 2017 and 2018, and USD
60 in 2019 and 2020 (Reuters, 2016)
The above plan makes it clear that the government of Sultanate of Oman is moving
towards well - diversified and not depending on oil exports extensively. The Government
policies and strategies rightly focus on having more manufacturing and service organizations
for contributing well to achieve the sustainable growth and efficiency. The educational and
training institutions play a key role in Sultanate of Oman in assuring the best possible
knowledge transfer who is highly needed for achieving excellence in innovation and
economic diversification. Number of educational and training institutions working in
Sultanate of Oman is the evidence of country’s progress towards achieving their economic
diversification priorities.
5.3. Human Development Focus across GCC Countries
Human development is the core for achieving innovation, which would highly result in
ensuring economic diversification. Innovation and economic diversification are feasible for
achieving provided human development policies and practice are pursued in vigor in any
country. Accordingly, the human development index data pertaining to GCC Countries been
analyzed and presented here. The human development index has been calculated using four
important indicators such as life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, expected years
of schooling, and gross national income per capita. (The global economy, 2018)
12
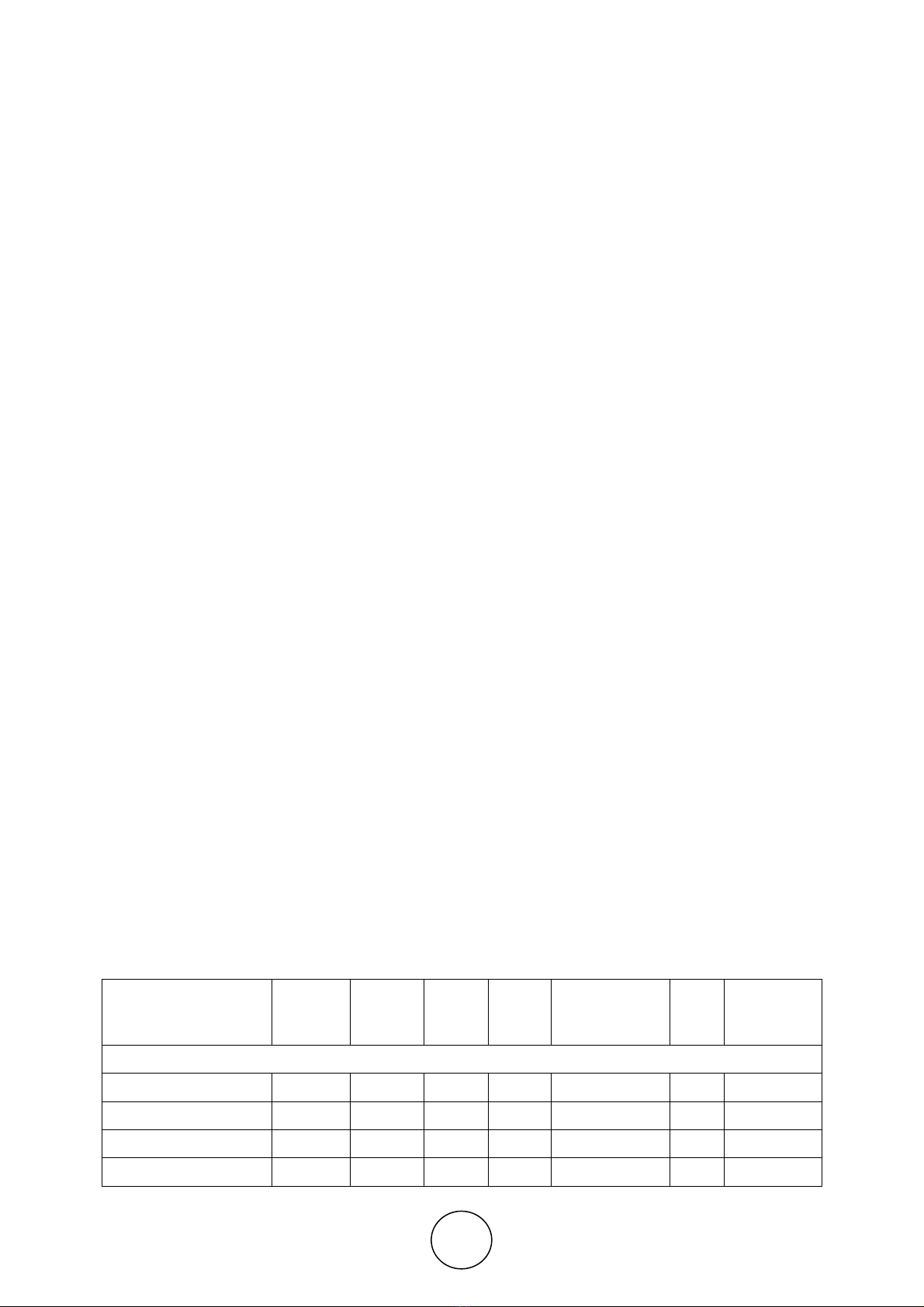
Table 2 Human Development Index of GCC countries over the period 2000 - 2017
Descriptive Statistics Bahrain Kuwait Oman Qatar Saudi Arabia UAE
GCC
Average
Index
(Index values ranging from 0- 1)
Mean 0.82 0.81 0.78 0.85 0.82 0.83 0.82
Standard Error 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01
Median 0.81 0.80 0.78 0.85 0.83 0.83 0.82
Mode 0.81 0.80 0.78 0.86 0.85 0.82 0.82


























