TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 490 - THÁNG 5 - SỐ 1 - 2020
131
hoàn toàn 8,3%, đáp ứng một phần 66,7%,
bệnh ổn định 25%.
- Nhóm bệnh nhân di căn phổi: đáp ứng một
phần 57,1%, bệnh ổn định 28,6%, bệnh tiến
triển 14,3%
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
1.GLOBOCAN 2018 (IARC) Section of Cancer
Information.
2. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib
or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947.
3. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients
with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-
cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a
multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3
study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735.
4. Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al.
Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-
line treatment for European patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell
lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label,
randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
2012;13(3):239.
5. Nguyễn Thị Thái Hòa, Mai Thanh Huyền, Vũ
Hà Thanh et al. Đánh giá kết quả điều trị bước 1
ung thư phổi không tế bào nhỏ giai đoạn IIIB-IV
có đột biến EGFR bằng thuốc ức chế Tyrosin
Kinase. Tạp chí ung thư học Việt Nam. 10/2016 .
6. Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, et al. Afatinib
versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line
treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-
small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations
(LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014 Feb;15(2):213-22. Epub
2014 Jan 15.
7. Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N. Phase III
study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in
patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with
EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(27):3327.
Epub 2013 Jul 1.
8. Yang JC, et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients
with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: a combined
post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and
LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol 2015;16(7):830-8.
KHẢO SÁT ĐẶC ĐIỂM CT VÀ MR TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN
BỆNH LÝ U HỐC MŨI XÂM LẤN NỀN SỌ TRƯỚC
Ngô Văn Công*
TÓM TẮT34
Giới thiệu: Bệnh lý u hốc mũi xâm lấn nền sọ
trước là bệnh lý nằm trong hốc sâu, khó nhìn thấy
biểu hiện một cách trực tiếp. Do đó, các Bác sĩ lâm
sàng khi chẩn đoán u vùng nền sọ trước khó đánh giá
một cách toàn diện về tổn thương của u và sự xâm
lấn của khối u với cấu trúc xung quanh bằng các biểu
hiện lâm sàng. Vì vậy, cần hổ trợ của CT và MR để
khảo sát đánh giá các tổn thương này. Phương pháp
nghiên cứu: nghiên cứu mô tả cắt ngang, được thực
từ tháng 9/2010 đến tháng 12/2015 tại Bệnh viện Chợ
Rẫy. Kết quả: Qua thời gian nghiên cứu, chúng tôi
thu thập 45 trường hợp u vùng nền sọ trước, có cả
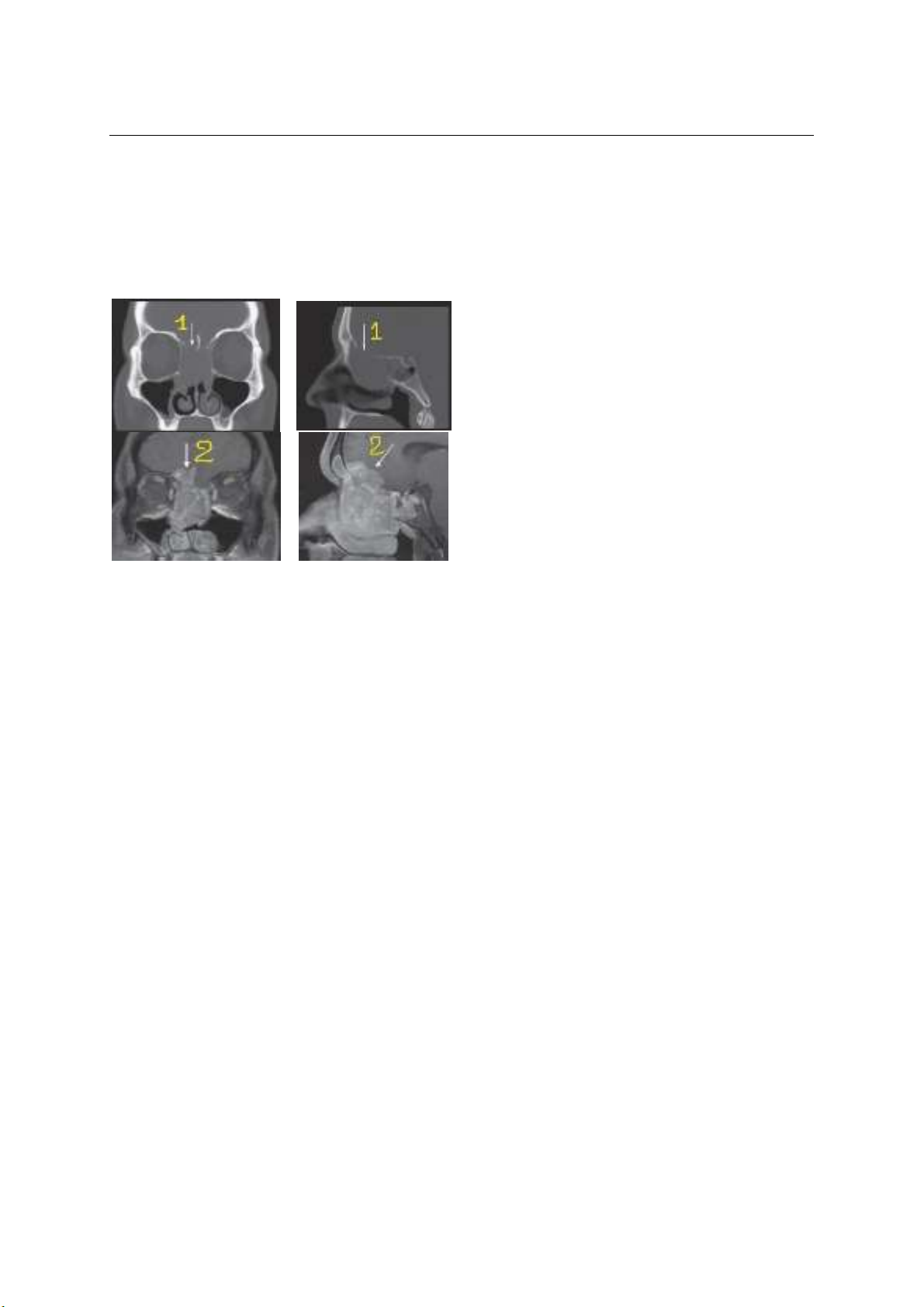
hình ảnh CT và MR. Hầu hết qua hình ảnh CT/ MR đều
xác định được khối u (100%). Trên hình ảnh CT cho
thấy có tổn thương phần xương nền sọ trước rõ ràng
hủy và khuyết xương nền sọ trước 93,3%. Hình ảnh
MR biểu hiện tổn thương u xâm lấn vào nhu mô não
75,6%, kèm theo các dấu hiệu phù não 11,1% , chèn
ép thần kinh thị 46,7%. Kết luận: Hình ảnh CT và MR
có một giá trị nhất định trong chẩn đoán bệnh lý u
vùng nền sọ trước. CT/ MR hổ trợ lẫn nhau trong chẩn
đoán và đánh giá sự xấm lấn và chèn ép của khối u
vùng nền sọ trước.
Từ khóa
: hình ảnh CT/ MR của u nền sọ trước
*BV.Chợ Rẫy
Chịu trách nhiệm chính: Ngô Văn Công
Email: congtmh@gmail.com
Ngày nhận bài: 17.2.2020
Ngày phản biện khoa học: 6.4.2020
Ngày duyệt bài: 20.4.2020
SUMMARY
TO ASSESS CHARACTERISTICS OF
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AND MAGNETIC
RESONANCE IN NASAL CAVITY AND
PARANASAL SINUS TUMORS INVADING
ANTERIOR SKULL BASE
Introduce: Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus
tumors invade anterior skull base is a disease located
in the deep cavity. Almost physicians arc difficult to
see them directly. So, it is difficult to evaluate whole
the tumors and invasion of the tumor with the
surrounding structures by clinical symtoms. Therefore,
CT and MR arc important approaches to improve and
diagnosis anterior skull base tumors. Research
method: cross-sectional descriptive study. Datas of
the study were collected from September 2010 to
December 2015 at Cho Ray Hospital. Results: We
collected 45 cases of Nasal cavity and paranasal sinus
tumors invade anterior skull base. All patients had to
take CT and MR (100%). On the CT images show
destruction of anterior skull base bone 93.3%. MR
images show invasion of tumor into the brain tissue
75.6%. Beside, there arc other signs such as brain
tissue edema 11.1%, optic nerve compression 46.7%
on MR images. Conclusion: CT and MR images have
important value in the diagnosis of anterior skull base.
CT / MR supports each other in the diagnosis and
assessment of invasion and compression of the
anterior skull base tumors.
Key words:
CT/MR image of anterior skull base tumor,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Skull Base Neoplasms