by
Dr TRẦN NGỌC ÁNH
Hà Nội Medical University

Objectives
1.Recognize the typical
clinical presentation for
IBS
2.Describe an appropriate
diagnostic plan and ROME
III
3.Prescribe an appropriate
therapeutic regimens
IBS- Dr Trần Ngọc Ánh
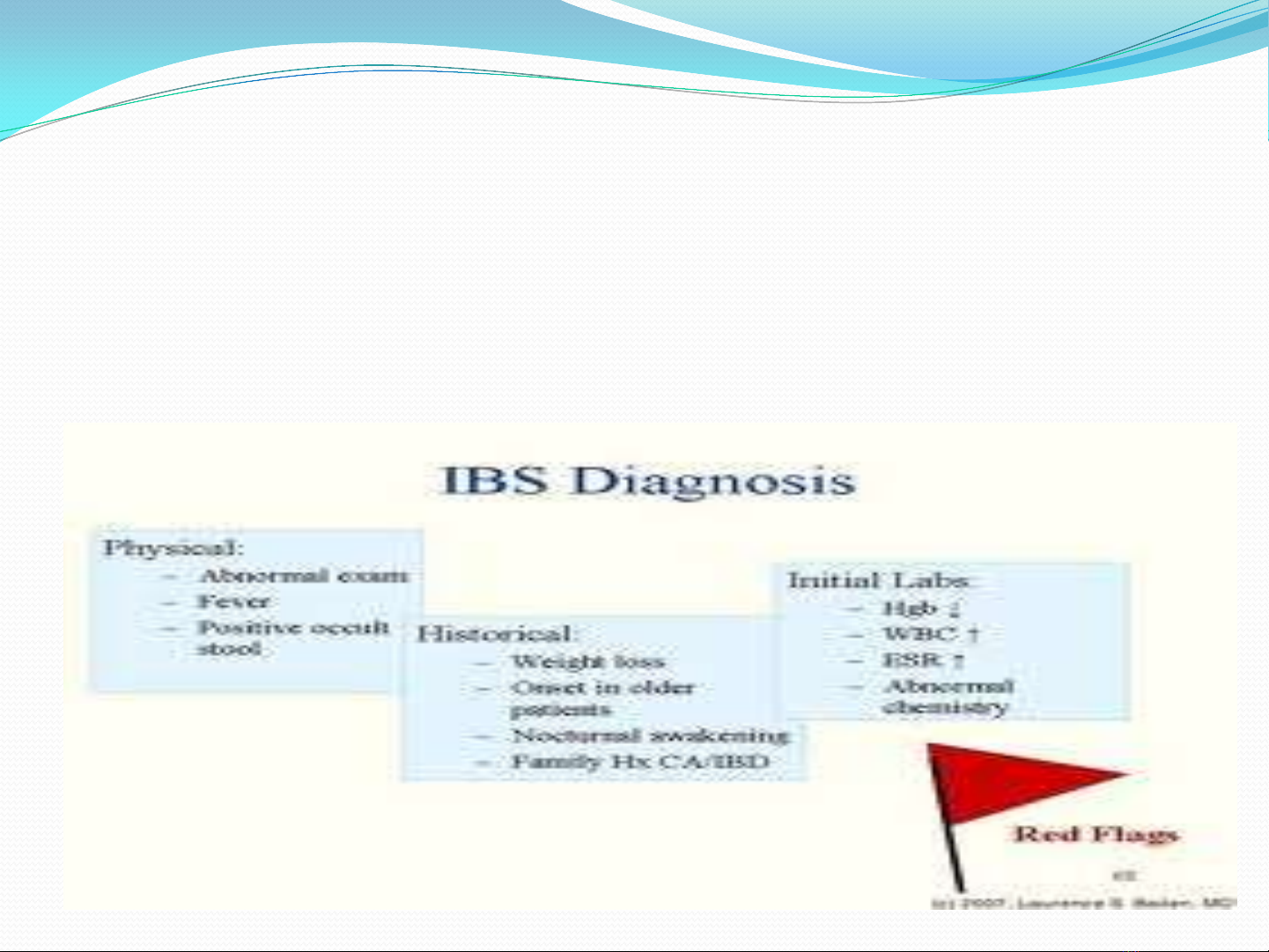
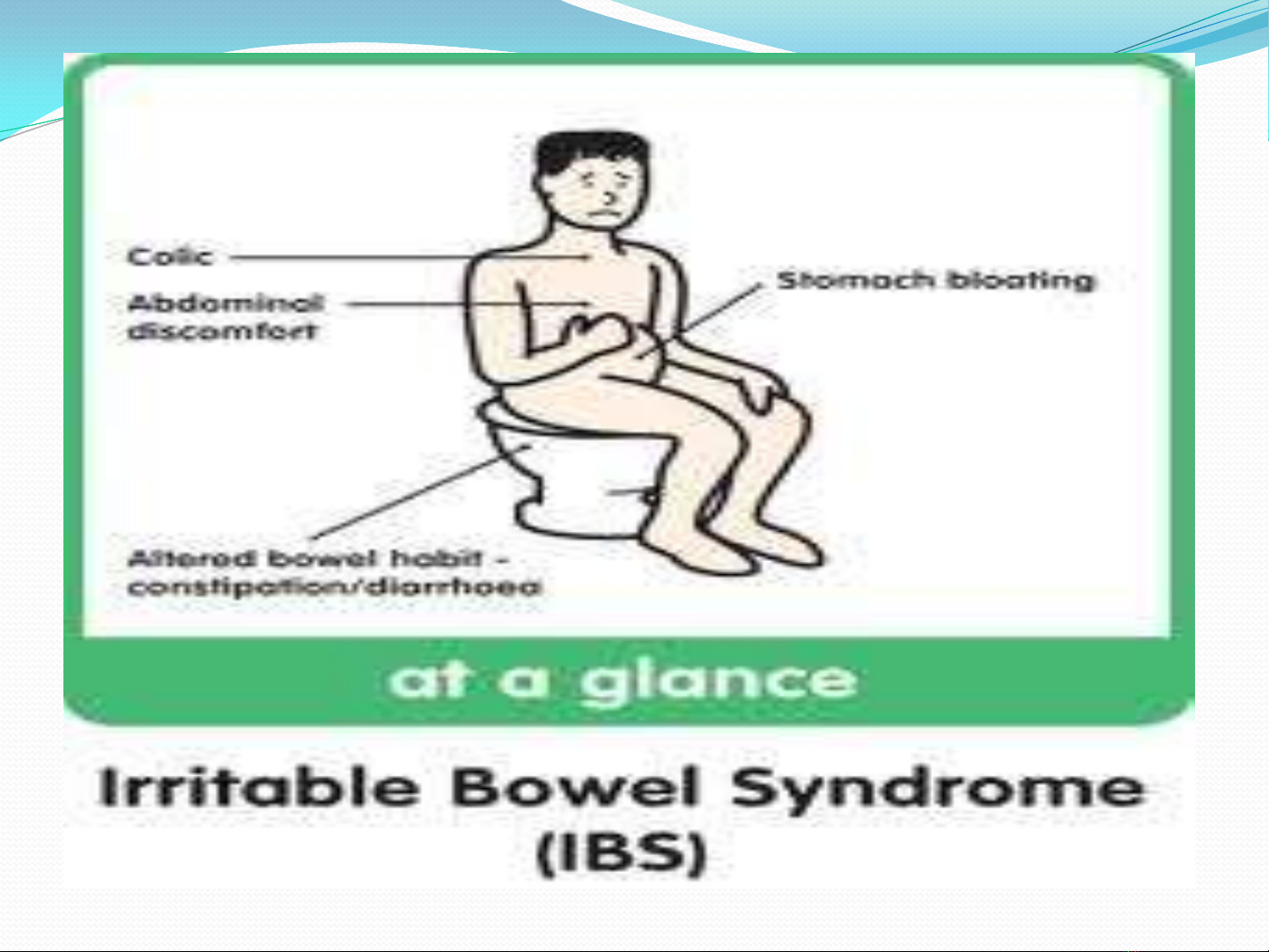
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
IBS- a functional bowel disorder : abdominal pain,
discomfort, altered bowel habits, absence of detectable
structural abnormalities
IBS-other functional disordes: fibromyalgia, headech,
backache, genitourinary symptoms
IBS- Dr Trần Ngọc Ánh
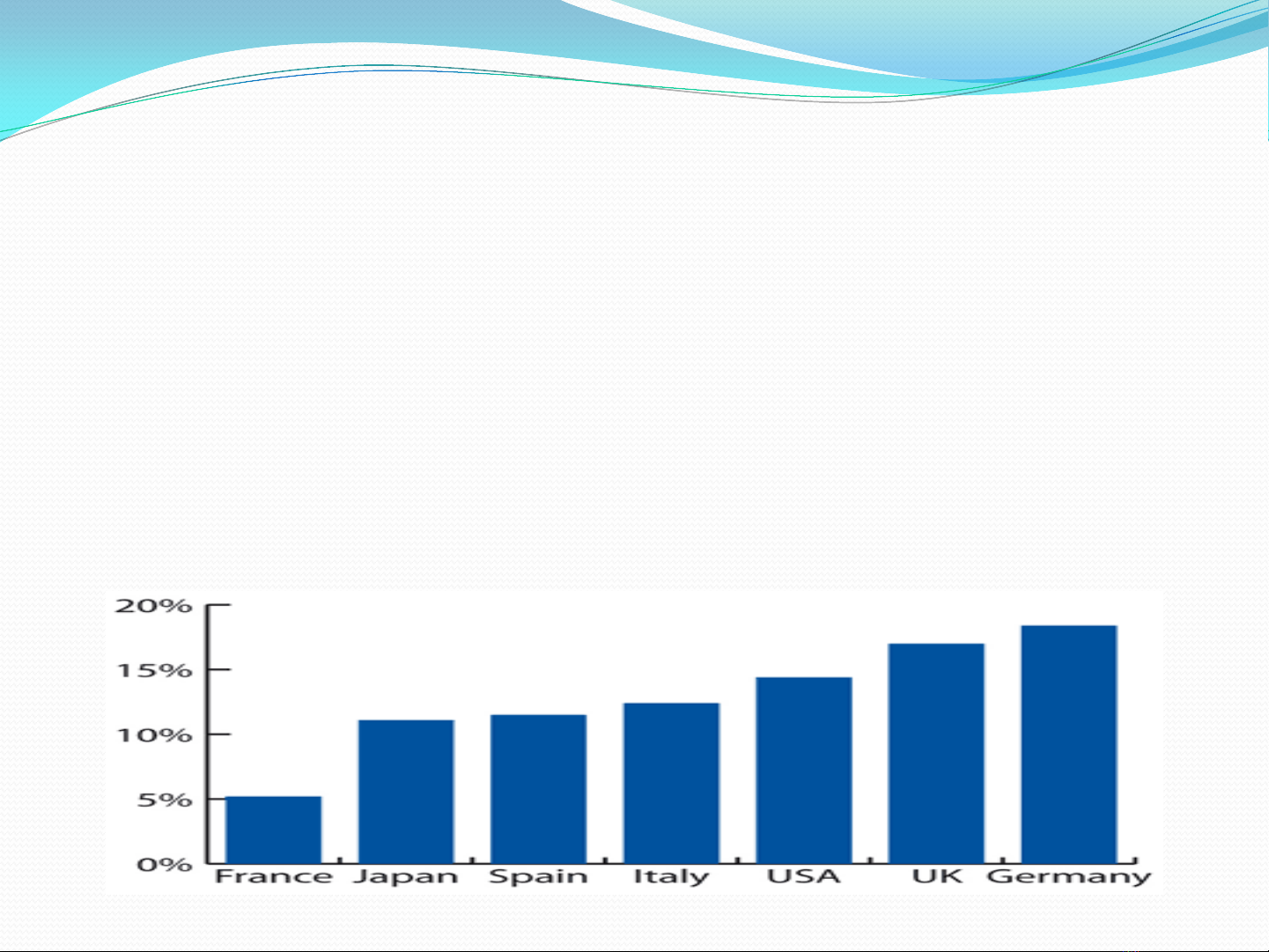
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Diagnosis: Clinical presentation
10-20% adult, adolescents: symptoms of IBS
W/M:2-3; 80% Severe in women
IBS- Dr Trần Ngọc Ánh
IBS- Dr Trần Ngọc Ánh


























