
Chapter 2:
RADIO PROPAGATION
1
Đ ng Lê Khoaặ
Email: dlkhoa@fetel.hcmuns.edu.vn
Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUS
Understanding RF Propagation
Goals
1. Estimate radio coverage area
2. Estimate link performance
3. Estimate network design parameters
1. Transmitters and their location
2. Transmit power
3. Antenna type
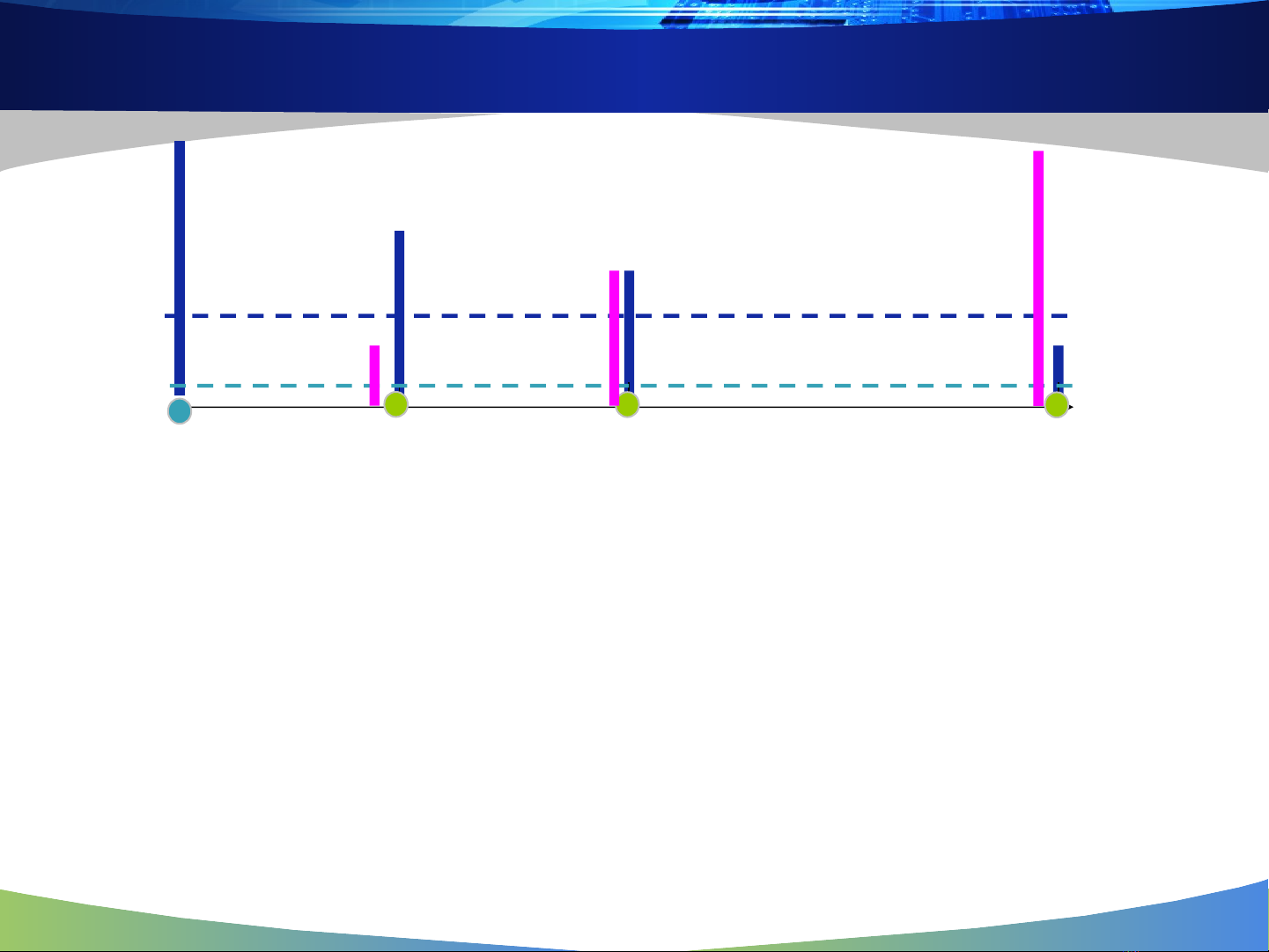
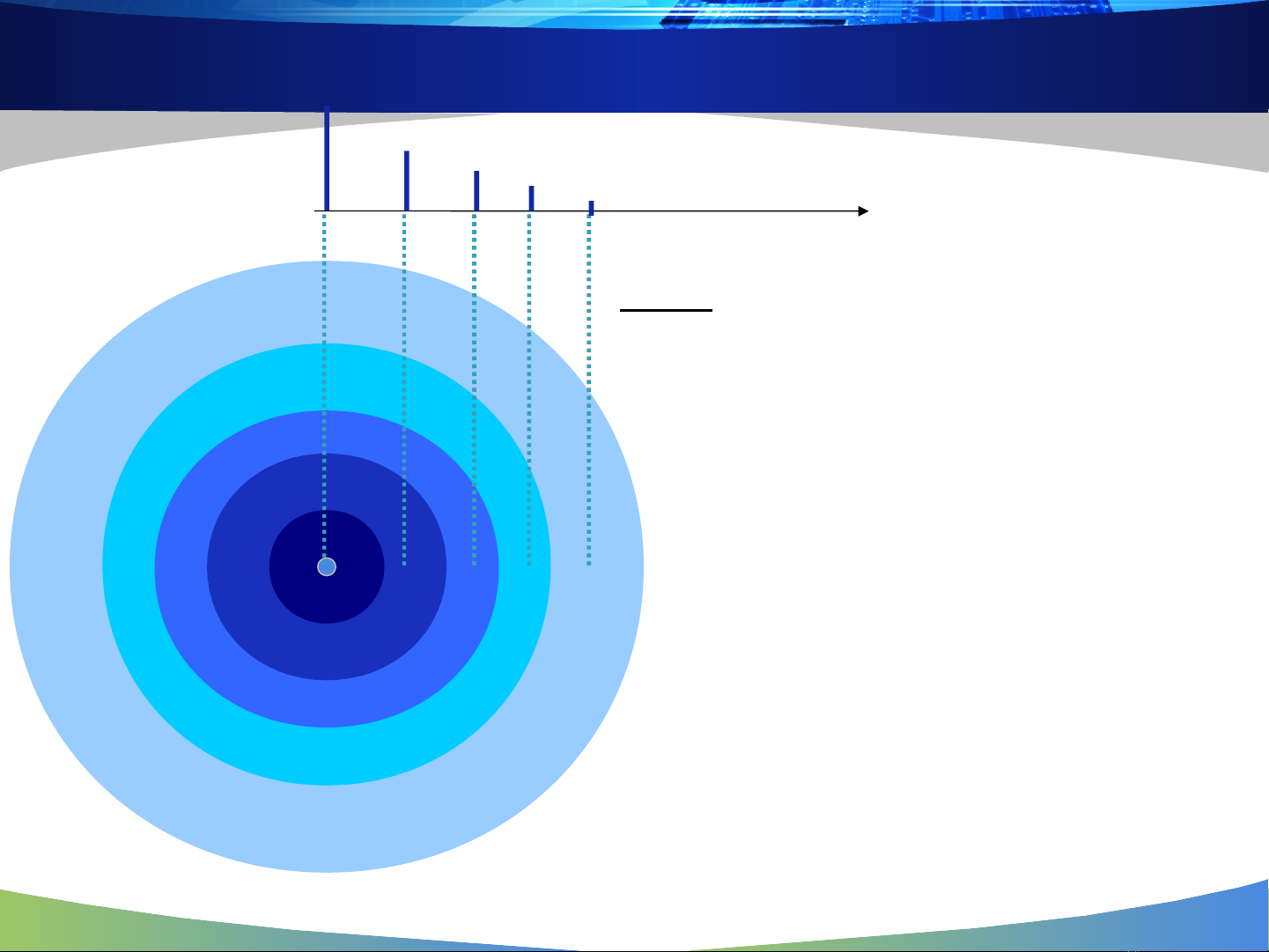
Conditions for correct reception
S/N ratio should be above a certain threshold (a function of
modulation scheme)
Signal power should be above the sensitivity threshold
What will happen if noise level increases?
What will happen in presence of another transmitter?
Pt
B CA
sensitivity
threshold
Noise
power
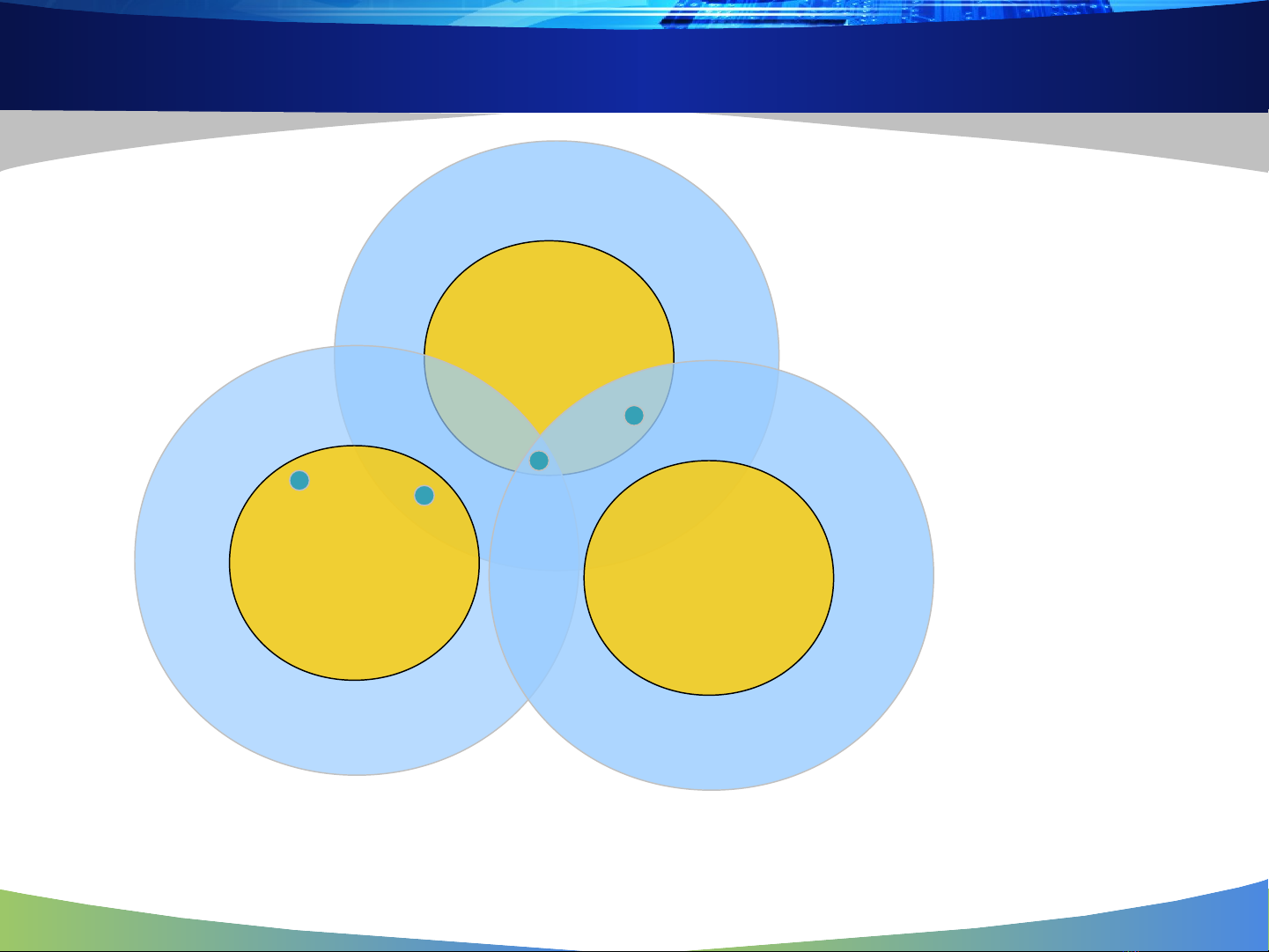
Interesting Scenarios
At which locations will
correct reception take
place?
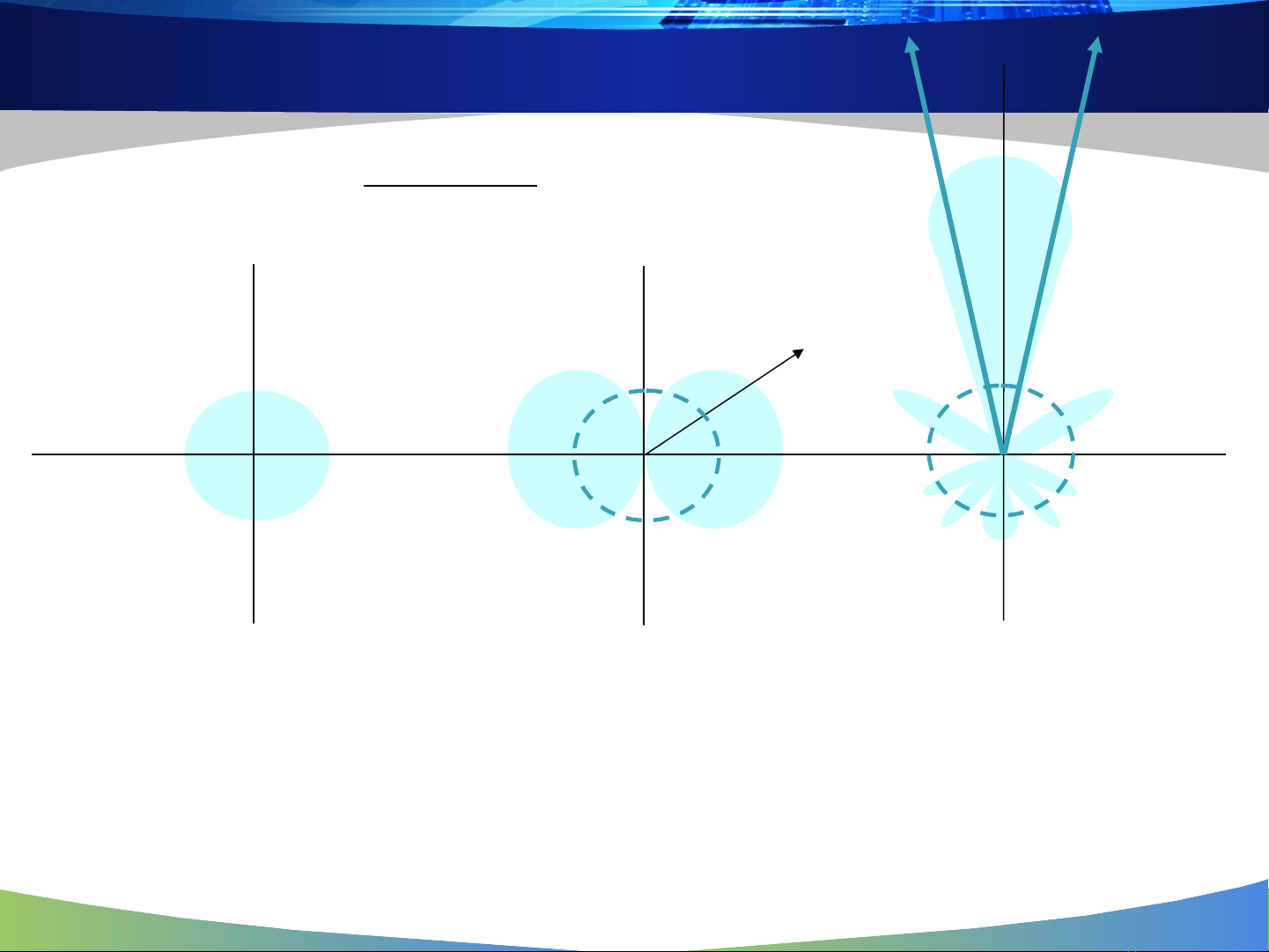
Antenna Basics
Isotropic Dipole High gain
directional
isotropic
ldirectiona
P
P
G
=
0 dBi2.2 dBi14 dBi


























