22
Research Article
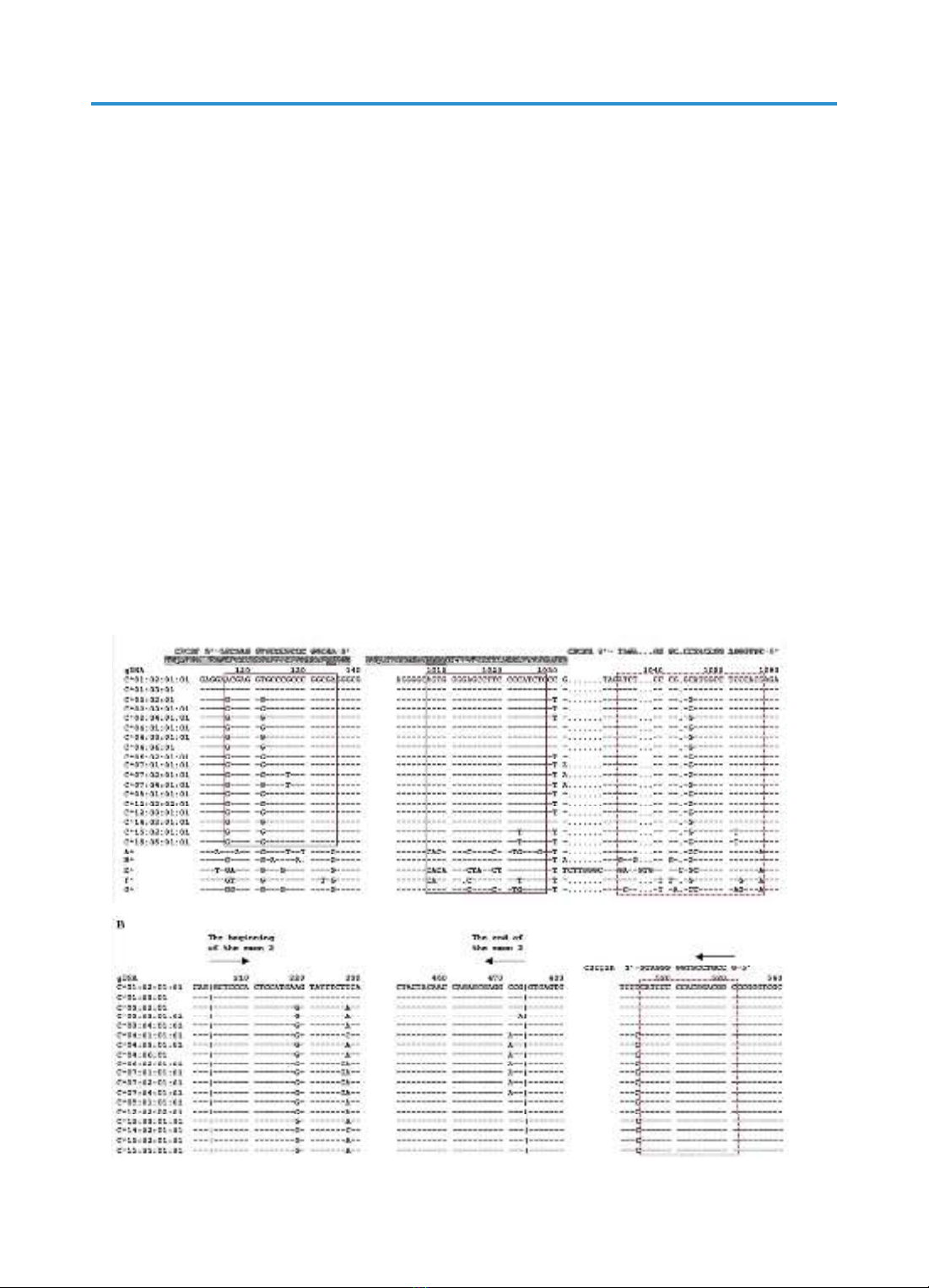
A simple sequencing protocol for genotyping the HLA-C locus by the
Sanger method
Tran Thu Ha Phama, Duc Minh Trana, Tiep Khac Nguyena, Thanh Huong Phunga*
a Faculty of Biotechnology, Hanoi University of Pharmacy, 13-15 Le Thanh Tong, Hoan Kiem, Hanoi, Vietnam
Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Drug Information, 2024, 16: 22-29
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history
Received 02 Feb 2024
Revised 23 April 2024
Accepted 24 April 2024
Keywords
HLA-C genotyping
Sanger
Sequencing
A B S T R A C T
The HLA-C gene, which belongs to the HLA superfamily (Human Leukocyte
Antigen), codes for the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC), which
plays crucial roles in the human immune system. This study aimed to develop a
simple sequencing protocol by the Sanger method using fewer primers and
reactions for genotyping the HLA-C gene than published protocols. The simple
protocol with three primers includes one PCR reaction and two sequencing
reactions. The primer set comprising SEQ ID1 and SEQ ID2 was used for the
PCR reaction to specifically amplify the exon 2 – exon 3 region of the HLA-C
locus, which contains the typical SNPs of each HLA-C allele. The PCR product
was purified and used as a template for the sequencing reactions. Two forward
primers, SEQ ID1 and SEQ ID3 were used for sequencing, in which, the SEQ
ID1 forward primer is located in the intron 1 region and the SEQ ID3 forward
primer is located in the intron 2 region of the HLA-C gene. Testing the simple
sequencing protocol on four samples of known HLA-C genotypes showed 100%
accurate results. The established Sanger sequencing protocol is simple to
implement, and reduces cost and time. Thus, this protocol can be used for
HLA-C sequencing for pharmacogenetic studies and applications.
*Corresponding author: Thanh Huong Phung, email: huongpt@hup.edu.vn
https://doi.org/10.59882/1859-364X/165
Journal homepage: jprdi.vn/JP
Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Drug Information
An official journal of Hanoi University of Pharmacy
1. Introduction
HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen - HLA)
is a superfamily of genes located on the short
arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.1 – 6p21.3),
encoding the major histocompatibility
complex (MHC), which plays a crucial role
in the function of the immune system [1]. The
HLA superfamily is divided into three classes,
each is further subdivided into numerous
types with highly complex polymorphism, of
which, HLA class I, comprising three main
types - HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C, is most
closely associated with the risk of adverse
drug reactions (ADRs) [1, 2]. In addition to a