
W-CDMA technology
and FOMA installation plan
3rd September, 2002
Network planning Dept.
NTT DoCoMo

2
Today’s Items
Principle of CDMA
- Frequency allocation
- Principle of DS-CDMA
- Transmit power control
Basic W-CDMA Transmission Technologies
- Two-layer spreading code assignment
- Inter-BS asynchronous mode
Characteristics of W-CDMA
- Statistical Multiplexing effect
- MS stand-by time
- Coherent RAKE reception (RAKE time diversity)
3G Roll Out Plan
- FOMA service content
- 3G Roll out plan
3
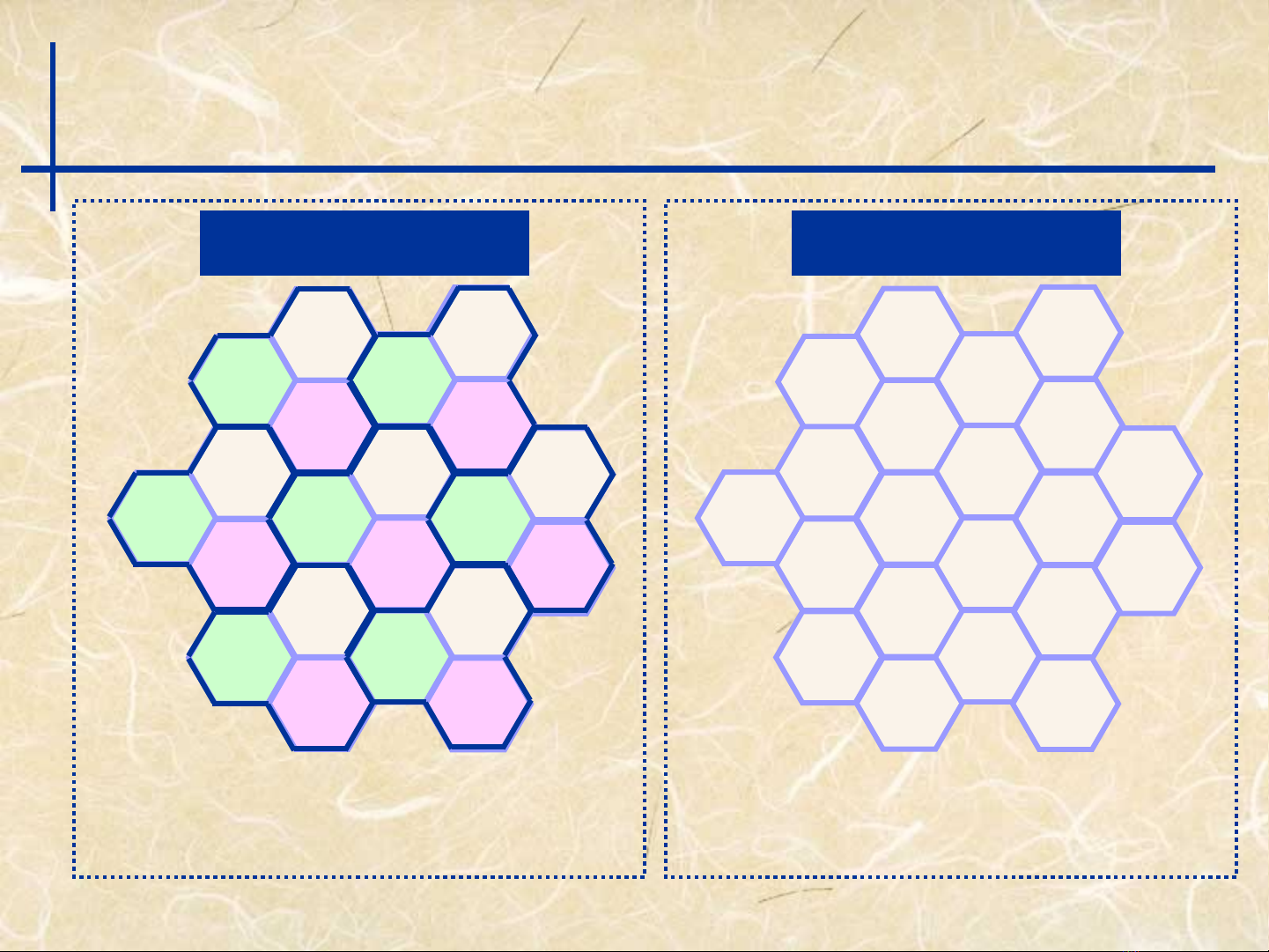
In case of 3 cell repetition
Frequency Allocation
f1
f1
f1f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f1
f2f2
f3
f1
f1
f3
f2
f1
f3
f1
f3
f2
f2
f1
f3
f3
f2
f3
f2
FDMA / TDMA CDMA
Same frequency in all area.
Take care of frequency allocation.
4
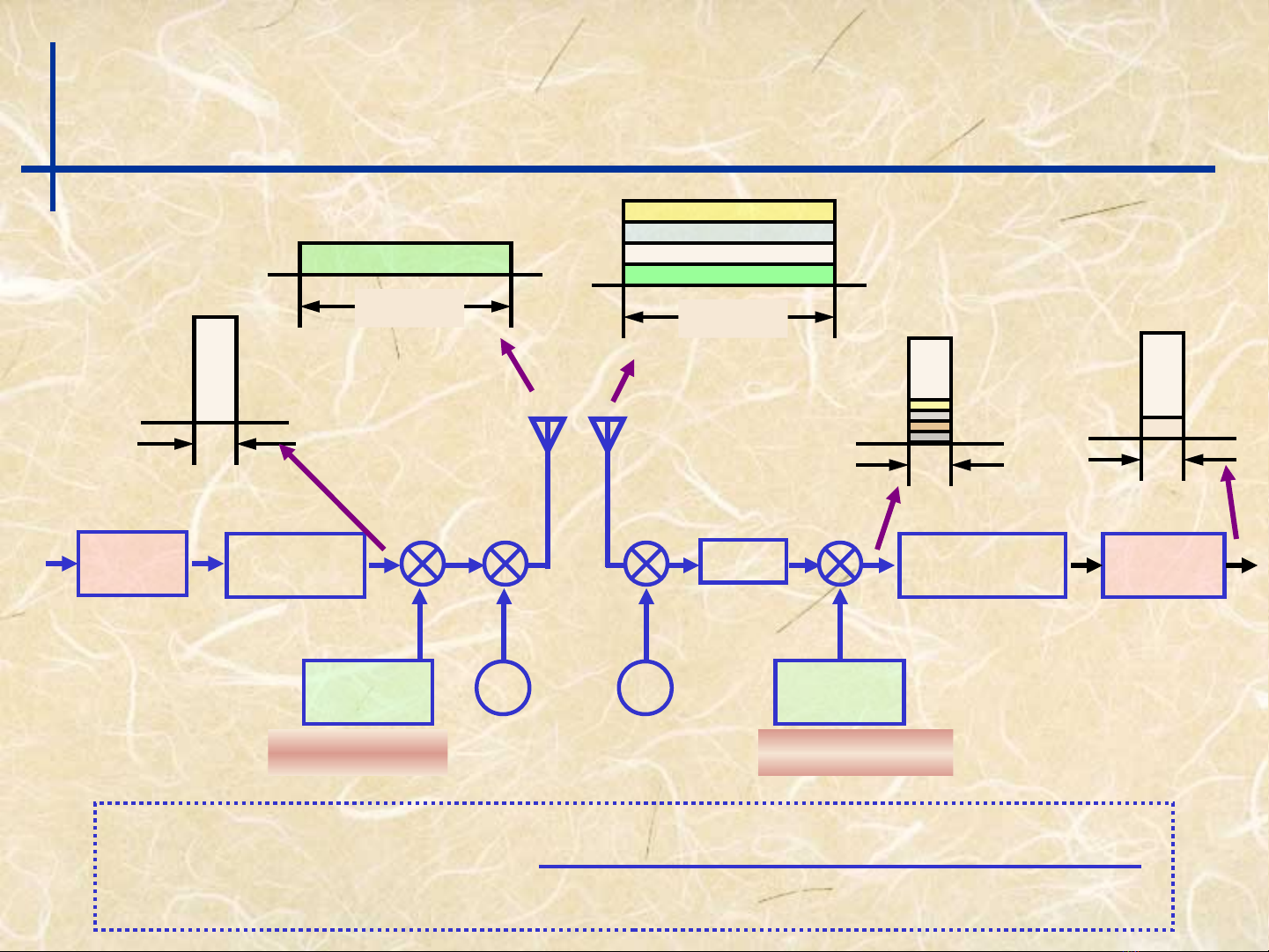
Principal Diagram
Frequency
Synthesizer
Channel
Coding
Data
Modulation
Spreading
Code ~
Spreading
~
Filter Data
Demodulation
Channel
Decoding
Spreading
Code
Frequency
Synthesizer Despreading
W
B(5MHz) B(5MHz)
WW
SF (spreading factor)=
Symbol rate of transmitted data
Chip rate of spread data
5
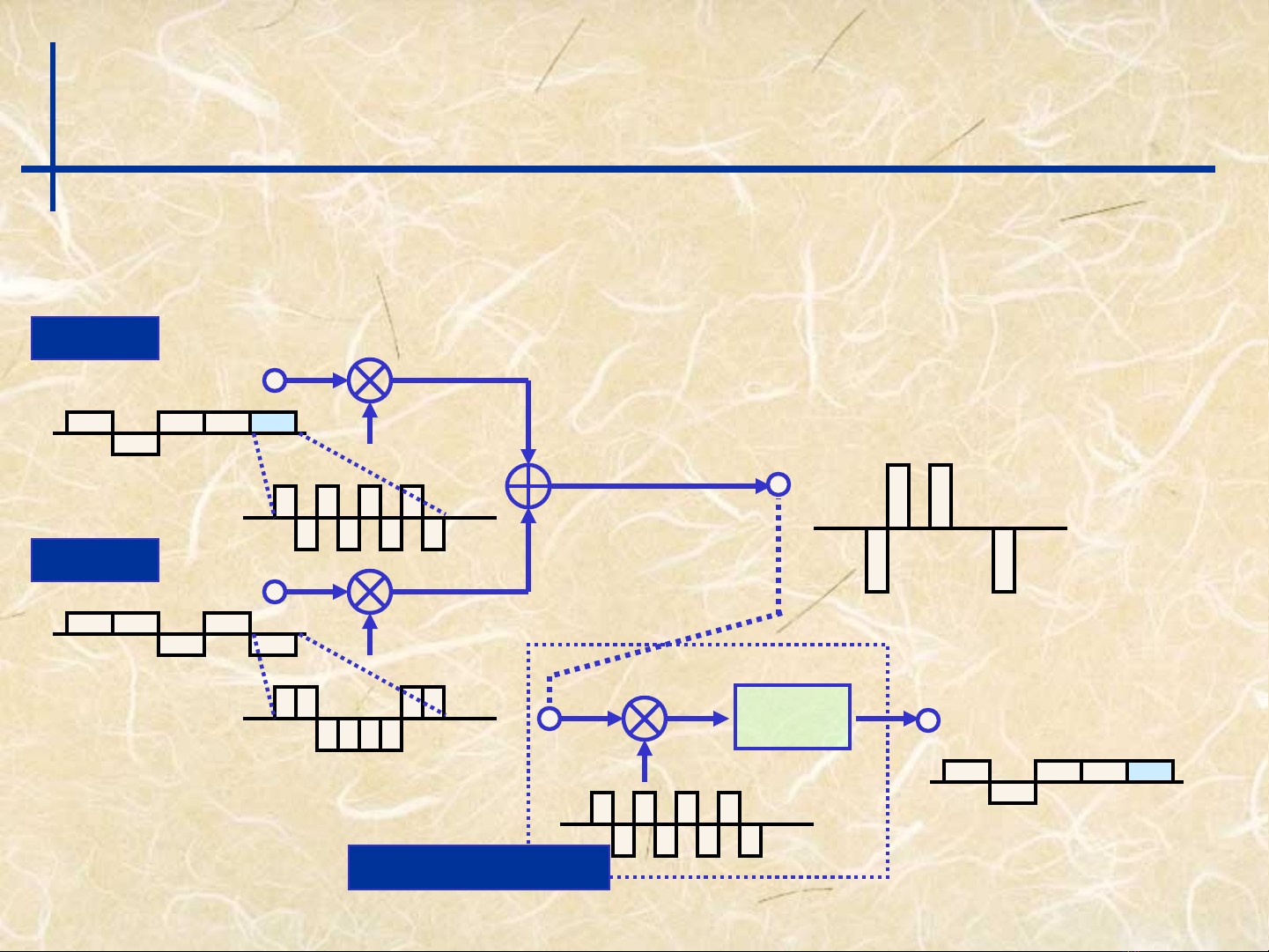
Principal Diagram
(Waveform of spreading codes in DS-CDMA)
1
-1
1 1 1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1 -1
-1
1
-1
1 1
-1-1-1-1
1 1
0
-2
0 0 0
2 2
-2
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1
-1
1 1 1
Integrate
& dump
User 1
User 2
Transmitted data
sequence
Spreading code
Spreading code
Composite signal
Spreading code
Recovered transmitted data
sequence for user 1
receiver User 1
Integration over the symbol length to recover
















![Chương trình đào tạo cơ bản Năng lượng điện mặt trời mái nhà [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260126/cristianoronaldo02/135x160/21211769418986.jpg)

![Chương trình đào tạo cơ bản Năng lượng gió [Tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260126/cristianoronaldo02/135x160/53881769418987.jpg)







