BIẾN CHỨNG CỦA VIÊM MŨI XOANG
Complicatious in Rhinosinusitis
PGS.TS Nguyễn Hữu Khôi
Bộ môn TMH – ĐHYD Tp HCM
2006

Complicatious in Rhinosinusitis
• Preantibiotic Era: BC mắt thường xảy ra.
Trong số này có 17% Meningitic, 20% Blindness.
• Thời đại KS: BC ít gặp, vẫn có BC nặng / tử vong.
• Điều kiện xảy ra BC:
- Med.Treatment: inadequate
- Host immunity: impaired.
- Organisms: Virulent & resistant.
- Surgical Intervention: delayed.
• Mũi xoang Cận kề
Viêm - Biến chứng Mắt - Não

Orbital Complications
• Orbit: close proximity to the sinus
Medially: Ethmoid & Sphenoid Sinus.
Superiorly: Frontal.
Inferiorly: Maxillary.
• Prevalent: Children > Aldults
• VX gây BC: 1st Ethmoid Simusittis
2st Frontal / Maxillary
3st Sfhenoid ±
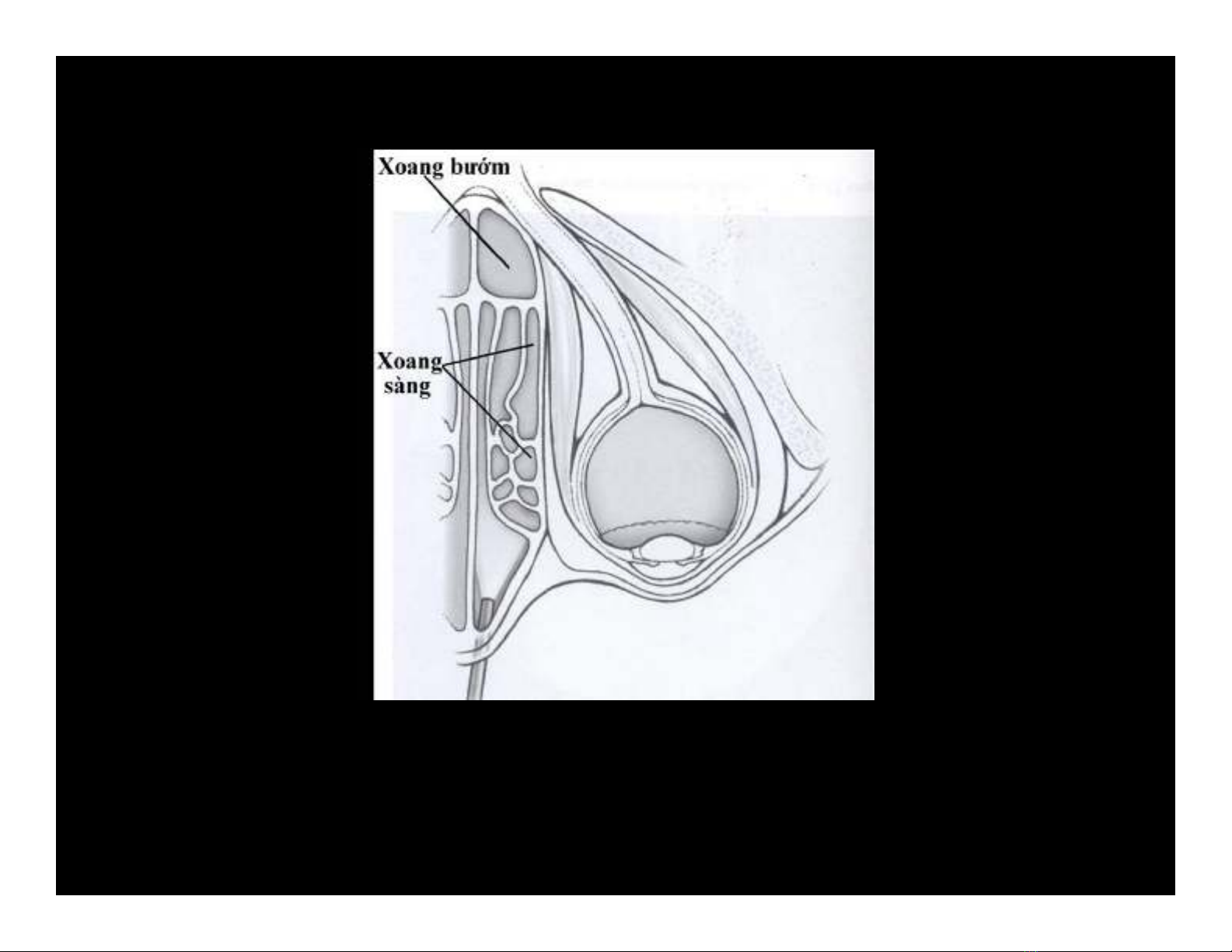
Orbital Complications
Thành ngoài xoang sàng xương giấy và thành ngoài
xoang bướm ngăn cách với ổ mắt: rất dễ bị tổn thương gây
biến chứng cho ổ mắt và dây thần kinh thị giác

ORBITAL EXTENSION OF SINUSITIS
Two routes
1. Direct Extension
- Through emgenital body dehischices.
open suture liues / foramina.
- By erosion of the bony barrier. Lamina papyracea
2. Retrograde Thromb phlebitis.
• Rich network of valveless veines.
( face, nasalcarity, Sinus = orbit)
• Arterial spread: possible / imlikely.
• Lymphatics: absent in the orbit.








![Bài giảng Vi sinh vật: Đại cương về miễn dịch và ứng dụng [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251124/royalnguyen223@gmail.com/135x160/49791764038504.jpg)