Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Drug Information, 2024, 15: 2-9
Journal homepage: jprdi.vn/JP
Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Drug Information
An official journal of Hanoi University of Pharmacy
*Corresponding author: Duc-Vinh Pham; e-mail address: vinhpd@hup.edu.vn 2
https://doi.org/10.59882/1859-364X/120
Research Article
Synergistic effect of Erythrina variegata L. and tamoxifen against the
growth of breast cancer cells
Van Thi-Hong Trana, Thi Van Anh Hoangb, Viet Hung Laic, Thi Hong Khanh Dod, Duc-Vinh
Phamb,*
aFaculty of Pharmacology and Biochemistry, National Institute of Medicinal Materials, 3B Quang Trung,
Hanoi, Vietnam
bFaculty of Pharmacology - Clinical Pharmacy, Hanoi University of Pharmacy, 13-15 Le Thanh Tong, Hanoi,
Vietnam
cCenter of Medicinal Material Resources, National Institute of Medicinal Materials, 3B Quang Trung, Hanoi,
Vietnam
dFaculty of Pharmacology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy – Vietnam National University, 144 Xuan
Thuy, Hanoi, Vietnam
A R T I C L E I N F O
A B S T R A C T
Article history
Received 04 Nov 2023
Revised 25 Jan 2024
Accepted 8 Feb 2024
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy and the second
leading cause of death in women. While tamoxifen (TAM) remains
to be a first-line agent for prevention and treatment of estrogen-
receptor (ER) positive breast tumors, TAM resistance represents one
of the biggest clinical challenges in breast cancer therapy. Therefore,
there has been growing interest in the identification of novel agents
including those of plant origin that enhance the TAM sensitivity of
breast cancer cells. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the
synergistic effect of Erythrina variegata extract (EVE) and TAM on
the suppression of breast cancer cell growth using MCF-7 cell model
and conventional bioassays such as MTT and colony formation
assay, cell cycle analysis, and immunocytochemistry. Interestingly,
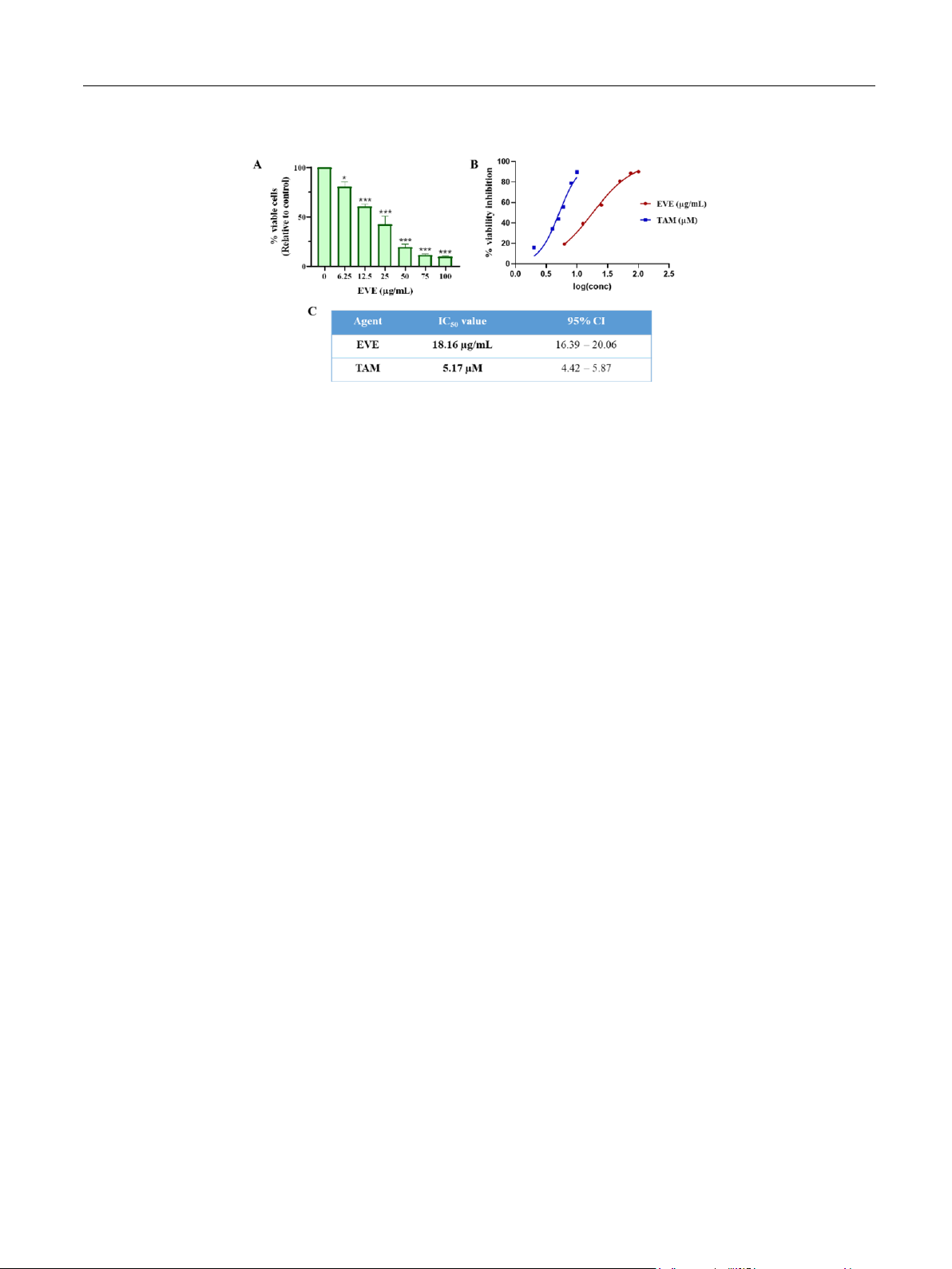
MTT assay in combination with Chou-Talalay analysis demonstrated
the potent synergism between EVE and TAM against MCF-7 cell
survival. Additionally, co-treatment of MCF-7 cells with EVE and
TAM more significantly suppressed colony formation, cell cycle
progression, and the nuclear expression of proliferative marker Ki67
compared to TAM alone. These findings imply that EVE potentiates
the anti-proliferative effect of TAM in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and
may become a promising agent in the treatment of ER positive breast
cancer.
Keywords
Breast cancer
Erythrina variegata
Hormon receptor
MCF-7 cells
Tamoxifen