
6/12/141 /20 MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
DANH SÁCH LIÊN K TẾ
(Linked List)
Nguy n Xuân Vinhễ
nguyenxuanvinh@hcmuaf.
edu.vn
C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ
DATA STRUCTURES
[214331]
6/12/142 /20 MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
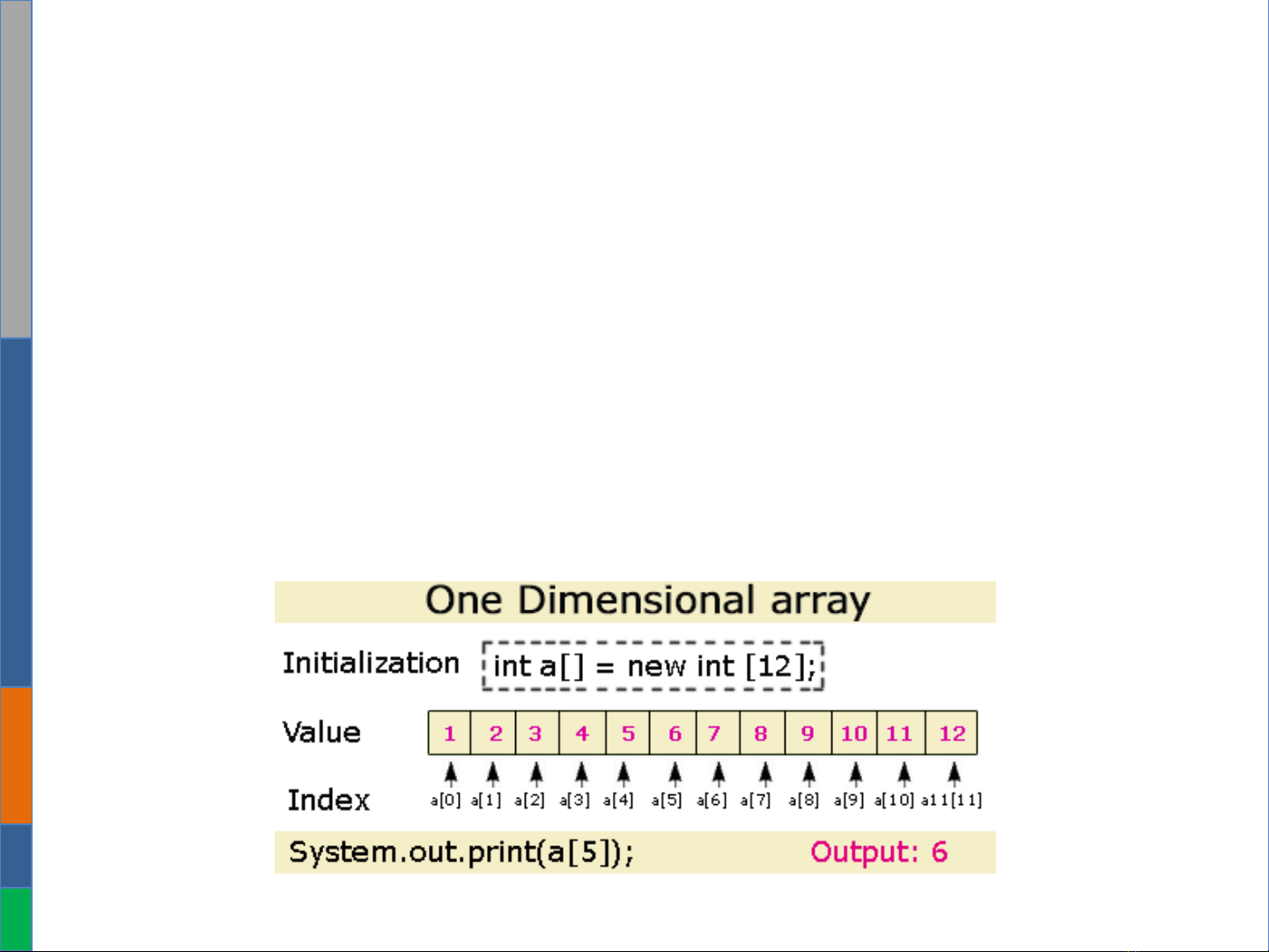
Review Arrays
•Pros
–Access quickly via array index.
–Easier to use.
•Cons
–Fixed size: the size of the array is static.
–One block allocation
–Complex position-based insertion/removal
6/12/143 /20 MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
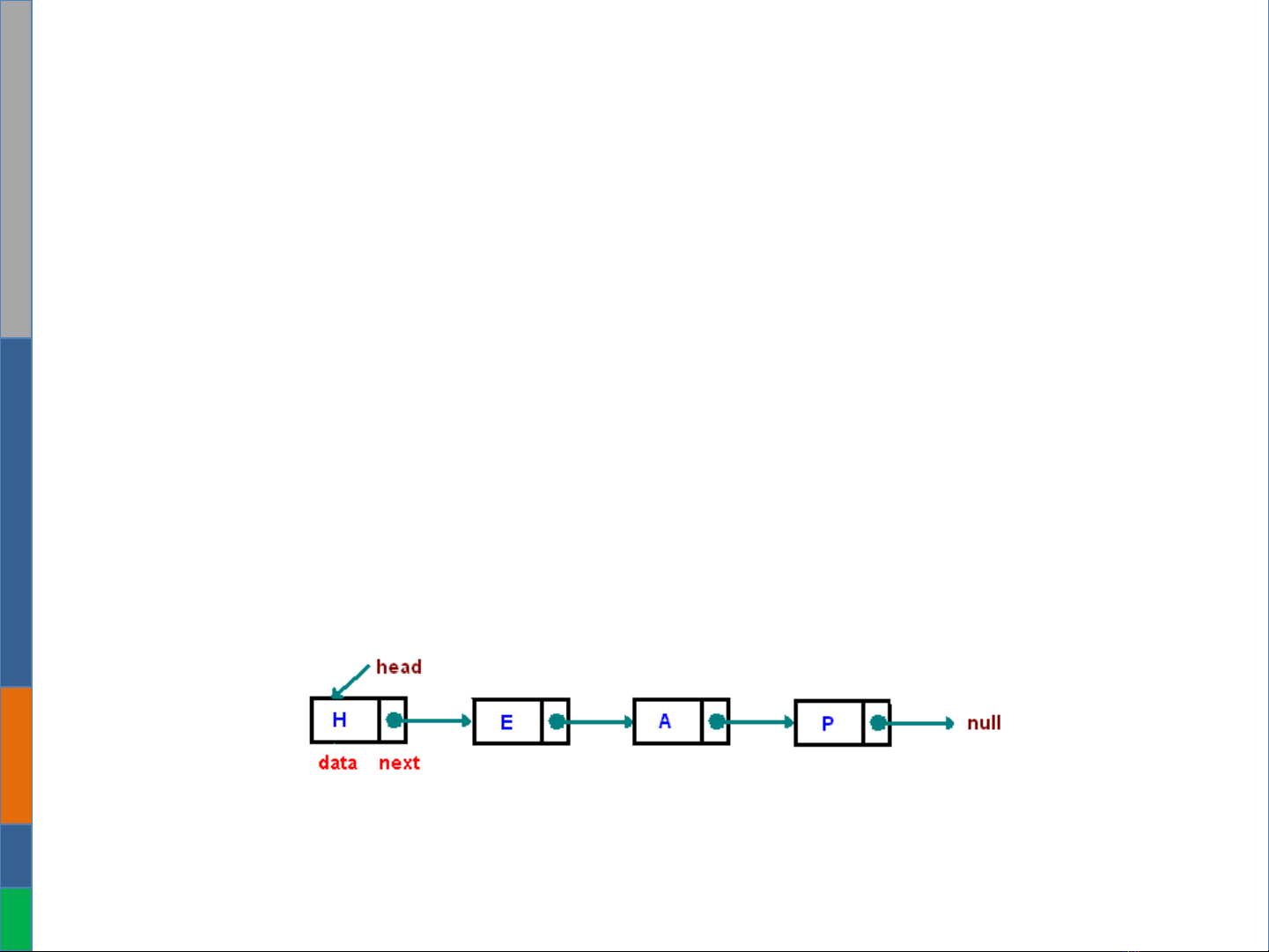
Linked List (Singly Linked List)
•A data structure consisting of a group of nodes which
together represent a sequence a linear structure.
•Each node is composed of a data and a reference(*).
•Allows more efficient insertion or removal of elements
from any position in the sequence.
•Reference of the last node point to null.
•Only need to handle the first (head) element.
(*) There might be two references, references can link to previous or next
element.
6/12/144 /20 MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
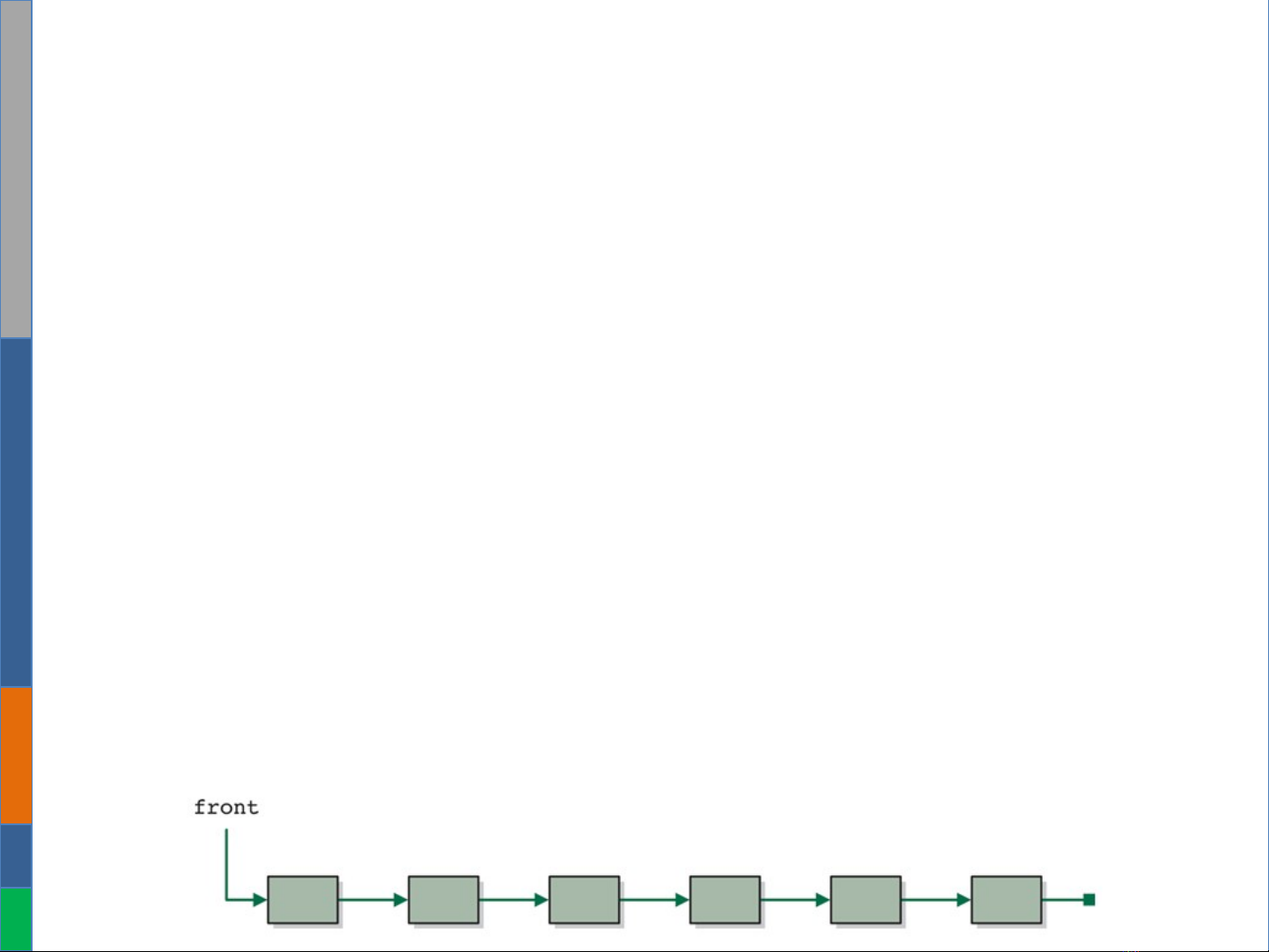
Pros and cons
•Pros
–Flexibility: insert/delete from any position in constant time.
–No single allocation of memory needed
–Dynamic allocation: the size is not required to be known in
advance
qCons
–There is no index to query element directly not allow random
access to element
–Complex to use and access.
–No constant time access to the elements.
Question: How to get the last element in the list?
6/12/145 /20 MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
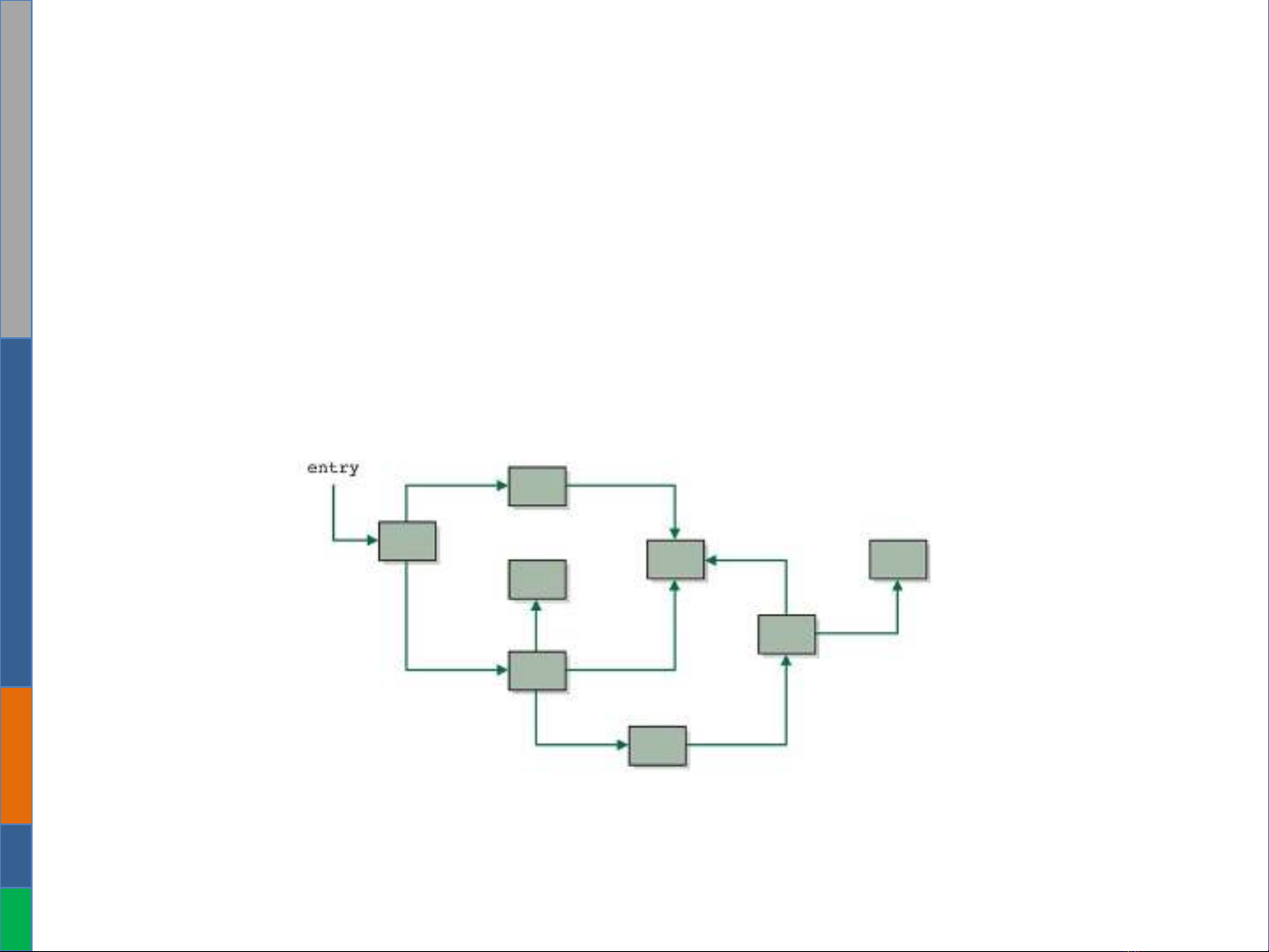
Non-linear Linked List (C u trúc phi tuy n ấ ế
tính)
•Normally, Linked List is a linear data structure.
•However, the complex reference also be a non-linear structure such
as Tree, Graph.

![Bài giảng Thực hành cơ sở dữ liệu Trường ĐH Công Nghệ [năm] mới nhất](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251120/oursky02/135x160/14661768233842.jpg)
























