1
QUANG HÔÏP
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis:
6CO2+ 6H2O C6H12O6+ 6O2
Chlorophyll
h
PHA TOÁI
Pha thu nhaän saûn phaåm pha saùng (ATP +
NADPH) ñeå toång hôïp höõu cô (Carbohydrate)
[khoâng phuï thuoäc vaøo aùnh saùng]
Quang hôïp
nhoùm thöïc vaät C3
Calvin cycle
Calvin cycle
The first product of CO
The first product of CO22fixation is 3
fixation is 3-
-phosphoglycerate
phosphoglycerate
M. Calvin & A. Benson exposed
green algae to 14CO2for short
periods of time in the presence of
light. They separated and
identified the labeled products by
paper chromatography.
pump
boiling
methanol
14CO2
14CO2-
CH2-O- P
H-C-OH
14C appeared first in
the carboxyl carbon of
3-phosphoglycerate.
light
algae
2
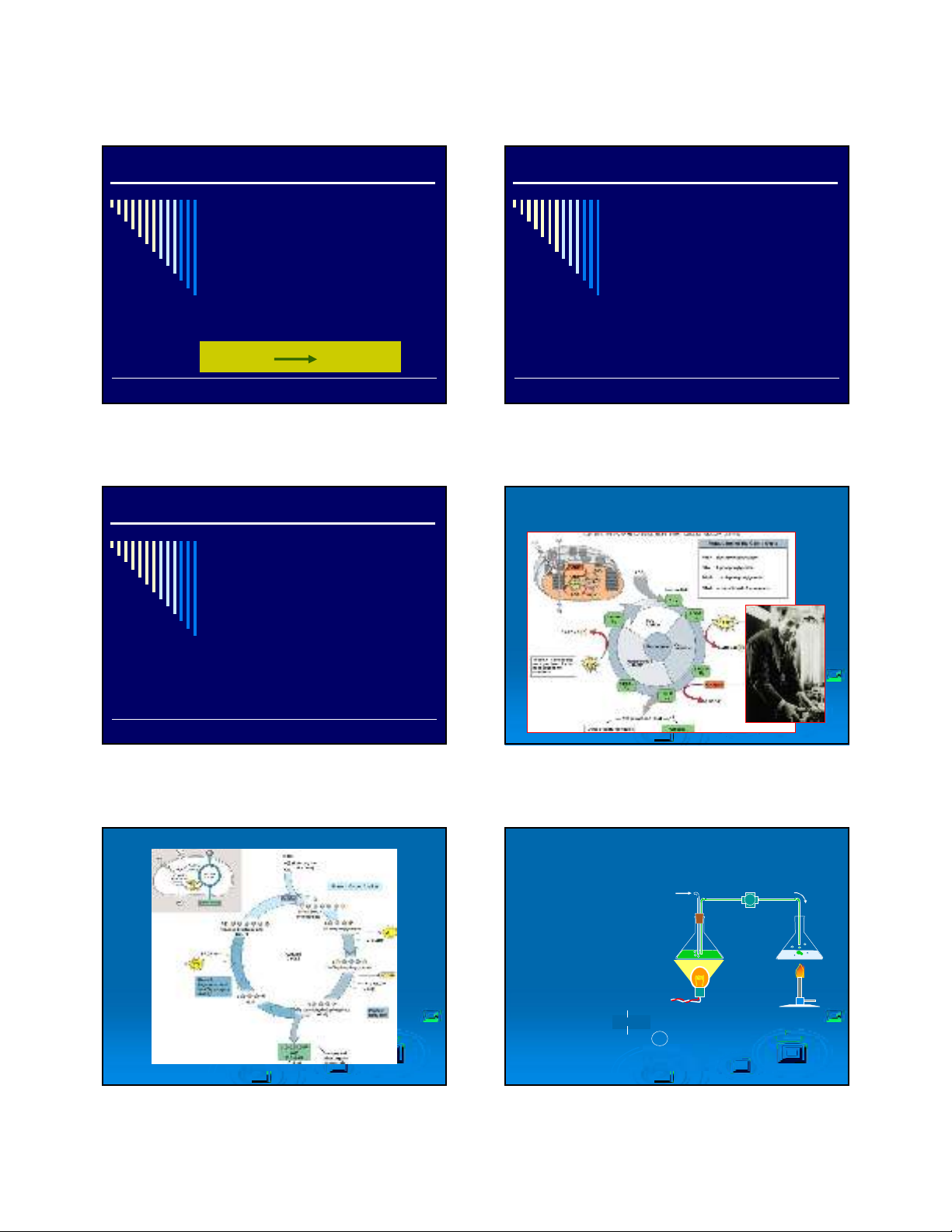
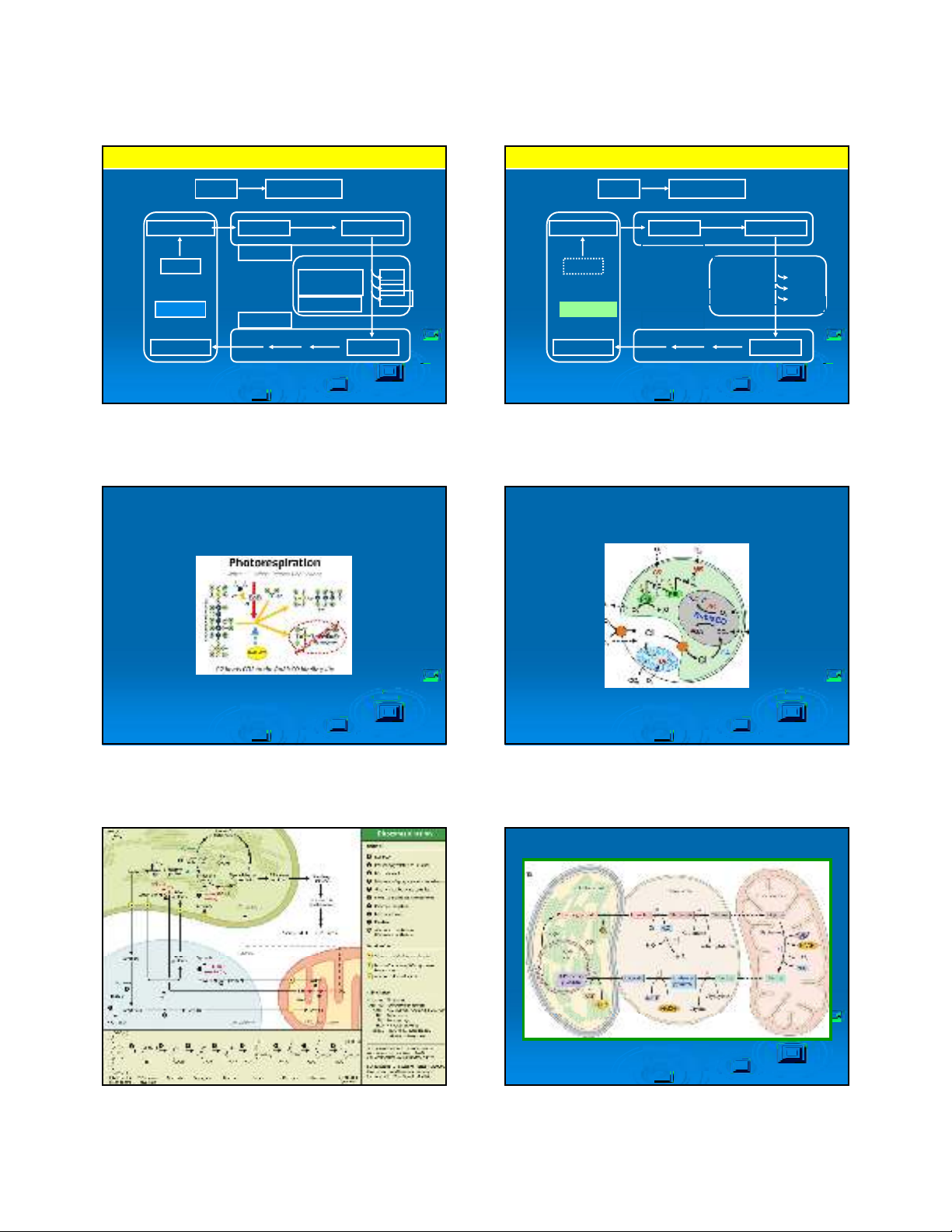
CHUOÃI CAÙC PHAÛN ÖÙNG ÑOÀNG HOÙA CARBON C3
CO2molecules are captured by
RuBP1 resulti ng in an unstable
intermediate that is immediately
broken apart i nto 2 PGA
6 molecu les of
CO2
12 molecules of
Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
PGA is phosphorylated
by ATP and reduced by
NADPH.
12 molecules
of glyceraldehyde-3-
phosphate (G3P)
12 mo lecules
of g lyceraldeh yde -3-
phosp hate (G3P)
Glucose and other
carbohydrate synthesis
6 molecules of ribose
phosphate (RP)
RuBP
regeneration
phase
Carbon
reduction
phase
CALVIN
CYCLE
CO2uptake
phase
6 molecules of
ribulose bisphosphate
(RuBP)
Light-dependent reactions Carbon fixation reactions
Light
reactions
Calvin
cycle
Chloroplast
36C
(6C)
6 x 5C = 30C
6C
36C
30C
6CO2+ 6H2OC6H12O6 + 6O2
6 CO2
12 ATPs
12 ADPs
12 NADPH,H+
12 NADP
3
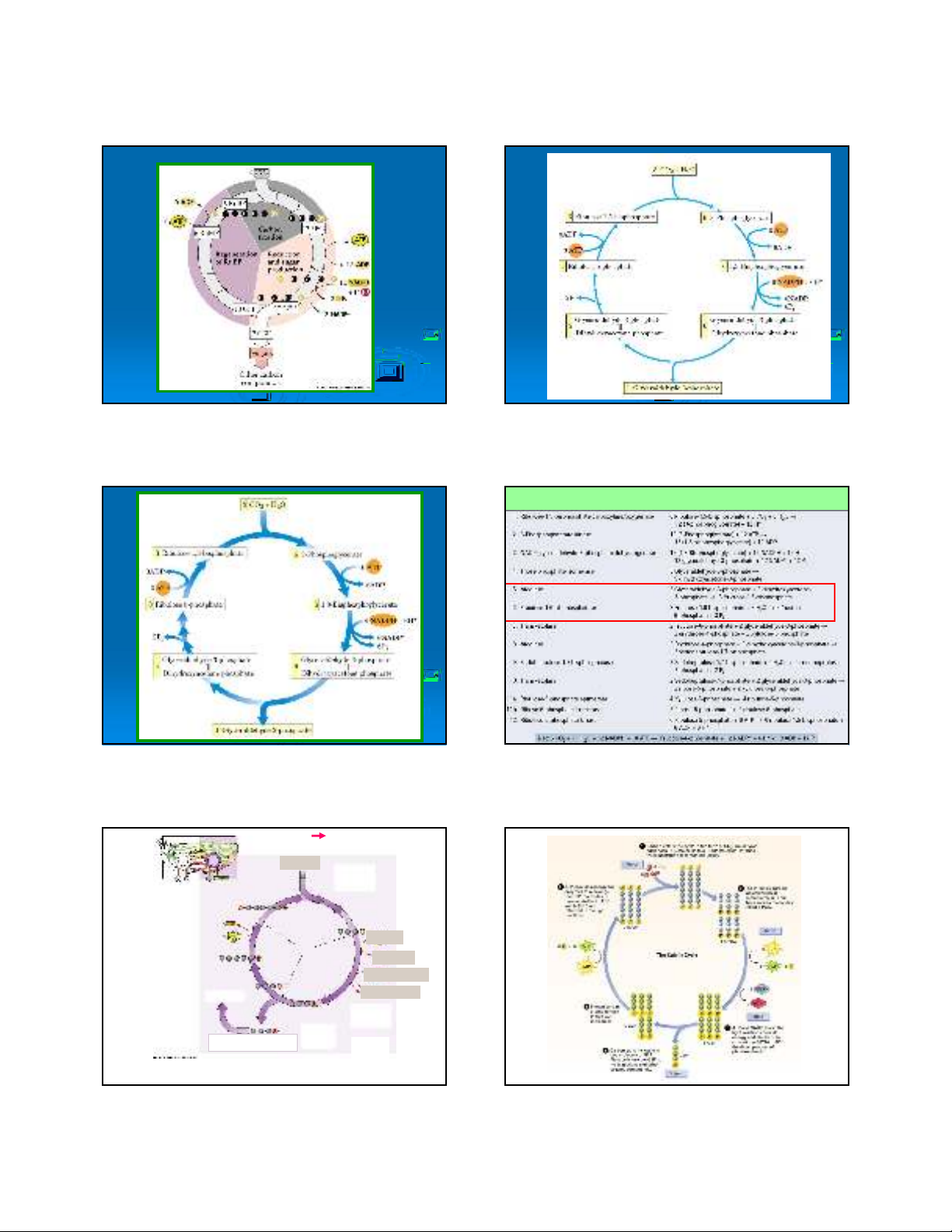
The Benson-Calvin cycle
3 RuBP
3 x C5
6 glycerate 3-P
(6 x C3)
carboxylation
3CO2
1 x C3 product 6 triose-P
(6 x C3)
reduction
6ATP + 6 NADPH
regeneration
3ATP
5 x C3
An
An antiporter
antiporter exchanges Pi with
exchanges Pi with triose
triose phosphates
phosphates
Ribulose 1,5 Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxidase
RUBISCO:
Ca
Caùùc
cenzyme
enzyme ñ
ño
oùùng
ng vai
vai tro
troøøquan
quan tro
troïïng
ng trong
trong
chu
chu tr
trì
ình
nh Calvin
Calvin ñö
ñöô
ôïïc
cñ
ñie
ieààu
uho
hoøøa
abô
bôûûi
ia
aùùnh
nh sa
saùùng
ng:
:
Rubisco
Rubisco
NADP:
NADP: Glyceraldehyde
Glyceraldehyde 3
3-
-phosphate
phosphate dehydrogenase
dehydrogenase
Fructose 1,6
Fructose 1,6-
-bisphosphatase
bisphosphatase
Sedoheptulose
Sedoheptulose 1,7
1,7 bisphosphatase
bisphosphatase
Ribulose
Ribulose 5
5-
-phosphate
phosphate kinase
kinase
Cô
Cô che
cheááñ
ñie
ieààu
uho
hoøøa
ath
thö
öô
ôøøng
ng thoâng
thoâng qua
qua vie
vieääc
ch
hì
ình
nh tha
thaøønh
nh hay
hay pha
phaùùbo
boûû
ca
caùùc
clieân
lieân ke
keáát
tdisulfide
disulfide
Rubisco gaén vaøo cô chaát
Nhạ
Nhạy c
y cả
ảm v
m vớ
ới
i á
ánh s
nh sá
áng m
ng mạ
ạnh
nh
Á
Ái l
i lự
ực v
c vớ
ới CO2
i CO2 th
thấ
ấp
p
Không ch
Không chị
ịu nhi
u nhiệ
ệt đ
t độ
ộ cao
cao
Tí
Tính 2
nh 2 m
mặ
ặt:
t:
•
•CO2
CO2
•
•O2
O2
>>> Qua
>>> Quang hô h
ng hô hấ
ấp >
p >>> kh
>> không nh
ông nhữ
ững không t
ng không tạ
ạo
o
đ
đườ
ường m
ng mà cò
à còn phân h
n phân hủ
ủy đ
y đườ
ường đ
ng đã tí
ã tích l
ch lũ
ũy
y
4
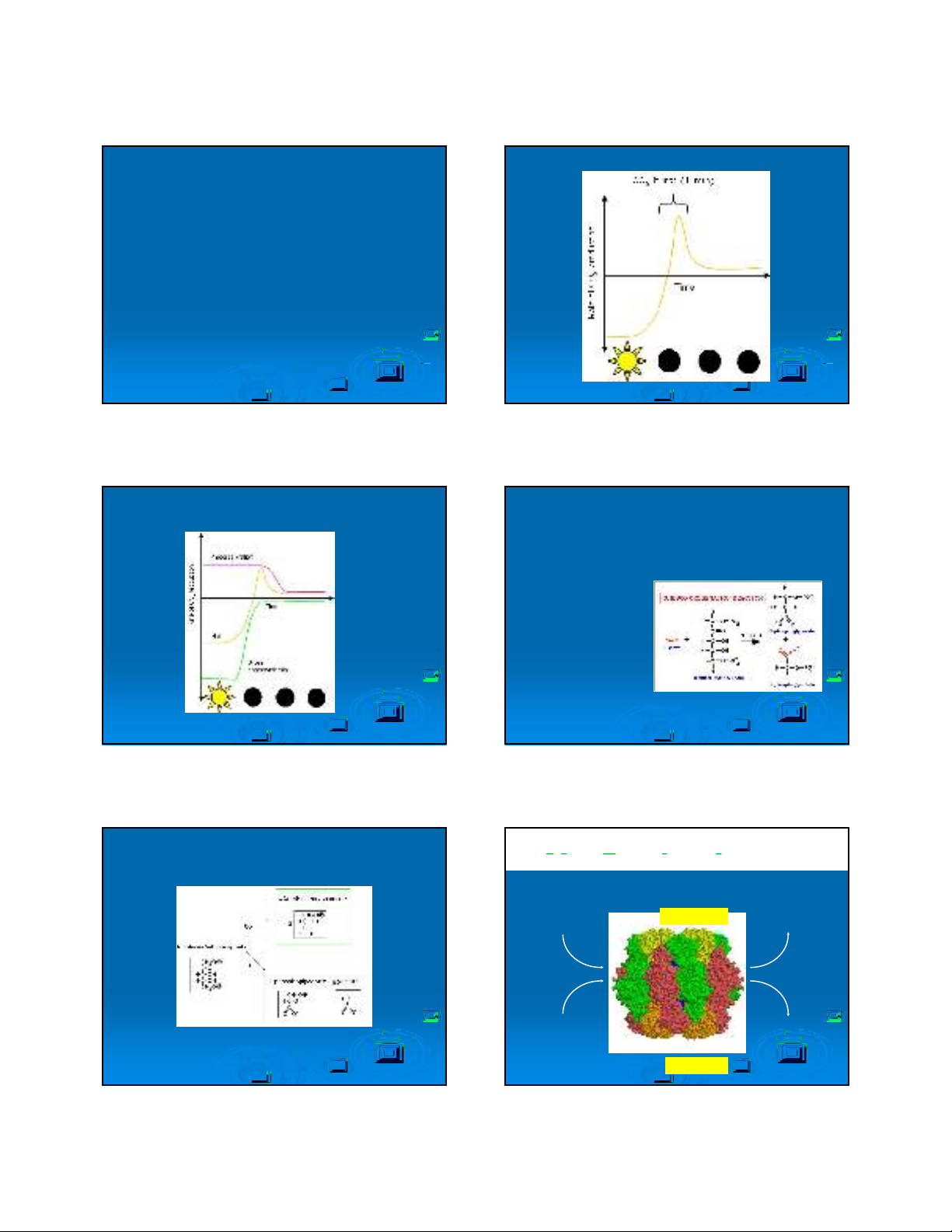
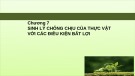
HIEÄN TÖÔÏNG QUANG HOÂ HAÁP
Enzyme
RUBISCO xuùc
taùc phaûn öùng vôùi
oxygen gaây ra
hieän töôïng
quang hoâ haáp
R
Rib
ibu
ulose
lose 1,5
1,5-
-bis
bisphosphate
phosphate c
carboxylase
arboxylase-
-o
oxygenase
xygenase (
(Rubisco
Rubisco)
)
C5 + C1
RuBP + CO2+ H2O
2 x C3
2 (glycerate 3-P)
carboxylase
oxygenase
C5
RuBP + O2
C3 + C2
glycerate 3-P +
glycollate 2-P
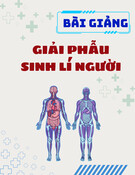
5
2 glycollate-2-P
chloroplast
Photorespiratory pathway
Rubisco
2 glycollate 2 glycine (C2)
peroxisome
glycerate-3-P
peroxisome
2 x C2 1 x C3 + CO2
glycine
decarboxylase
mitochondrion
CO2
NH3
NADH
serine (C3)
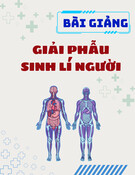
2 glycollate-2-P
chloroplast
Photorespiratory pathway/Quang hoâ haáp
Rubisco
2 glycollate 2 glycine (C2)
peroxisome
glycerate-3-P
peroxisome
2 x C2 1 x C3 + CO2
NADH
glycine
decarboxylase
mitochondrion
CO2
NH3
serine (C3)

















![Hướng dẫn giải chi tiết bài tập phân li, phân li độc lập: Tài liệu [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251204/lethu2868@gmail.com/135x160/84711764814448.jpg)

