Close Window
Assessment System
1. Assessment Selection
2. Assessment Settings
3. Take Assessment
Take Assessment - ROUTE Chapter 3 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)
Time Remaining:
1
Which OSPF network type requires the election of a DR/BDR?
broadcast
point-to-point
point-to-multipoint
point-to-multipoint nonbroadcast
2
In an OSPF hub-and-spoke topology, what needs to be done to ensure that the spoke routers would never be
selected as DR and BDR?
Because nonbroadcast networks do not elect a DR/BDR, nothing needs to be done.
All routers must be configured with an OSPF interface priority of 0 (ip ospf priority) to disable the
DR/BDR election process.
All spoke routers need to be configured with an OSPF interface priority of 0 (ip ospf priority) so that they
will not become the DR/BDR.
One of the spoke routers will need to be configured as the DR by setting the OSPF interface priority higher
than 1 (ip ospf priority).
3
A network administrator is implementing OSPF in a portion of the network and must ensure that only specific
routes are advertised via OSPF. Which network statement would configure the OSPF process for networks
192.168.4.0, 192.168.5.0, 192.168.6.0, and 192.168.7.0, now located in the backbone area, and inject them into
the OSPF domain?
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 1
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.15.255 area 1
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
4
What two advantages does authentication provide that should be considered when planning an OSPF
implementation? (Choose two.)
It reduces OSPF information exchange overhead.
It encrypts routing tables to prevent unauthorized viewing.
It prevents routing information from being falsified in transit.
It ensures that routing information comes from a valid source router.
It ensures that OSPF routing information takes priority over RIP or EIGRP updates.
5
When will a router in an OSPF nonbackbone area receive a default route from the ABR or ASBR? (Choose
three.)
when the area is a normal area
when the area is a NSSA stub area
when the area is a totally stubby area
when the area is a NSSA totally stubby area
when the area is connected to the backbone area using a virtual link
when the area is a normal area and the ASBR has been configured with the default-information originate
always command
6
What are two reasons for creating an OSPF network with multiple areas? (Choose two.)
to protect against the fact that not all routers support the OSPF backbone area
to ensure that an area is used to connect the network to the Internet
to reduce SPF calculations
to reduce use of memory and processor resources
to simplify configuration
7
What does OSPF use to calculate the cost to a destination network?
bandwidth
bandwidth and hop count
bandwidth and reliability
bandwidth, load, and reliability
8
Which three items must match between OSPF neighbors in order to form an adjacency? (Choose three.)
hello/dead interval
area ID
priority ID
authentication type
adjacency type
router process ID
9
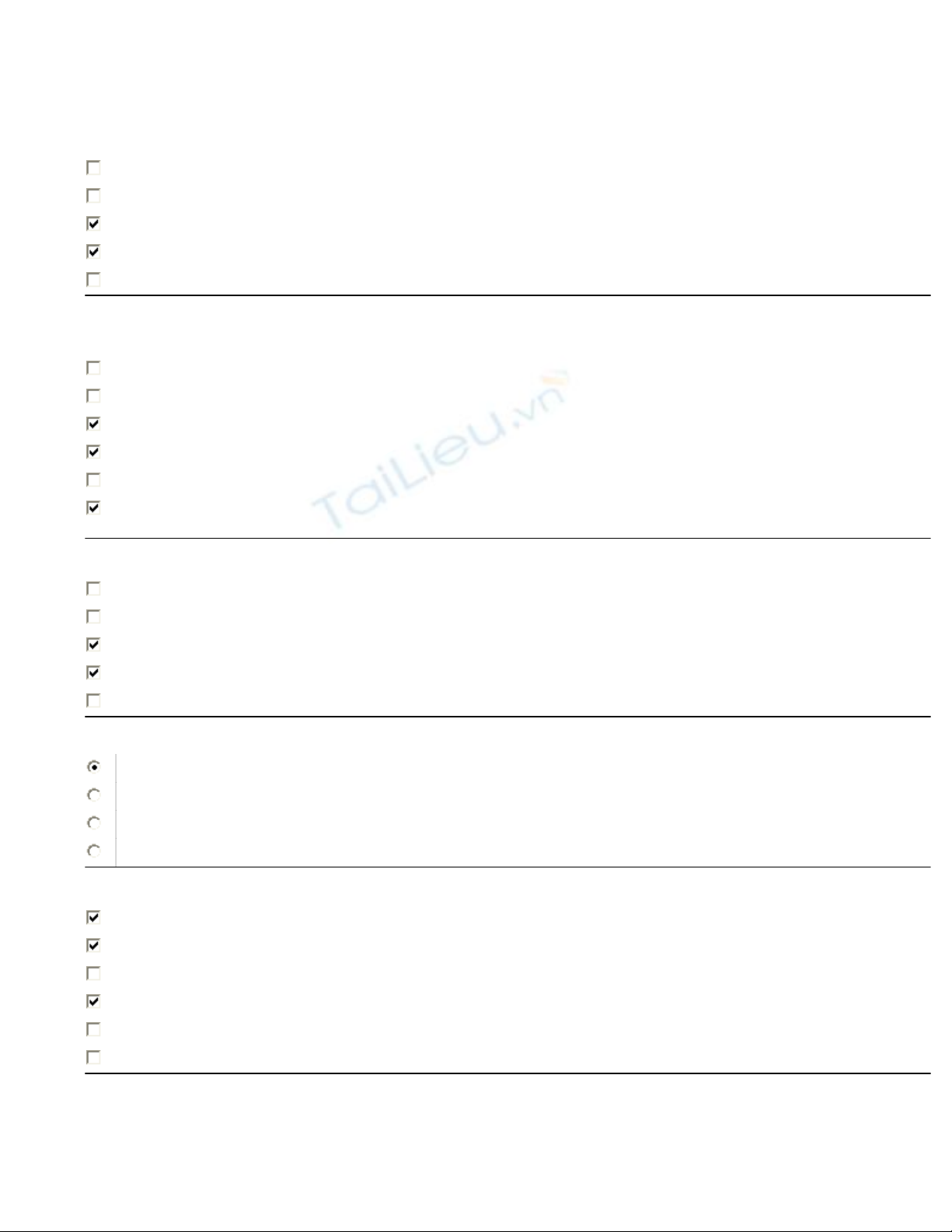
Refer to the exhibit. When OSPF is operational and converged, what neighbor relationship is developed between
Router1 and Router2?
A FULL adjacency is formed.
A 2WAY adjacency is formed.
Router2 will become the DR and Router1 will become the BDR.
Both routers will become DROTHERS.
10
A fully converged five router OSPF network has been running successfully for several weeks. All configurations
have been saved and no static routes are used. If one router loses power and reboots, what information will be in
its routing table after the configuration file is loaded but before OSPF has converged?
All routes for the entire network will be present.
Directly connected networks that are operational will be in the routing table.
Because the SPF algorithm has not completed all calculations, no routes will be in the table.
A summary route for all previously learned routes will automatically appear in the routing table until all
LSPs have been received by the router.
11
What are two effects of using multiple OSPF areas that reduce bandwidth and router overhead? (Choose two.)
prevention of a flood of queries
reduction in the size of the LSDB
reduction in the size of the neighbor table
limits on the propagation of type 1 and 2 LSAs
decrease in the number of DR and BDR elections
12
What is the function of the OSPF LSU packet?
to announce new OSPF information
to confirm receipt of certain types of OSPF packets
to request more information about any entry in the BDR
to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers
13

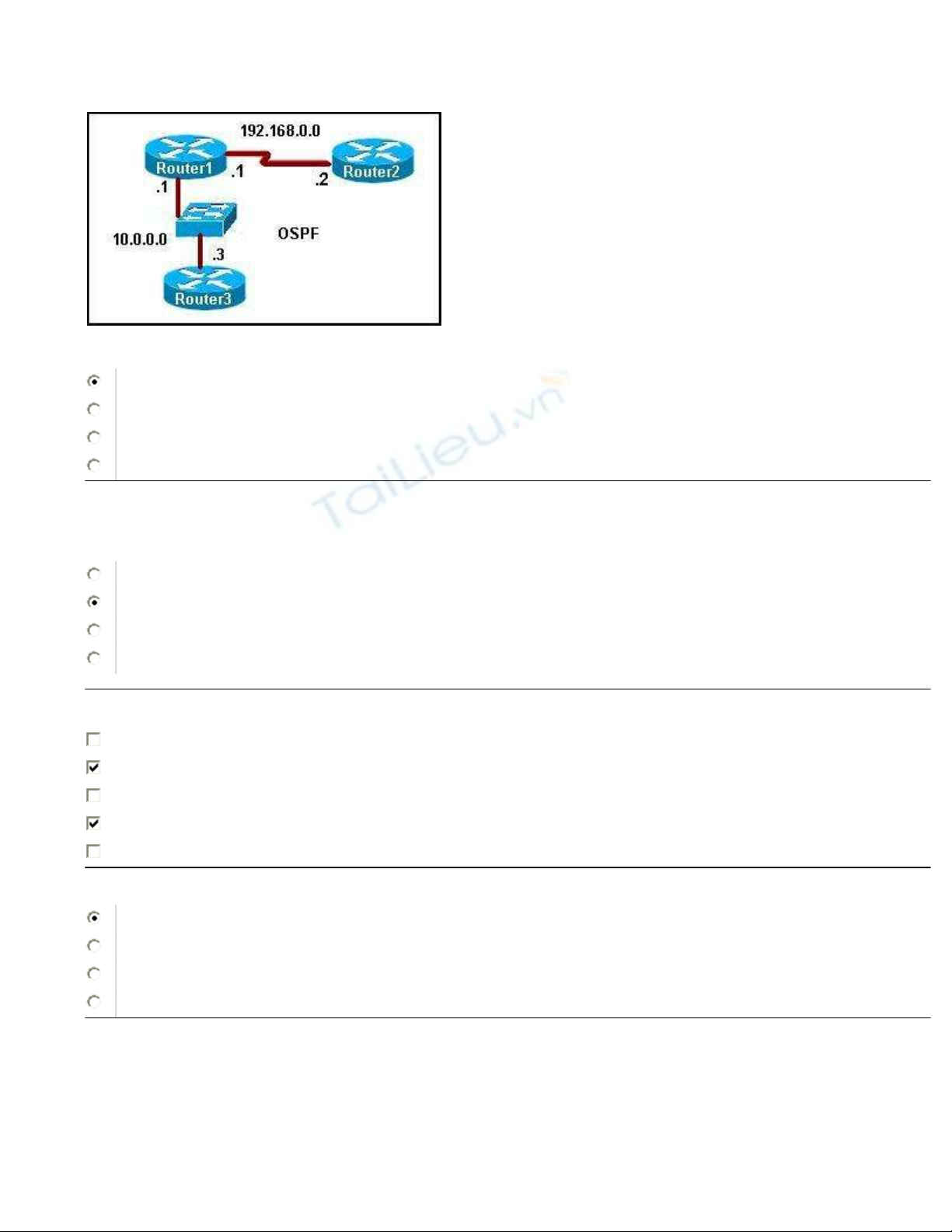
Refer to the exhibit. How does the router treat the authentication of OSPF packets that enter and leave
FastEthernet interface 0/0?
OSPF packets are sent with authentication key 10 only.
OSPF packets are sent with authentication key 20 only.
Two copies of every OSPF packet are sent, one with key 10 and one with key 20.
Key 10 is used to authenticate incoming packets and key 20 is used to authenticate outgoing packets.
14
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of OSPF packets are represented by the debug command output?
link-state request packets sent with plain-text authentication
hello packets sent with a MD5 hashed authentication key id of 100
hello packets sent in simple authentication with a password of youngest
link-state update packets sent encrypted with a 100 bit authentication key








![Bài giảng Cáp mạng, vật tải truyền - GV. Lê Bá Thi [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2016/20160409/o0tchya0o/135x160/4531460212639.jpg)





![Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Mạng máy tính: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251001/kimphuong1001/135x160/15231759305303.jpg)
![Câu hỏi ôn tập An toàn mạng môn học: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250919/kimphuong1001/135x160/30511758269273.jpg)






![Giáo trình Công nghệ mạng không dây (Nghề Quản trị mạng máy tính, Trình độ Cao đẳng) - Trường Cao đẳng Thủ Thiêm [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250916/kimphuong1001/135x160/13561758013095.jpg)



