
Tuyển tập Hội nghị Khoa học thường niên năm 2024. ISBN: 978-604-82-8175-5
562
THE KNOW-WANT-LEARN PROCEDURE AS
A SUGGESTED APPROACH IN READING ACTIVITIES
FOR ENGLISH MAJORS
Le Hong Nhung
Thuyloi University, email: lehongnhung@tlu.edu.vn
1. INTRODUCTION
From years to years, reading remains a
lifelong learning skill essential both in
academic settings and throughout life. The
pivotal role of reading, acting as a keystone
for a successful university student’s life, was
emphasized by Anderson et al. (1985)
“Without the ability to read well, the
opportunities for personal fulfillment and job
success will inevitably be lost” (p.40). Despite
its importance, the motivation for reading
among students often stems not from intrinsic
interest, but from external obligations imposed
by teachers (Liu G.L. et al., 2024). This lack
of motivation can be attributed to students'
inability to recognize the benefits of reading
and the reasons behind their academic reading
(Guthrie & Wigfield, 2000). To help students
become more engaged and aware of the true
purpose of reading, the KWL (Know-Want-
Learn) strategy is introduced in this paper as
one of the recommended strategies used in
reading lessons.
First introduced by Ogle (1986), KWL is a
teaching and learning strategy designed to
help students gain knowledge by constructing
meanings through non-fiction texts across
various domains. Ogle, as cited in Zhang
(2010) also claims KWL is a teaching model
specifically intended to enhance active
reading comprehension of expository text of
English for Specific Purposes (ESP) students.
Carr and Ogle (1987) describe KWL as a
method that enhances reading by activating
students’ prior knowledge and promoting a
deeper engagement with the text. As a result,
this paper aims to serve as a reference by
providing a suggested procedure to apply
KWL approach in reading activities for
English majors at Thuyloi university.
2. METHOD
KWL strategy involves three fundamental
concepts, which are Know- identifying what
students already know, Want- deciding what
they want to find out and Learn- recalling
what they have learned from the reading.
The initial step of KWL is to get students
engaged in the topic reading by activating
their relevant background knowledge.
Various activities can facilitate this
engagement, such as interactive discussion,
answering questions, computer-assisted
activation, interpreting topic-related pictures,
etc. In the next step, based on these previous
ideas, students can set a purpose for reading
and determine the new information they aim
to gather by formulating some questions or
identifying uncertainties, which trigger them
to keep reading in order to get those
answered. Lastly, during and after reading,
students make notable comments on their
acquired knowledge while building a
connection between questions asked and
information encountered.
Tuyển tập Hội nghị Khoa học thường niên năm 2024. ISBN: 978-604-82-8175-5
563
3. A SUGGESTED PROCEDURE OF
KWL IN READING ACTIVITIES
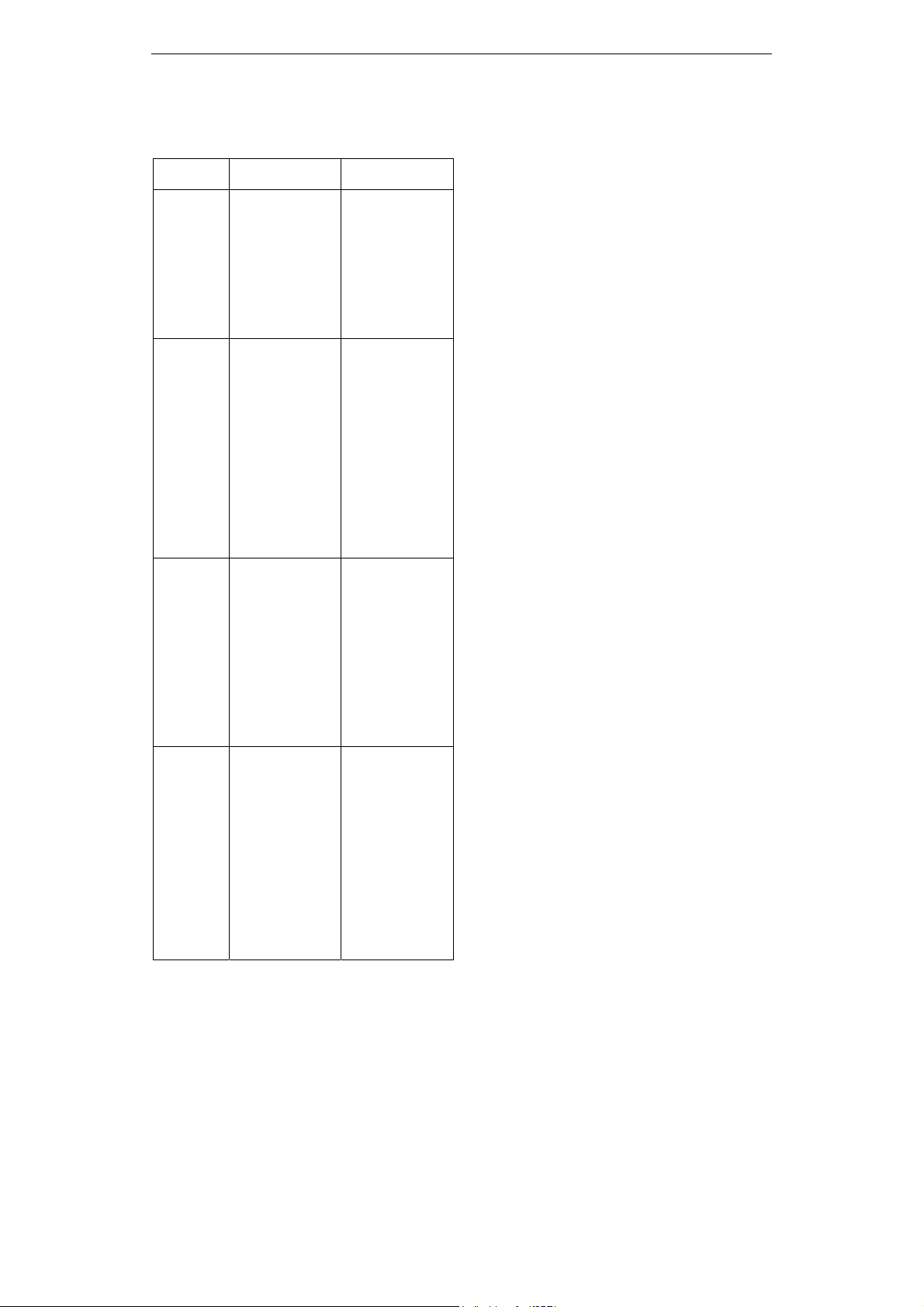
Table 1. A step-by-step procedure of KWL
strategy in reading activities
Steps Teacher (T) Students (Ss)
Orientation - Brief Ss on the
key points of the
KWL strategy,
including its
primary steps,
purpose and how
to structure each
step.
- Note down key
points and build
an overview of the
strategy through
T’s instructions.
Know - Introduce the
topic.
- Ask Ss what
they already know
about the topic.
- Give Ss 3
minutes to scan
the text and share
their ideas
- Write down Ss’
ideas.
- Brainstorm
words, terms, or
phrases from
personal
experience.
- List as many
relevant ideas as
possible.
- Take notes on all
necessary
information.
Want - Have Ss read the
article and list
their questions.
- Encourage Ss to
set their purpose
for reading while
generating
questions.
- Make
predictions about
the given article
by brainstorming
and reading it.
- List some
uncertainties
about the articles
in form of
questions.
Learn - Summarize all
questions
answered by Ss.
- Ask Ss to write
3-4 ideas to sum
up their
understanding of
the topic.
- Have Ss read
and evaluate their
summary.
- Continue reading
to find answers to
all questions.
- Summarize the
article with 3-4
key ideas.
- Research any
questions not
answered by the
article.
4. A TYPICAL APPLICATION OF THE
KWL PROCEDURE IN “READING
SKILLS 2” COURSE
The course “Reading Skills 2”, lasting 30
periods, is designed for English majors at
Thuyloi University. It aims to equip them
with a broad range of vocabulary on
contemporary topics and necessary text-
processing strategies that they can apply
effectively and confidently in everyday
situations and in academic environments at
level B2 of the Common European
Framework of Reference for Languages.
Here is an example of how KWL strategy
can be applied in a lesson in “Reading Skills
2” course. For teaching Unit 3A, titled “How
Safe Is Our Food?” (from the book Reading
Explorer 4, 3rd edition, by Nancy Douglas
and David Bohlke, National Geographic
Learning, 2019), students are typically asked
to answer reading comprehension questions in
forms of multiple-choice or True/ False/ Not
given formats. Instead of following the
questions instructed in the book, the teacher
can choose to apply KWL strategy as follows:
Orientation: The teacher and students
should engage in an oral discussion before
proceeding with the other steps to ensure
clarity on all necessary information. While
gradually building an overview of this
strategy, the teacher can jot down all
necessary points being discussed.
Know: The first step focuses on building
the connection between the students’ prior
knowledge and the content of the article. The
teacher introduces the title of the lesson and
prompts students with questions such as “Do
you think the food we consume every day is
safe? Why or why not? What causes food
poisoning, and how can we avoid it? What do
you know about good and bad bacteria?
Where are they from? How important is the
immune system in humans?”. These questions
can be raised by the teacher and students or
taken from the “Before you read” section as
suggestions. Students should be given at least
3-5 minutes to brainstorm relevant ideas and
try to answer all the given questions.

Tuyển tập Hội nghị Khoa học thường niên năm 2024. ISBN: 978-604-82-8175-5
564
Want: This step is the time for students to
read the article and set their own reading
purpose by listing out the questions they want
to know. Possible questions might include:
“Why are people eating more imported food
now? Why is even a single disease-causing
bacterium dangerous? What is PulseNet used
for? How can humans reduce the risk of
unsafe food? What are the damaging effects
of the contaminated food and water? What
are the roles of bacteria in our bodies? Is
there any hope of decreasing the risk of
contamination while producing the
international food?”. The teacher helps
identify the potential gaps and contradictions
in their knowledge and assists students in
formulating the questions they want to
answer about the topic.
Learn: In the last step of the process, the
teacher stimulates students to make presentations
to share interesting information with the class
and promotes further reading if they still have
unresolved questions. Students are also tasked
with delivering a presentation on food-related
topics for the next class session.
5. CONCLUSION
In conclusion, KWL strategy is a suggested
teaching-learning method that can be applied
to English majors in reading activities.
Hopefully, KWL strategy will serve as both a
recommended teaching method for teachers
and an approach for students’ independent
study. By following the step-by-step procedure
well-guided by the teacher, learners are
encouraged to shape their knowledge by first
eliciting what they already know, examining
what they want to know, and recalling what
they learn about a specific topic. It is hoped
that this research will also help English
teachers gain insight into the KWL approach
and use this knowledge to improve their
teaching competence.
6. REFERENCE LIST
[1] Anderson, R. Hiebert, E. Scott, J. & Wilkinson,
I. (1985). Becoming a nation of readers: The
report of the commission on reading.
Washington DC: National Institute of Education
and the Center for the Study of Reading.
[2] Carr, E., & Ogle, D. (1987). K-W-L Plus: A
Strategy for Comprehension and
Summarization. Journal of Reading, 30(7),
626-631. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40031872.
[3] Guthrie, J. T., & Wigfield, A. (2000).
Engagement and Motivation in Reading. In
M. L. Kamil, P. B. Mosenthal, P. D.
Pearson, & R. Barr (Eds.), Handbook of
Reading Research (3rd Ed.). New York,
NY: Longman.
[4] Liu G.L., Zhang Y., and Zhang R. (2024).
Examining the relationships among motivation,
informal digital learning of English, and
foreign language enjoyment: An explanatory
mixed-method study. ReCALL, 36(1):72-88.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S0958344023000204.
[5] Ogle, D. M. (1986). K-W-L: A Teaching
Model That Develops Active Reading of
Expository Text. The Reading Teacher, 39(6),
564-570. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20199156.
[6] Zhang. F (2010). The integration of the
Know-Want-Learn (KWL) Strategy into
English Language Teaching for Non-
English Majors. Chinese Journal of Applied
Linguistics (Bimontly). 33 (4), 77-86.
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/43024974.pdf.















![Đề cương môn Tiếng Anh 1 [Chuẩn Nhất/Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251130/cubabep141@gmail.com/135x160/51711764555685.jpg)







![Mẫu thư Tiếng Anh: Tài liệu [Mô tả chi tiết hơn về loại tài liệu hoặc mục đích sử dụng]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250814/vinhsannguyenphuc@gmail.com/135x160/71321755225259.jpg)


