Characters, String and Selections
Faculty of Information Technology, Hanoi University
2
What You Are About To Achieve
❖The previous lecture introduced fundamental programming techniques and taught
you how to write simple programs to solve basic problems. By the end of this
lecture, we are going to:
❑Understand the use of basic math functions such as min, max, and abs to
manipulate numeric values.
❑Explore the capabilities of random number generation using the random function
for various use cases.
❑Learn how to manipulate and analyze characters and strings through various
string methods and properties.
❑Master conditional statements using if, if else, and nested if to control the flow of
your program.
❑Implement decision-making logic using switch statements for clearer, structured
branching.
❑Apply the ternary operator for concise conditional expressions.
3
❖Mathematical Functions
❖Characters
❖String
❖Selections – Conditions
❖Selections - IF
❖Selections - Switch
❖Selections – Ternary
❖Common Errors and Pitfalls
❖Final Touches
4
Mathematical Functions
❖Java provides many useful methods in the Math class for performing common
mathematical functions. A method is a group of statements that performs a specific task.
You have already used the pow(a, b) method in the previous lecture. This section
introduces other useful methods in the Math class. They can be categorized as:
❑Trigonometric methods
❑Exponent methods
❑Service methods
❖Service methods include the rounding, minimum, maximum, absolute, and random
methods. In addition to methods, the Math class provides two useful double constants, PI
and E (the base of natural logarithms). You can use these constants as Math.PI and Math.E
in any program.
5
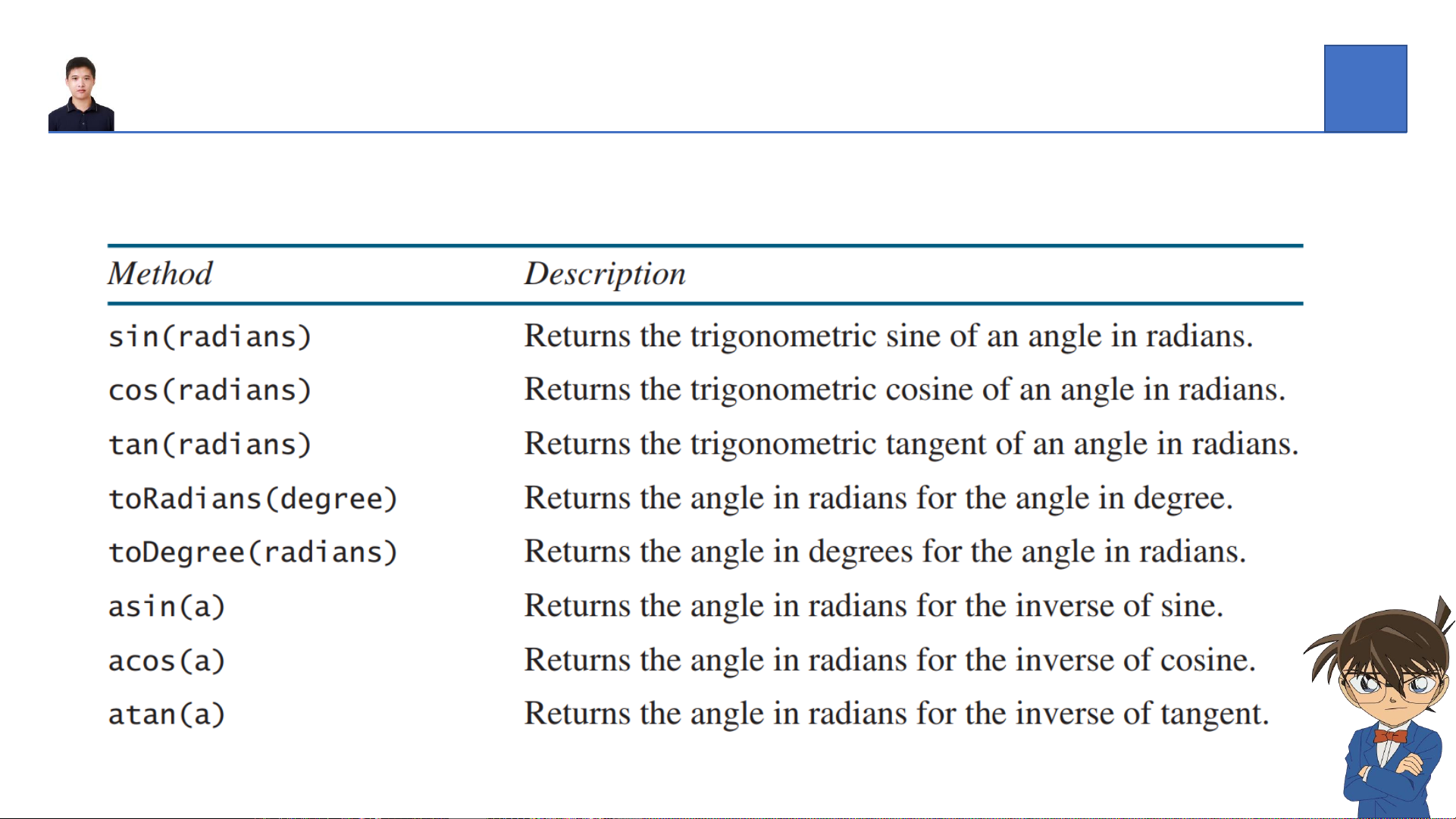
Mathematical Functions – Trigonometric methods
❖The Math class contains the following methods as shown below for performing
trigonometric functions:

![Bài giảng Thực hành cơ sở dữ liệu Trường ĐH Công Nghệ [năm] mới nhất](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251120/oursky02/135x160/14661768233842.jpg)
















![Bài giảng Cơ sở lập trình Chương 7: Trường ĐH Kinh tế Đà Nẵng [Full]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260212/hoatrami2026/135x160/75411771906936.jpg)
![Bài giảng Cơ sở lập trình Chương 6: Trường ĐH Kinh tế Đà Nẵng [Full/Chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260212/hoatrami2026/135x160/79741771906937.jpg)






