
19.1
Chapter 4:
Network Layer

2
Outline
Introduction
Network layer overview
IPv4 address
IPv4 Protocol
Network routing
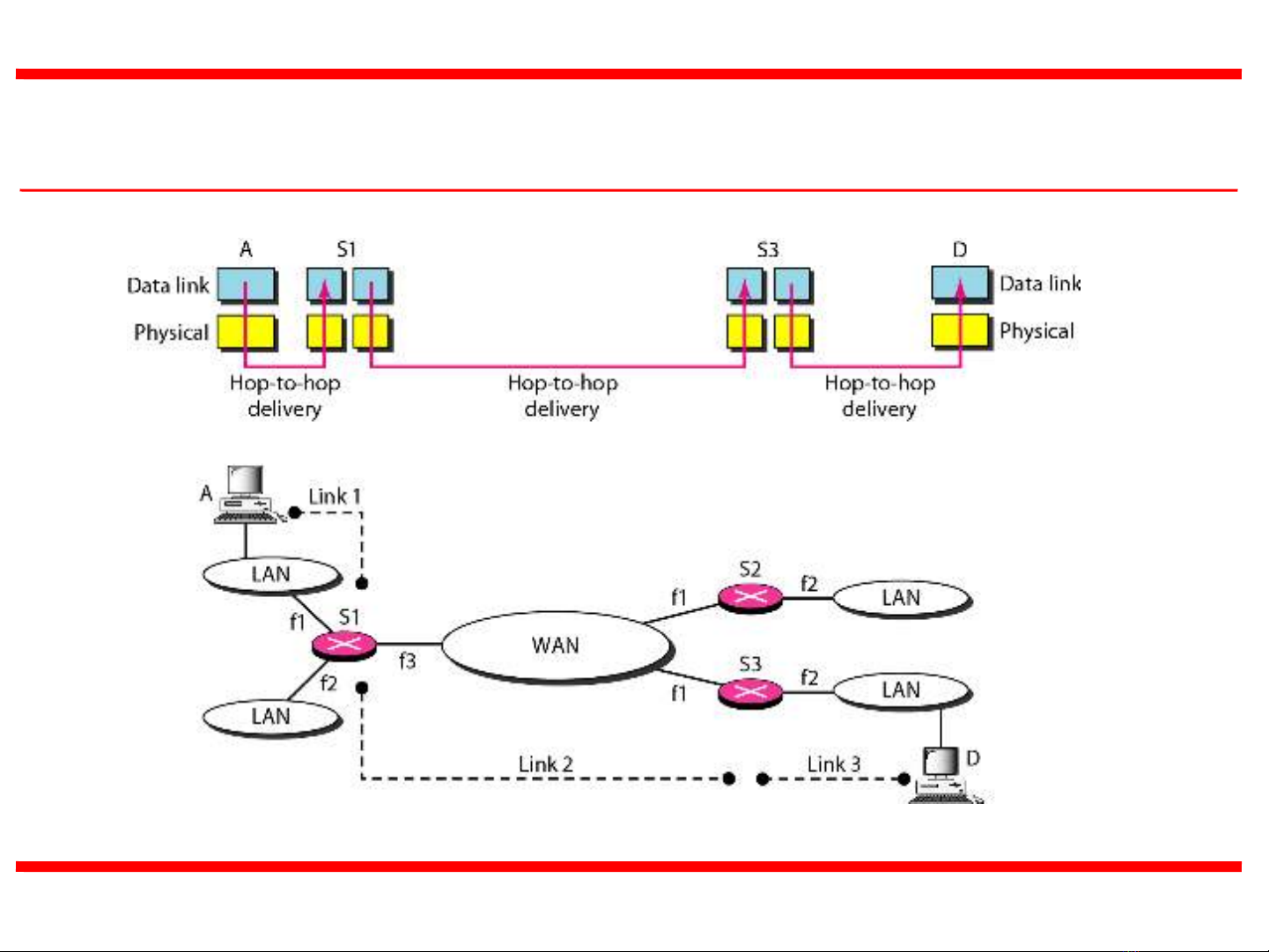
19.3
Figure 1 Links between two hosts
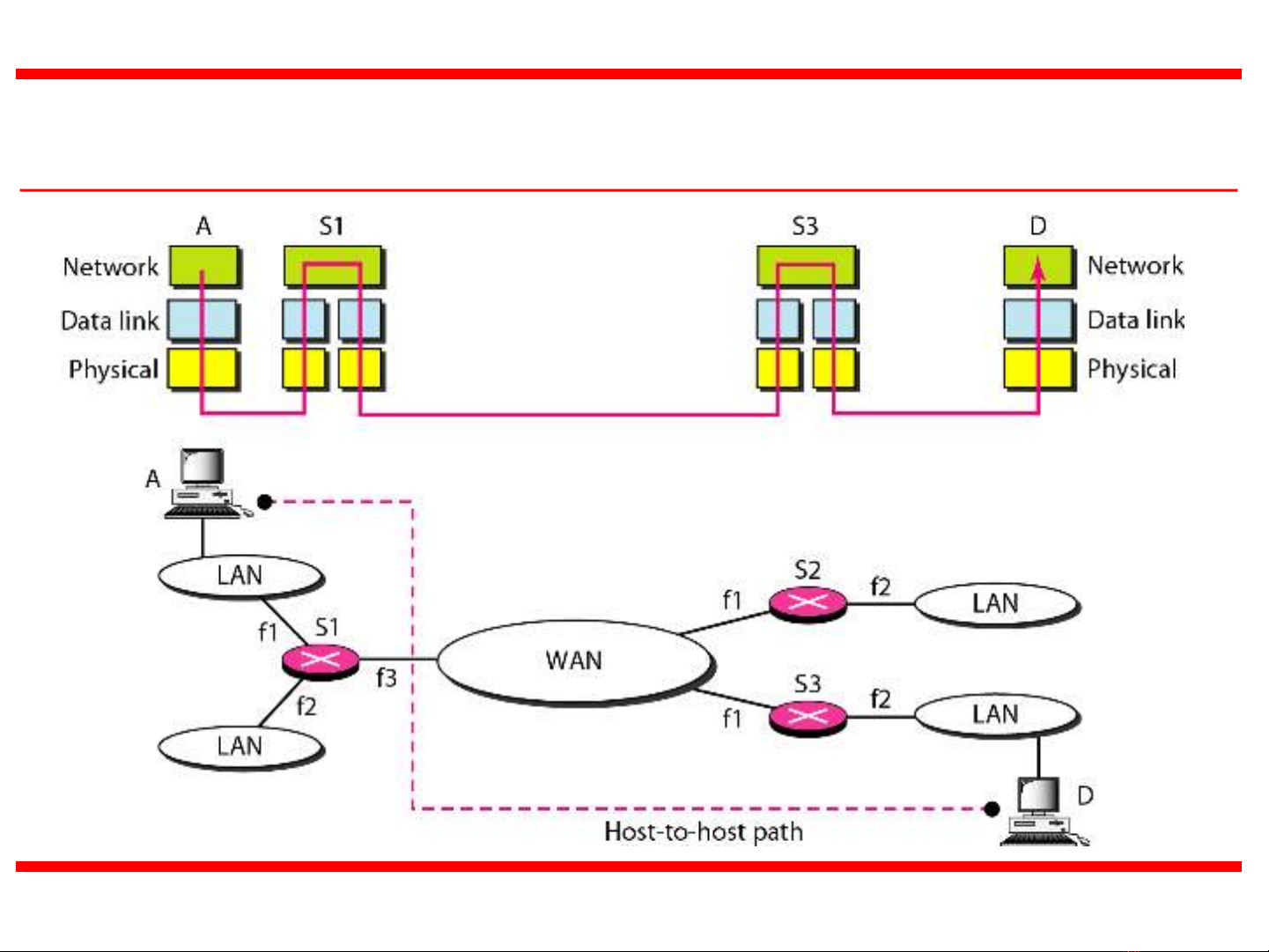
19.4
Figure 2 Network layer in an internetwork
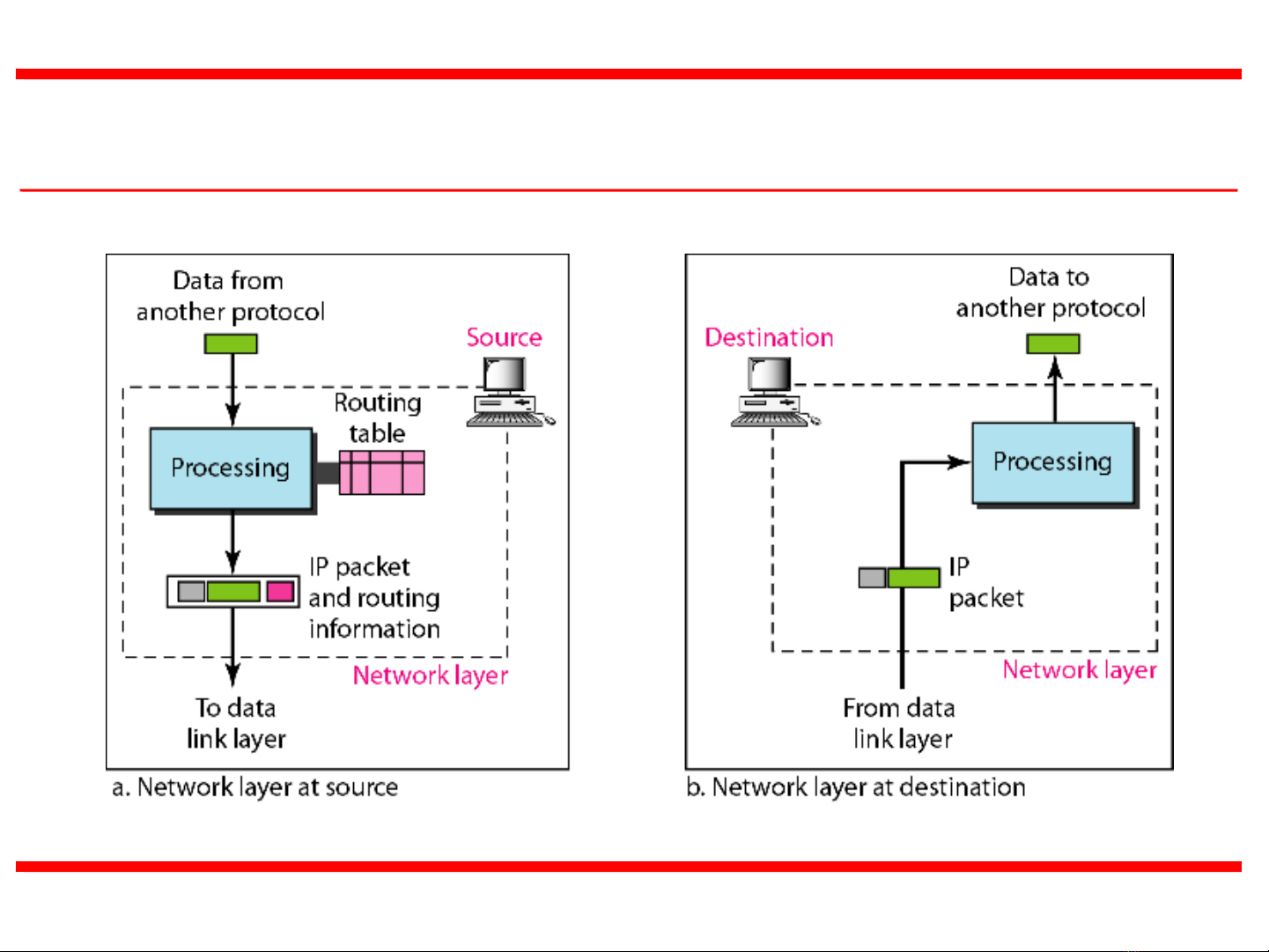
19.5
Figure 3 Network layer at the source, router, and destination







![Giáo trình Triển khai hệ thống mạng Trường Cao đẳng nghề Số 20 [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2024/20240830/xuanphongdacy04/135x160/177320125.jpg)




![Đề thi học kì 2 môn Nhập môn Mạng máy tính [kèm đáp án]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251014/lakim0906/135x160/23811760416180.jpg)



![Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Mạng máy tính: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251001/kimphuong1001/135x160/15231759305303.jpg)
![Câu hỏi ôn tập An toàn mạng môn học: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250919/kimphuong1001/135x160/30511758269273.jpg)






![Giáo trình Công nghệ mạng không dây (Nghề Quản trị mạng máy tính, Trình độ Cao đẳng) - Trường Cao đẳng Thủ Thiêm [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250916/kimphuong1001/135x160/13561758013095.jpg)

