8/26/2012
1
Ch3 - DAS 1
Ch. 3 DAS
DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEMS
• DAS overview
• Measurement, sensors, transducers
•Conditioners, các bộ chuẩn hóa tín hiệu
• MUX, S&H, ADCs
• Microcontrollers and Data Processing
• Database
• Case studies: monitoring systems
Ch3 - DAS 2
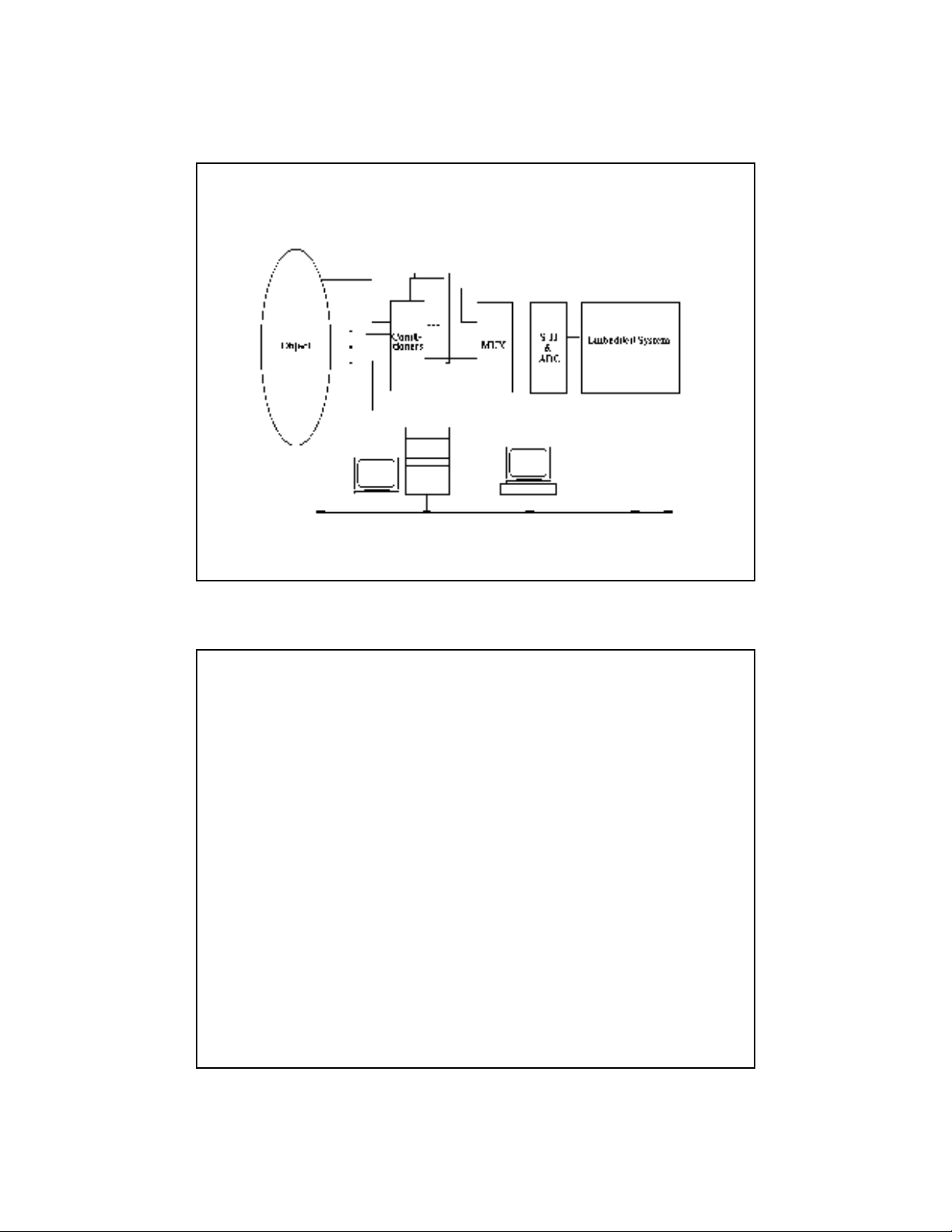
3.1. DAS Overview
• Define:
– Data Acquisition System: The system for acquiring
data (status, metric information) from industrial
processes (or environment) then update to
database, one of importance part of a SCADA,
DCS…
– The collection of sensors and communication links
to sample or collect and then return data to a
central location for further processing, display, or
archiving.
• Structure: next
8/26/2012
2
Ch3 - DAS 3
3.1. DAS Overview
Ch3 - DAS 4
• Student’s define for structure:
– Object:
– Sensor:
– Conditioner: WorkBench, LabView
– MUX:
– S&H:
– ADC:
– Embedded System
– Computer Desktop: database and networking
3.1. DAS Overview
8/26/2012
3
Ch3 - DAS 5
• Operate:
– Process
– Sensor
– Conditioner
– MUX
– S&H and ADC
– ES
– Database system
3.1. DAS Overview
Ch3 - DAS 6
• Classification:
– The number of data elements/points,
– Distance/wide area
– Rate of signal
– Address of application and type of information:
• Industrial fields: level, flow, temperature, pressure,… in
cement, paper, textile, steel mill, mechanical factories…
• Civil engineering: dams, bridges, underground/ under-
water constructions, high building… => constructions
supervision system
• Environmental supervision system
3.1. DAS Overview
8/26/2012
4
Ch3 - DAS 7
• Transportation: Vehicles, ship, aero plane: velocity,
accelerate, gasoline ratio, safety equipment,
Navigation…; Traffic signals
• Bio-medicine: Cardiograph, Monitoring, smart garden
and growth
• Defense: DGPS,
• Entertainment:
• Smart house: temperature, lighting, air conditioning
(heating/ freezing), plant watering, auto-answering,
smart cooking… iBMS
3.1. DAS Overview
Ch3 - DAS 8
• Questions and Answers
• Student’s examples
3.1. DAS Overview
8/26/2012
5
Ch3 - DAS 9
3.2 Measurement
• Sensor Defines:
–Là thiết bị nhận các tín hiệu vật lý từ thế giới thật (nhiệt, ás,
âm thanh, áp suất…), tạo ra các tín hiệu điện tương ứng.
(A device that responds to a physical stimulus in real world (heat, light, sound, pressure, motion, flow,
and so on), and produces a corresponding electrical signal)
–Là một phần của thiết bị đo, nó đáp ứng trực tiếp ứng với
sự thay đổi của môi trường (The part of a measuring instrument which responds
directly to changes in the environment)
• Transducers are ENERGY CONVERTERS or
MODIFIERS
–Là thiết bị thay đổi năng lượng từ dạng này sang dạng khác
(A device for converting energy from one form to another)
– For example, a thermocouple transduces heat energy into
electrical energy
•(Tuy nhiên trong thực tế thường hay coi là 1)
Ch3 - DAS 10
•Transducers, sensors và phép đo
•Calibration, interfering và thay đổi tín hiệu vào
• Static sensor characteristics
• Dynamic sensor characteristics
3.2.1. Sensor characteristics














![Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Mạng máy tính: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251001/kimphuong1001/135x160/15231759305303.jpg)
![Câu hỏi ôn tập An toàn mạng môn học: Tổng hợp [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250919/kimphuong1001/135x160/30511758269273.jpg)






![Giáo trình Công nghệ mạng không dây (Nghề Quản trị mạng máy tính, Trình độ Cao đẳng) - Trường Cao đẳng Thủ Thiêm [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250916/kimphuong1001/135x160/13561758013095.jpg)



