1
Trường Đại học Bách Khoa Hà Nội
Khoa Điện tử Viễn thông
Thông tin di động
Mobile Communications
TS. Đỗ Trọng Tuấn
Bộ môn Kỹ thuật thông tin
Hà Nội, 9-2010
2
2
Mạng thông tin di động 3G
UMTS / W-CDMA
(Universal Mobile Telecommunications System)
ξ1. Khái quát về UMTS
3
3
IMT-DS Direct Spread CDMA: W-CDMA / UMTS
New from 3GPP; UTRAN FDD
IMT-2000 : ITU’s umbrella name for 3G which stands for International
Mobile Telecommunications 2000
Rel.99, Rel.4
4
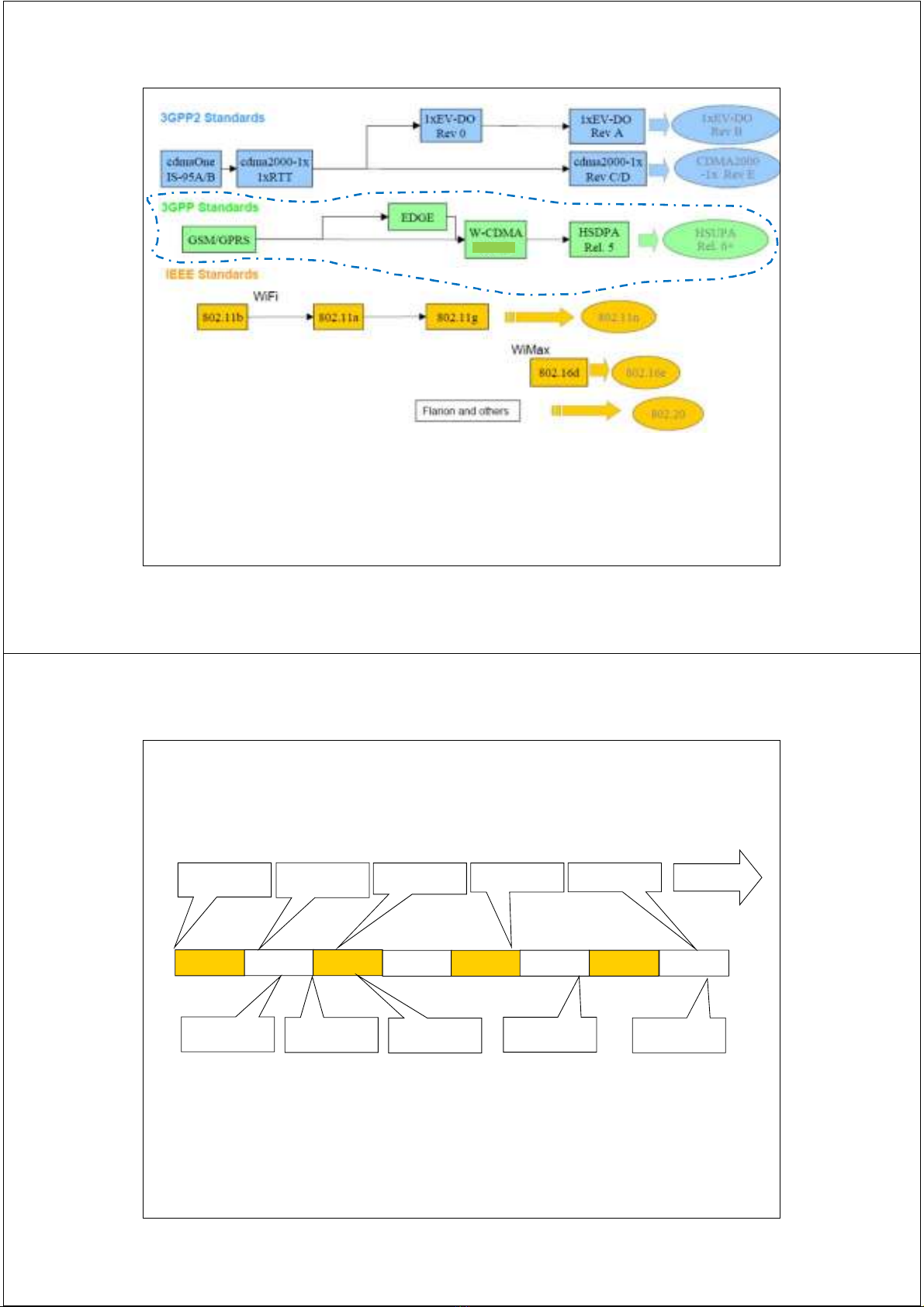
WCDMA Background and Evolution
2000 2002 2004 2006 2007
2005
2003
2001
3GPP Rel -99
12/99
3GPP Rel 4
03/01
3GPP Rel 5
03/02
3GPP Rel 6
2H/04
3GPP Rel 7
06/07 Further
Releases
Japan
Europe
(pre-
commercial)
Europe
(commercial)
HSDPA
(commercial)
HSUPA
(commercial)
5
5
UMTS general characteristics
Multimedia Service & high data rates:
WCDMA radio access
Support of QoS mechanisms
Volume-based pricing scheme
Service flexibility, wide bit-rate range and granularity:
Packet- and Circuit- oriented services,
“always on” connectivity, multiple services on one connection,
Additional requirements:
Dual- mode/ coexistence with GSM & inter-system Hand Off,
Channel characteristics negotiation.
Environment Max Bitrate Max Speed Cell Size
Rural outdoor 144 Kbps 500 Km/h Macro
Suburban outdoor 384 Kbps 120 Km/h Macro/Micro
Indoor 2.048 Mbps 10 Km/h Micro/Pico
6
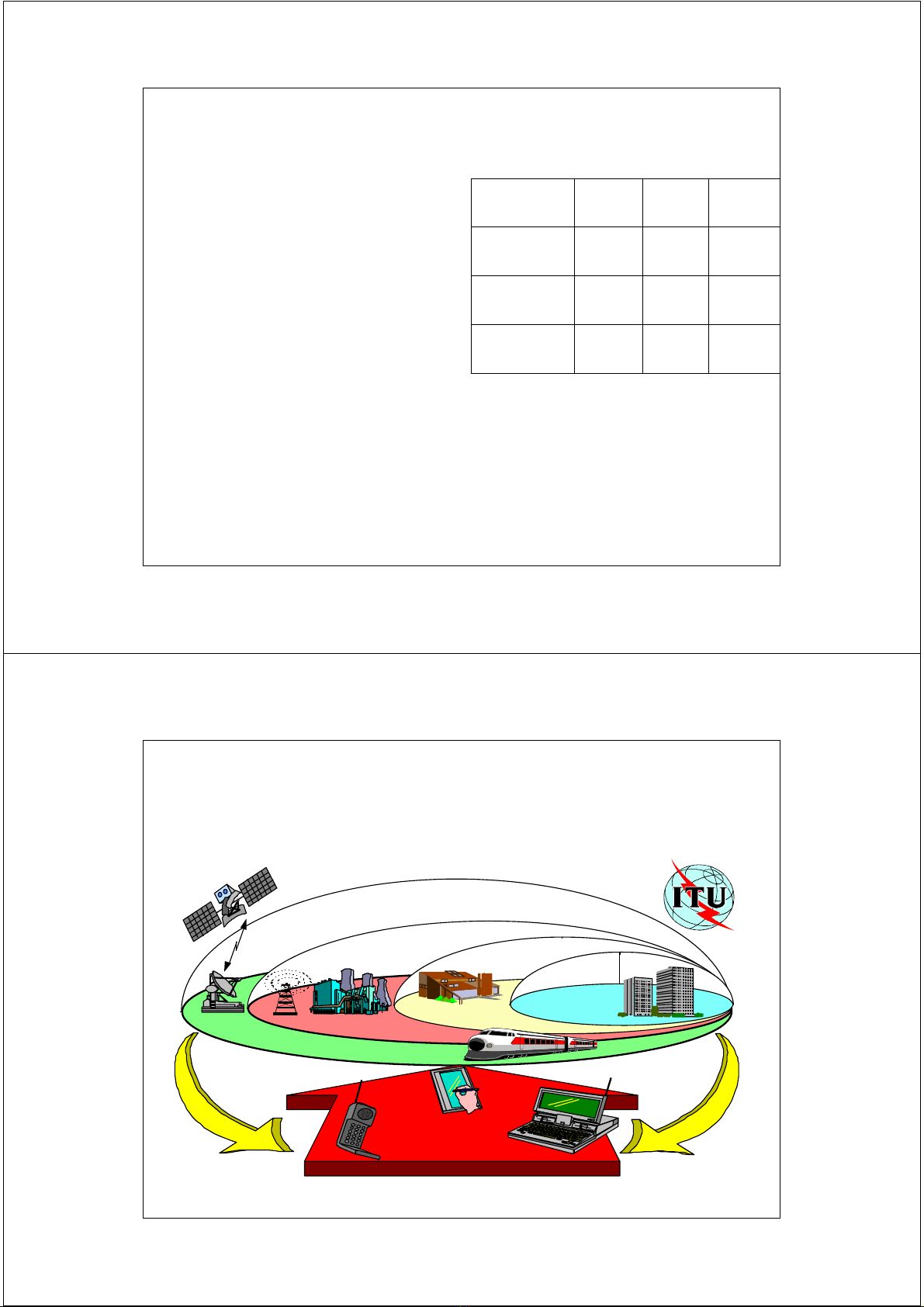
IMT-2000 Vision Includes
LAN, WAN and Satellite Services
Satellite
Macrocell Microcell
Urban In-Building
Picocell
Global
Suburban
Basic Terminal
PDA Terminal
Audio/Visual Terminal

7
7
UMTS Characteristics
UMTS FDD (Frequency Division Duplex)
Uplink: 1920 - 1980 MHz
Downlink: 2110 - 2170 MHz
190 MHz duplex distance
5MHz (variable) carrier spacing
12 bands in Uplink & Downlink
…
12 Uplink
Bands
190 MHz 5 MHz Frequency
12 Downlink
Bands
…
8
8
Ngày 16/4/2008, BộTT&TT đã ban hành Quyếtđịnh số
25/2008/QĐ-BTTTT vềviệcphêduyệtQuyhoạch băng tầncho
các hệthống thông tin di động tếbào sốcủaViệt Nam trong
các dảitần 821 ÷ 960 MHz và 1710 ÷ 2200 MHz. Theo Quyết
định này, các đoạnbăng tần 1900 ÷ 1980 MHz, 2010 ÷ 2025
MHz và 2110 ÷ 2170 MHz đượcdànhchohệthống IMT–2000.
Hiện4giấyphép3Gđượcấnđịnh 3 kênh tầnsốcho hướng
xuống (trong dải 2110 ÷ 2170 MHz) và 3 kênh tầnsốcho
hướng lên (trong dải 1920 ÷ 1980 MHz).
9
9
UMTS Specifications
Duplex method: FDD
Channel spacing: 5 MHz
Carrier chip rate: 3.84 Mcps
Timeslot structure: 15 slots/frame
Framelength: 10 ms
Modulation: QPSK
Detection: based on pilot symbols
Intra-frequencyHandover: soft
Inter-frequencyHandover: hard
Spreading Factors: 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512
10
10
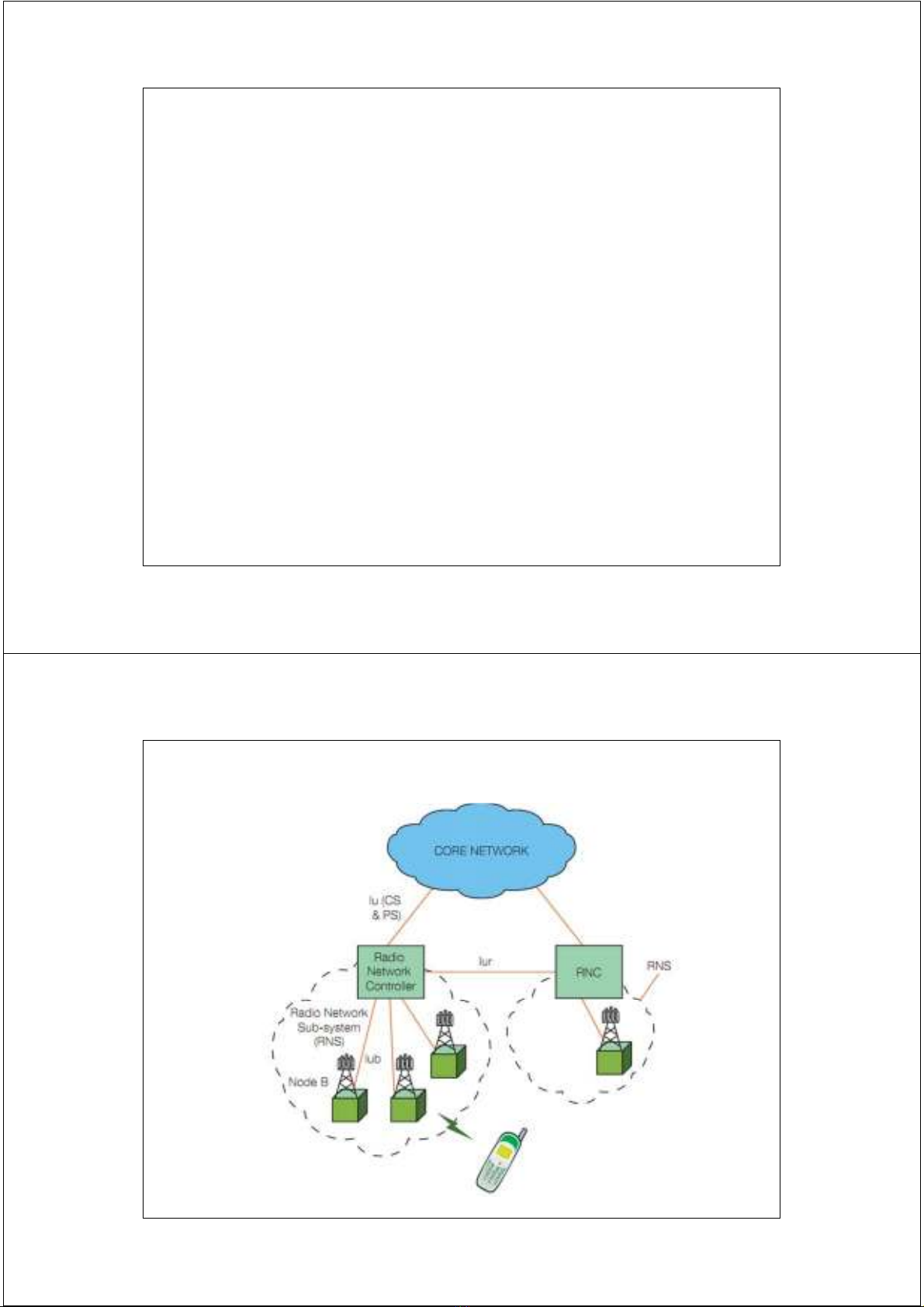
UMTS Network Architecture




















![Đề thi cuối kì Nhập môn Mạng máy tính: Tổng hợp [Năm]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251110/nminhthoi53@gmail.com/135x160/38281762757217.jpg)



![Đề thi học kì 2 môn Nhập môn Mạng máy tính [kèm đáp án]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251014/lakim0906/135x160/23811760416180.jpg)

