TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 543 - THÁNG 10 - SỐ ĐẶC BIỆT - 2024
391
NGHIÊN CỨU TÌNH TRẠNG RỐI LOẠN NUỐT VÀ CÁC YẾU TỐ LIÊN QUAN
Ở BỆNH NHÂN ĐỘT QUỴ CẤP
Tạ Văn Tuấn1, Đường Thị Ngọc Hà1, Nguyễn Thị Khánh Linh1,
Nguyễn Thị Cúc1, Nguyễn Văn Tuyến1
TÓM TẮT51
Đặt vấn đề: rối loạn nuốt (RLN) là tình
trạng thường gặp sau đột quỵ. Đánh giá tình
trạng RLN ở bệnh nhân (BN) đột quỵ cấp giúp
đưa ra các chăm sóc về chế độ ăn hợp lý, giảm
thiểu các biến chứng. Mục tiêu: Đánh giá tình
trạng RLN và các yếu tố liên quan ở các BN Đột
quỵ cấp. Đối tượng và phương pháp: Gồm 194
BN ĐQ cấp nhập viện trong 72 giờ đầu, được
điều trị tại Trung tâm Đột quỵ Bệnh viện TWQĐ
108 từ tháng 12/2018 - 09/2021 thỏa các tiêu
chuẩn chọn được đưa vào nghiên cứu. Kết quả:
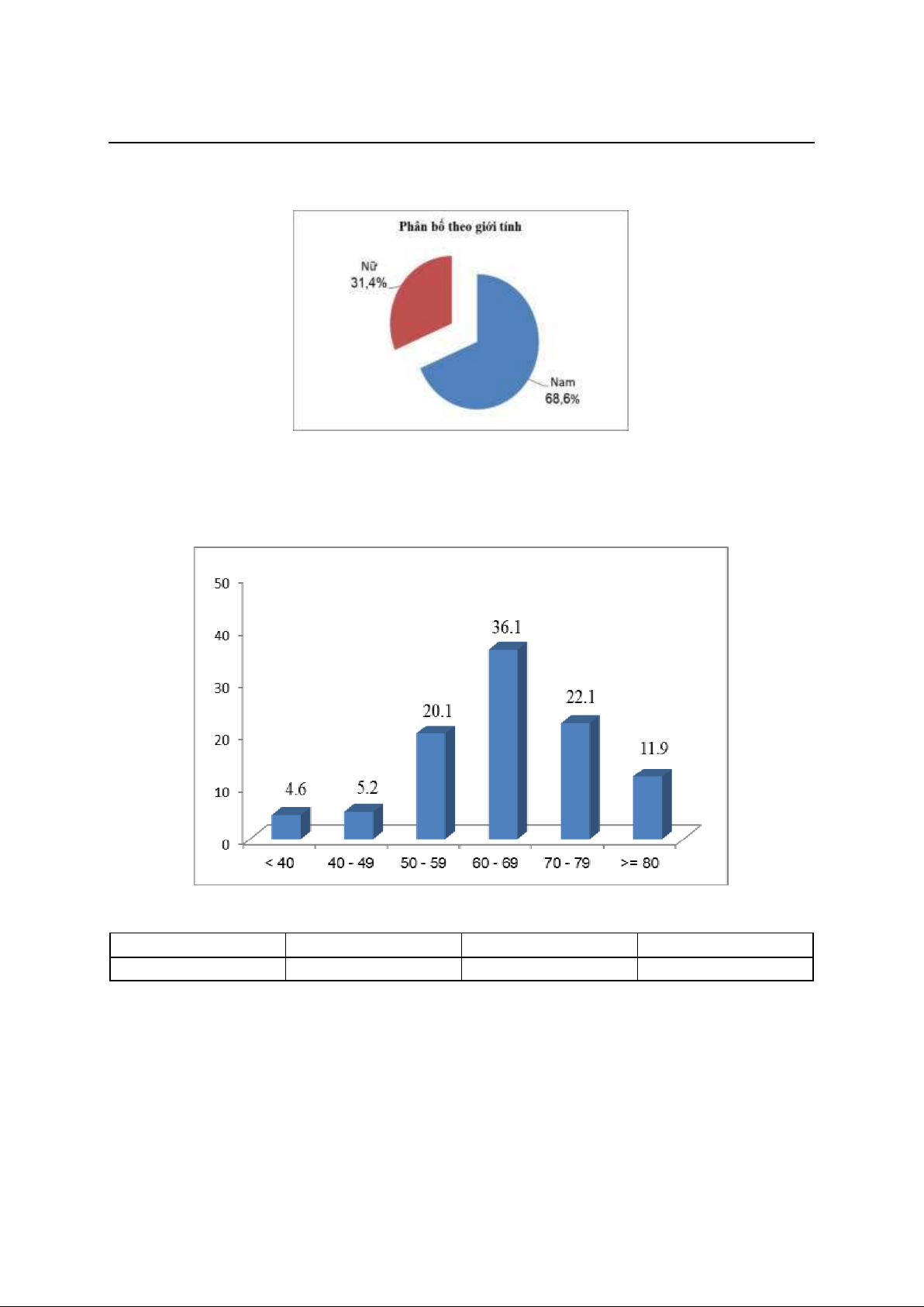
Nam 133 (68,6%), 61 nữ 61 (31,4%); tuổi trung
bình: 64,54± 13,84) tuổi; tỷ lệ BN nhồi máu não
(NMN): 71,1%. Có 76,3% BN khi vào viện RLN
qua sàng lọc bằng GUSS (39,2% mức độ nặng,
76,3% phải sonde ăn nuôi dưỡng), chiếm 39,2%
tổng số BN đột quỵ. Tỷ lệ viêm phổi (14,2%) ở
BN RLN và m bệnh nhân đột quỵ não cấp không
có rối loạn nuốt với p< 0,01. Tại thời điểm ra
viện còn 14,9% bệnh nhân còn rối loạn nuốt
nặng, có 29 BN còn sonde ăn (chiếm 14,9%).
Kết luận: Bệnh nhân đột quỵ não cấp có tỷ lệ rối
loạn nuốt cao, làm tăng nguy cơ viêm phổi.
Từ khóa: Rối loạn nuốt, đột quỵ não, viêm
phổi.
1Bệnh viện TWQĐ 108
Chịu trách nhiệm chính: Nguyễn Thị Cúc
ĐT: 0333403638
Email: cucnguyenqy41@gmail.com
Ngày nhận bài: 14/8/2024
Ngày gửi phản biện: 16/8/2024
Ngày duyệt bài: 27/8/2024
SUMMARY
STUDYING SWALLOWING
DISORDERS AND FACTORS
RELEVANCE IN ACUTE STROKE
PATIENTS
Background: Swallowing disorder is a
common condition after stroke. Assessing the
status of swallowing disorder in acute stroke
patients helps provide appropriate dietary care
and minimize complications. Objective: To
evaluate the status of swallowing disorder and
related factors in acute stroke patients. Subjects
and methods: Includes 194 acute stroke patients
admitted to the hospital within the first 72 hours,
treated at the Stroke Center of Central Hospital
108 from December 2018 to September 2021,
meeting the selection criteria to be included in
the study. Result: Male 133 (68.6%), 61 female
61 (31.4%); Average age: 64.54 ± 13.84 years
old; Rate of patients with cerebral infarction:
71.1% to 76.3% of patients admitted to the stroke
hospital were screened with GUSS (39.2% had
severe severity, 76.3% required feeding tube),
accounting for 39.2% of the total number of
stroke patients. The rate of pneumonia (14.2%)
in patients with swallowing disorder and acute
stroke patients without swallowing disorders was
p < 0.01. At the time of discharge, 14.9% of
patients still had severe swallowing disorders,
and 29 patients still had feeding tubes
(accounting for 14.9%). Conclude: Patients with
acute stroke have a high rate of swallowing
disorders, increasing the risk of pneumonia.
Keywords: Swallowing disorders, brain
stroke, pneumonia.