TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 478 - THÁNG 5 - SỐ 1 - 2019
73
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
1. Trần Nguyễn Thu Thủy (2016), "Đánh giá thang
điểm TIMI và GRACE trong dự đoán mức độ bệnh
động mạch vành ở bệnh nhân nhồi máu cơ tim cấp
không ST chênh lên", Đại học Y học Phạm Ngọc
Thạch. Luận Văn Thạc Sỹ Y học.
2. Cakar M. A., Sahinkus S., Aydin E. et al.
(2014), "Relation between the GRACE score and
severity of atherosclerosis in acute coronary
syndrome", J Cardiol. 63 (1), pp. 24-28.
3. de Araujo Goncalves P., Ferreira J., Aguiar C.
et al. (2005), "TIMI, PURSUIT, and GRACE risk
scores: sustained prognostic value and interaction
with revascularization in NSTE-ACS", Eur Heart J.
26 (9), pp. 865-872.
4. Go A. S., Mozaffarian D., Roger V. L. et al.
(2013), "Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013
update: a report from the American Heart
Association", Circulation. 127 (1), pp. e6-e245.
5. Mahmood M., Achakzai A. S., Akhtar P. et al.
(2013), "Comparison of the TIMI and the GRACE
risk scores with the extent of coronary artery
disease in patients with non-ST-elevation acute
coronary syndrome", J Pak Med Assoc. 63 (6), pp.
691-695.
6. Neeland I. J., Patel R. S., Eshtehardi P. et al.
(2012), "Coronary angiographic scoring systems:
an evaluation of their equivalence and validity", Am
Heart J. 164 (4), pp. 547-552.e541.
7. Roffi M., Patrono C., Collet J. P. et al. (2016),
"2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute
coronary syndromes in patients presenting without
persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for
the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in
Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment
Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology
(ESC)", Eur Heart J. 37 (3), pp. 267-315.
8. Barbosa C. E., Viana M., Brito M. et al. (2012),
"Accuracy of the GRACE and TIMI scores in
predicting the angiographic severity of acute
coronary syndrome", Arq Bras Cardiol. 99 (3), pp.
818-824.
ỨNG DỤNG KỸ THUẬT REALTIME-PCR XÁC ĐỊNH ĐỘT BIẾN GEN
BRAF V600E TỪ MẪU MÁU VÀ MẪU MÔ PHỦ PARAFIN
Ở BỆNH NHÂN UNG THƯ TUYẾN GIÁP
Bùi Thị Lành*, Nguyễn Thị Trang*
TÓM TẮT20
BRAF là gen tổng hợp protein B-raf chịu trách
nhiệm kiểm soát hoạt động phát triển và phân chia
của nhiều loại tế bào trong cơ thể. Đột biến gen BRAF
làm cho các tế bào bất thường này nhân lên một cách
không kiểm soát và hình thành ung thư. Theo nhiều
nghiên cứu, đột biến tại codon 600 của exon 15
(V600E) là đột biến phổ biến nhất trên gen BRAF. Đột
biến này là nguyên nhân dẫn đến nhiều bệnh ung thư
trong đó có ung thư tuyến giáp. Mục tiêu: Hoàn
thiện kỹ thuật realtime-PCR để xác định đột biến gen
BRAF V600E ở mẫu máu và mẫu mô phủ parafin của
bệnh nhân ung thư tuyến giáp. Đi tưng và
phương pháp nghiên cu: 50 mẫu máu và 21 mẫu
mô phủ parafin của bệnh nhân ung thư tuyến giáp, 21
mẫu chứng của người khỏe mạnh bình thường. Sử
dụng kỹ thuật REALTIME PCR để xác định đột biến
gen BRAF V600E từ mẫu máu và mẫu mô phủ parafin.
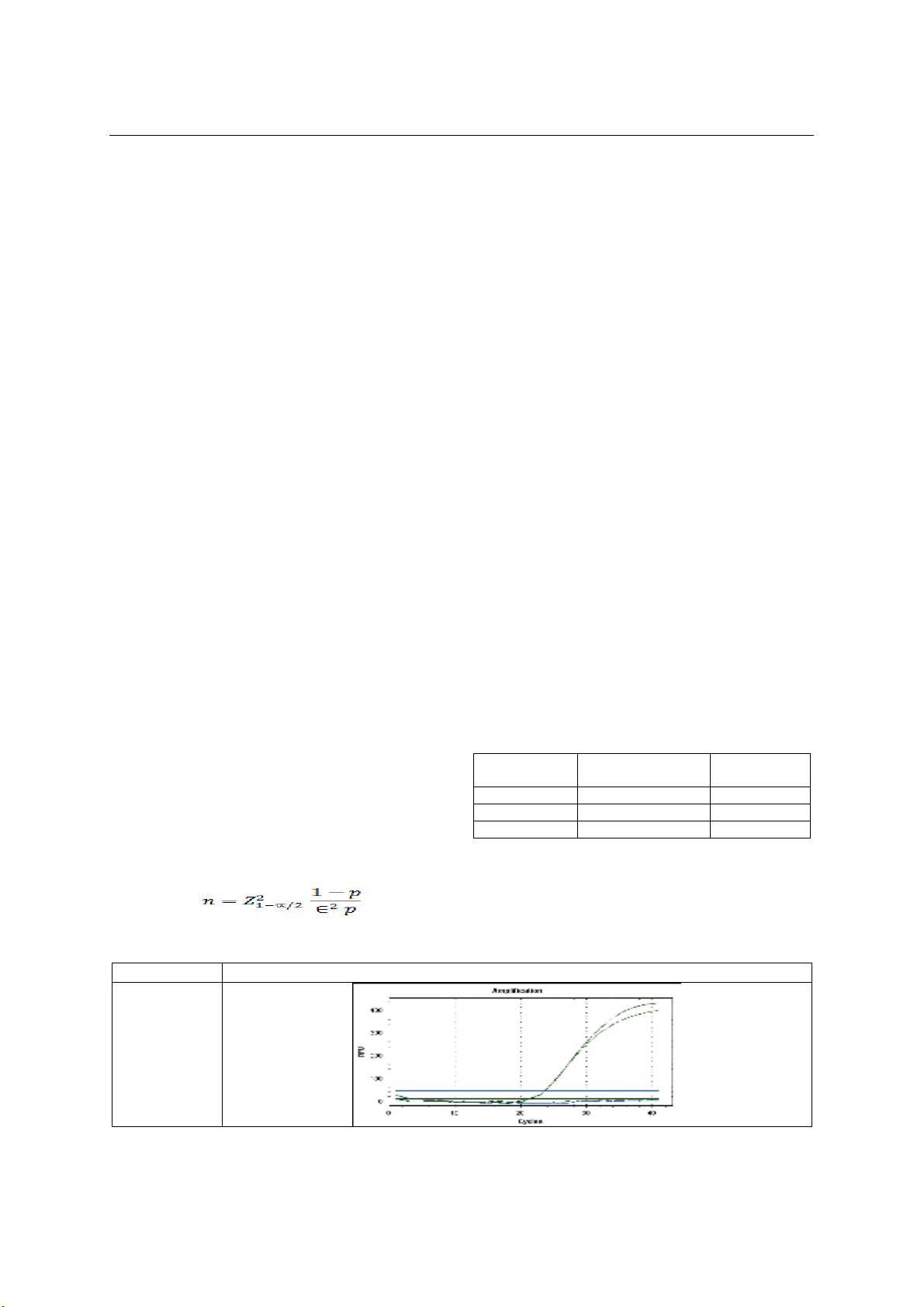
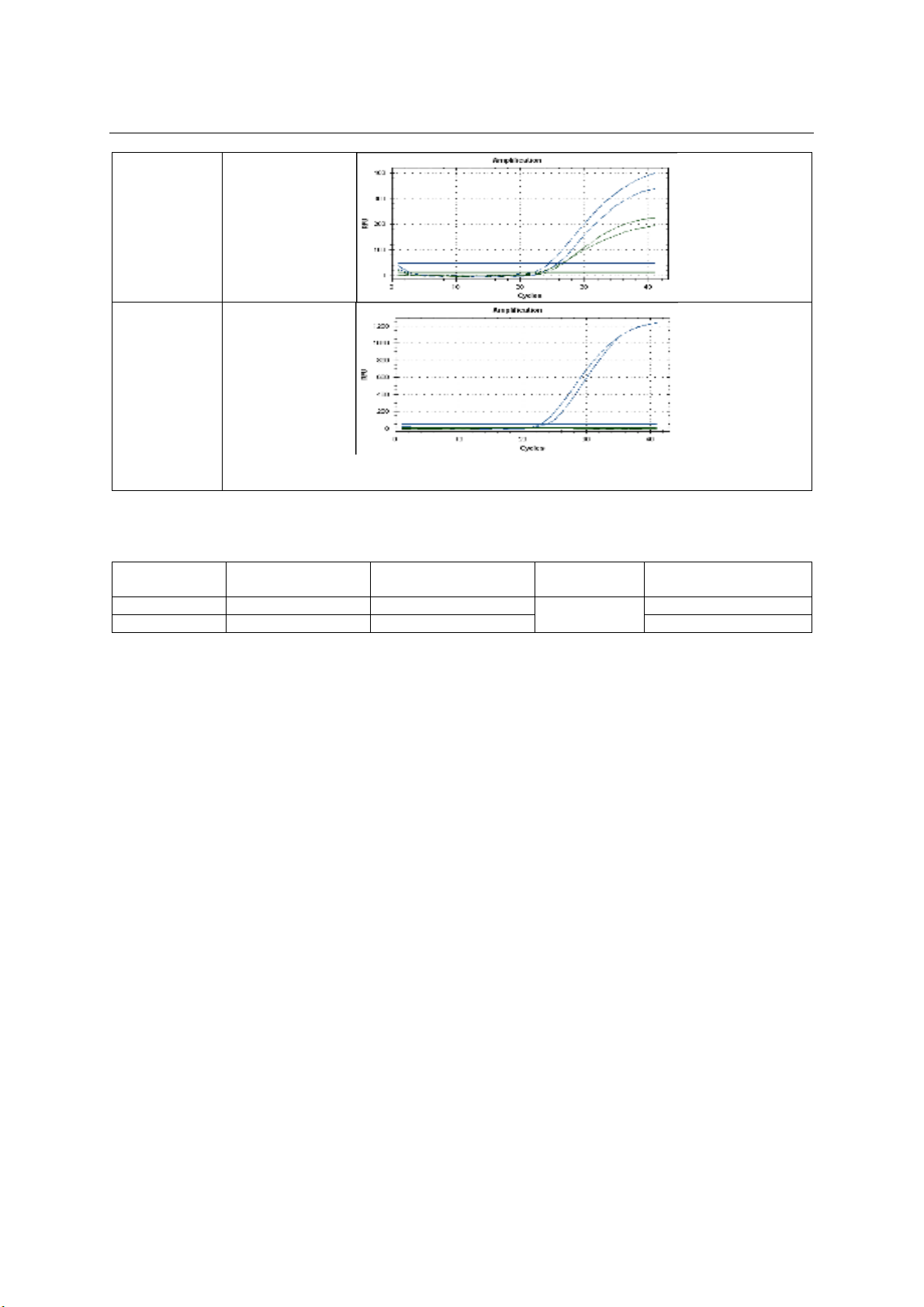
Kết quả: Tỷ lệ xuất hiện đột biến ở mẫu máu là 4%
(2 trường hợp dị có kết quả dị hợp tử); mẫu mô là
33,33% trong đó 4,76% là đồng hợp tử, 28,57% là dị
hợp tử. Trong khi đó ở nhóm chứng không ghi nhận
bất kỳ trường hợp nào mang alen đột biến. Kiểu gen
DHT+ĐHT có nguy cơ gây bệnh ung thư tuyến giáp
*Trường Đại học Y Hà Nội
Chịu trách nhiệm chính: Nguyn Thị Trang
Email: trangnguyen@hmu.edu.vn
Ngày nhận bài: 2.3.2019
Ngày phản biện khoa học: 18.4.2019
Ngày duyệt bài: 23.4.2019
cao gấp 22 lần so với kiểu gen bình thường. Kết
luận: Hoàn thiện thành công quy trình kỹ thuật
REALTIME-PCR để xác định đột biến gen BRAFV600E
từ mẫu máu và mẫu mô phủ parafin ở bệnh nhân ung
thư tuyến giáp.
Từ khóa:
Ung thư tuyến giáp, Realtime-PCR,
BRAF V600E
SUMMARY
REALTIME-PCR APPLICATION FOR
DETERMINING MUTATION V600E OF GENE
BRAF FROM BLOOD SAMPLE AND PARAFIN
EMBEDDED TISSUE SAMPLE IN THYROID CANCER
Background: BRAF gene is known as a tumor
suppressor gene in Thyroid cancer (TC), which plays a
role in DNA repair. The mutation in BRAF have been
associated with different types of cancer. The present
study was aimed at studying the association between
BRAF V600E mutation and TC. Material and
method: Peripheral blood was collected from 50
patients and 50 normal healthy controls into a test
tube containing EDTA were extracted by DNA-express
and 21 tissue samples were removed parafin by
xylene, extracted DNA by Qiagen kit. We analyzed
mutations V600E within BRAF gene in 71 patients with
TC and 21normal healthy controls according to
Realtime -PCR by BRAF V600E kit (Rusian). Results:
The prevalence of mutation V600E in BRAF was 4.0%
and 33,33%, from blood samples and tissue
respectively. In the control group, no mutation was
reported. The heterozygous and homozygous