(c) SE/FIT/HUT 2002 3
Xén tỉa - Clipping
Nhiệm vụ cơ bản trong đồ họa là giữcác
phần của đối tượng lựa chọn nằm bên
ngoài đồ hoạ.
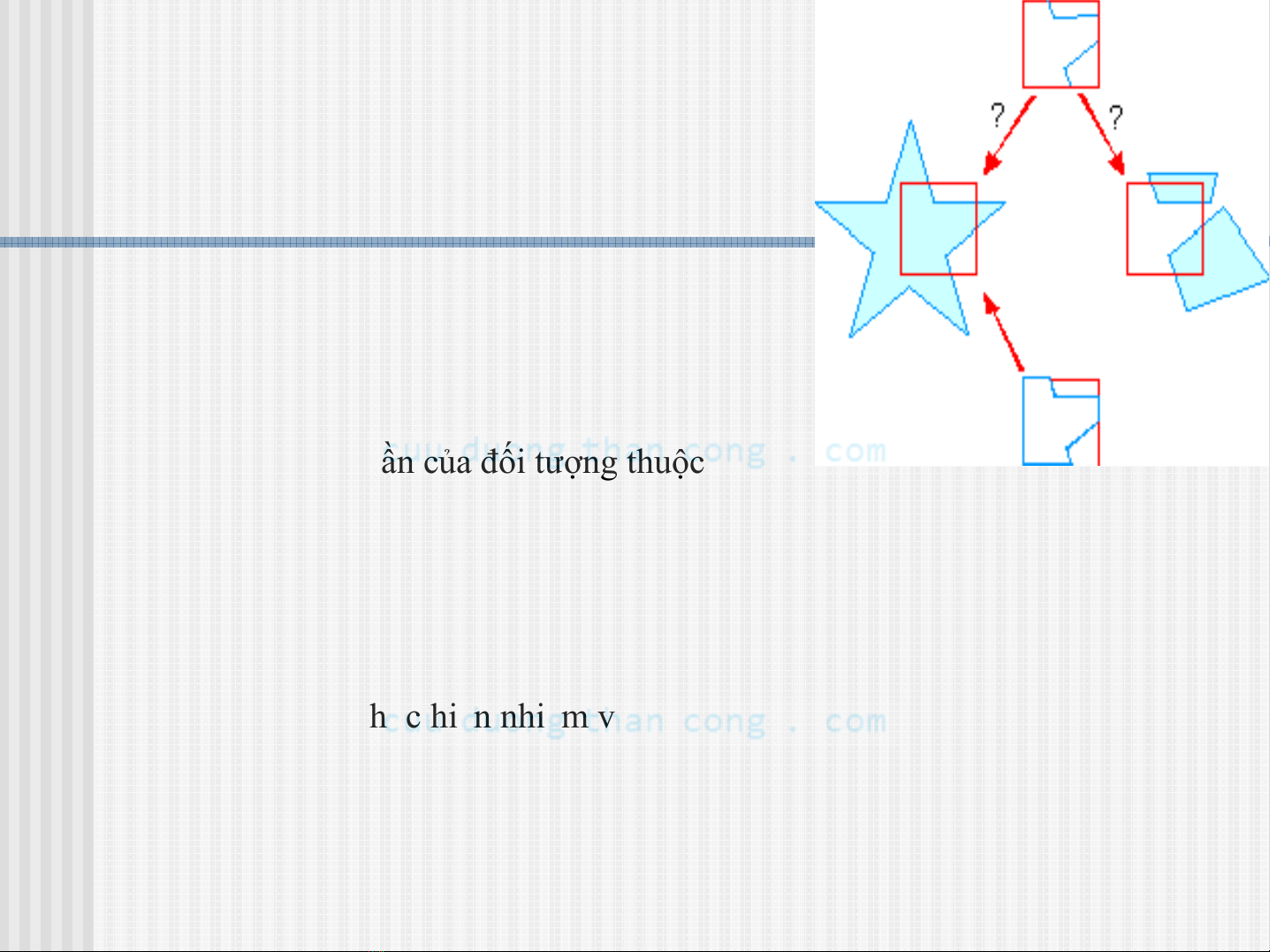
Xén tỉalàviệc di chuyển tất cảcác đối
tượng hoặc các phần của đối tượng thuộc
mô hình ngữcảnh ra bên ngoài của sổthế
giới thực
Việcloạitừng điểmảnh củađốitượng
thường chậmnhấtlàkhiđốitượng mà
phầnlớnnằm ngoài cửasổhiểnthị.
Kỹthuật thực hành là cần thiết để nâng
cao tốc độ trong thực hiện nhiệm vụ
Định nghĩa
Clipping điểm
xmin ≤x ≤xmax
ymin ≤y ≤ymax

(c) SE/FIT/HUT 2002 4
Clipping đoạnthẳng
Lines are defined by their endpoints, so it should be
possible just to examine these (in a similar way to points) and
determine whether or not to clip without considering every
pixel on the line
We often have windows that are either very large, i.e. nearly
the whole scene fits inside, or very small, i.e. most of the
scene lies inside the window
Hence, most lines may be either trivially accepted or rejected

(c) SE/FIT/HUT 2002 5
GiảithuậtCohen Sutherland
Outcode
The Cohen-Sutherland line-clipping algorithm is particularly
fast for “trivial” cases, i.e. lines completely inside or outside
the window.
Non-trivial lines, i.e. ones that cross a boundary of the
window, are clipped by computing the coordinates of the new
boundary endpoint of the line where it crosses the edge of the
window
Each point on all lines are first assigned an “outcode”
defining their position relative to the clipping rectangle





![Bài giảng Đồ hoạ kỹ thuật 1: Phần 1 - Trường ĐH Thuỷ Lợi [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2023/20230131/baphap06/135x160/672431589.jpg)