2
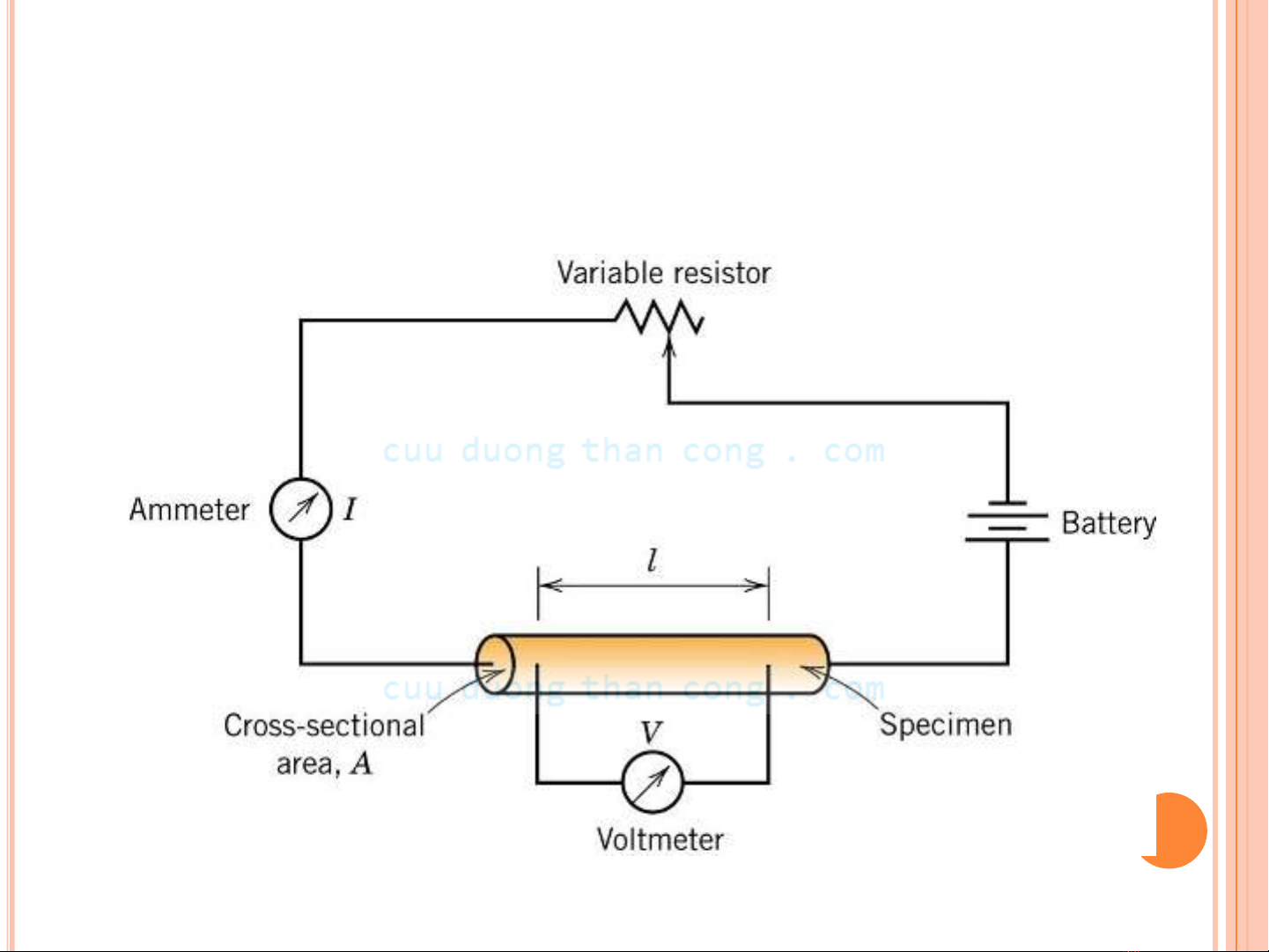
• Ohm's Law: V = I R
voltage drop (volts = J/C)
C = Coulomb
resistance (Ohms)
current (amps = C/s)
1
• Conductivity,
• Resistivity, :
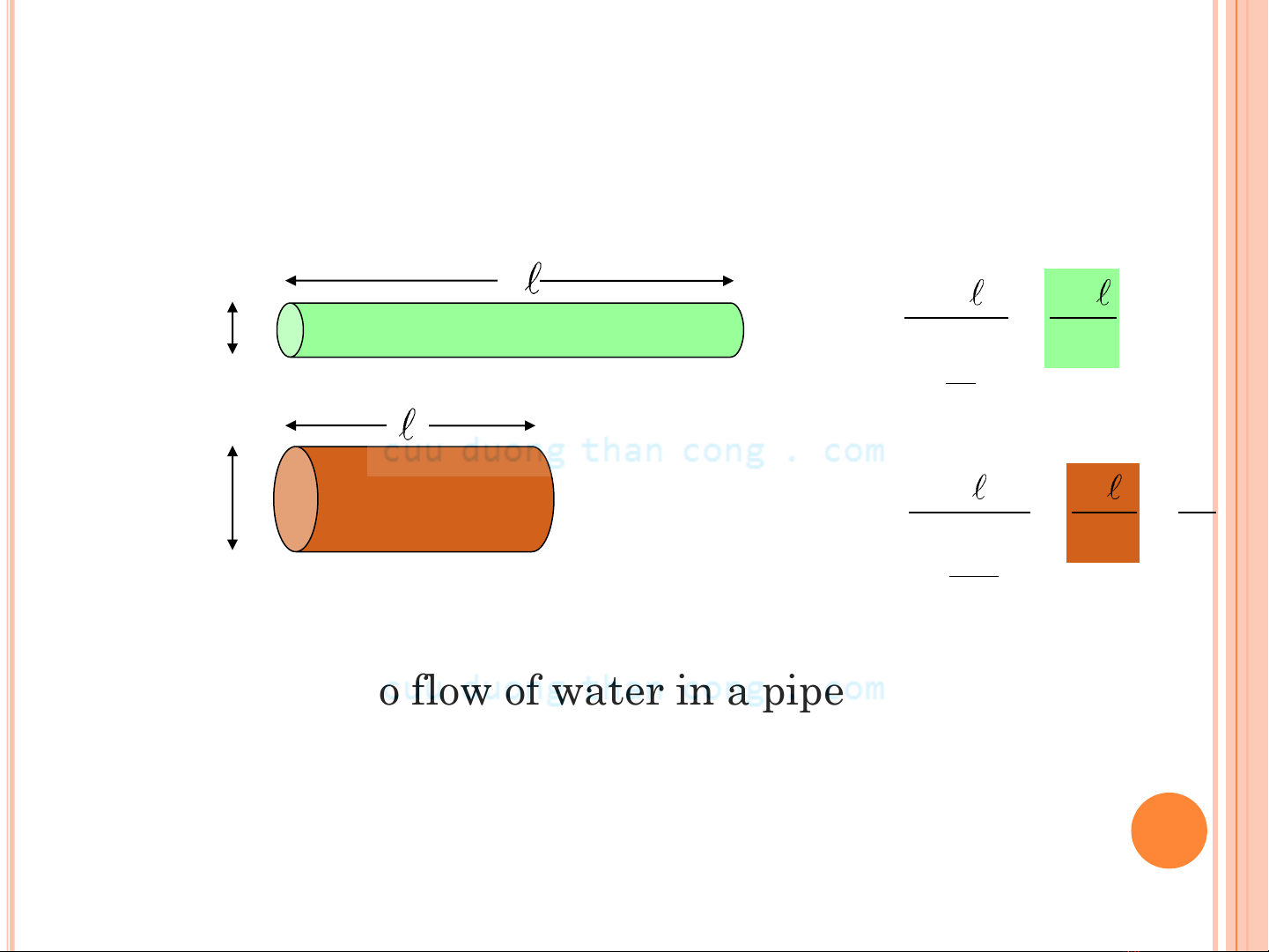
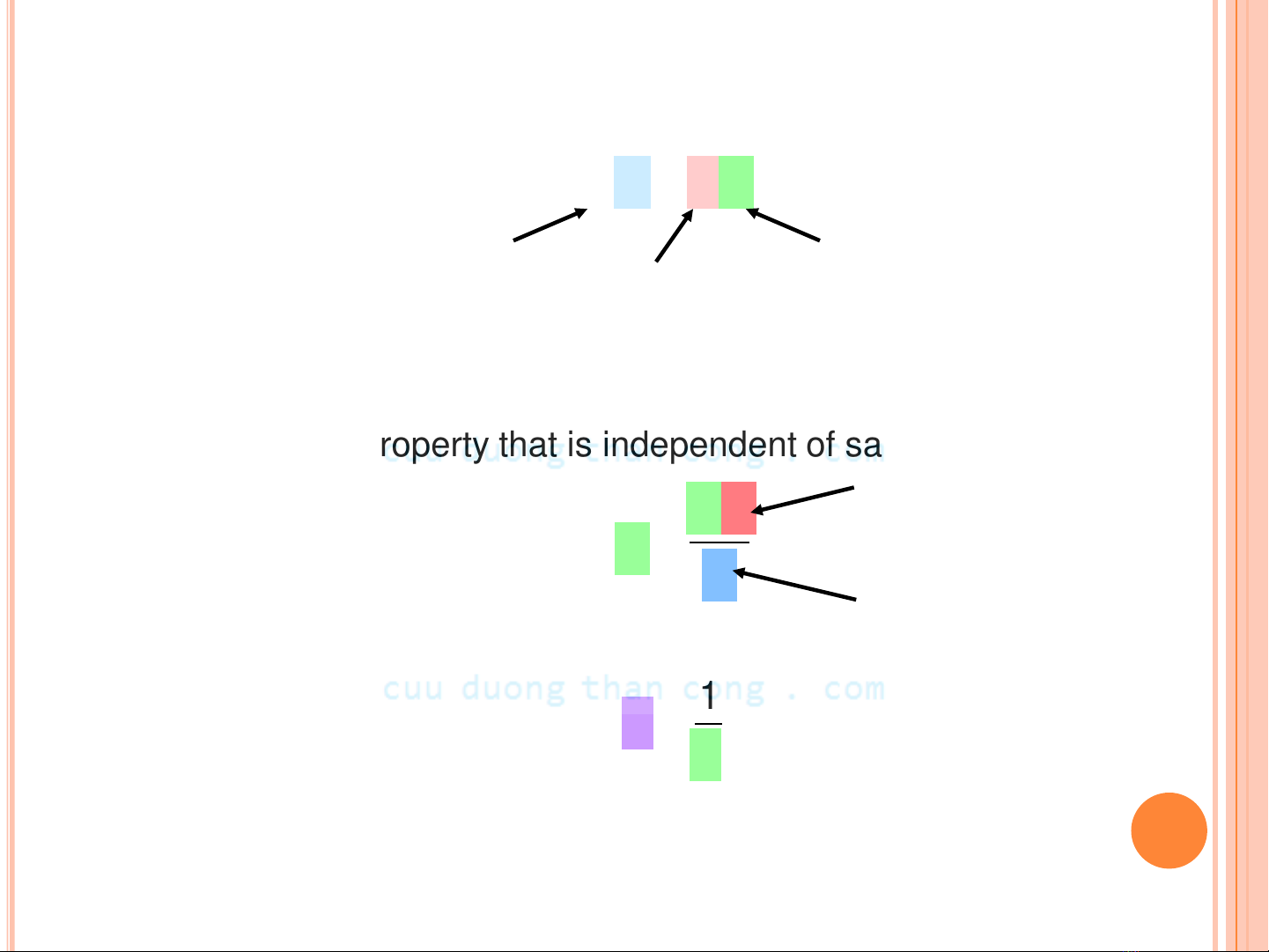
-- a material property that is independent of sample size and
geometry
RA
l
surface area
of current flow
current flow
path length
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt