TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 543 - THÁNG 10 - SỐ ĐẶC BIỆT - 2024
385
ĐÁNH GIÁ TÌNH TRẠNG RỐI LOẠN NUỐT VÀ CÁC YẾU TỐ LIÊN QUAN
Ở BỆNH NHÂN NHỒI MÁU NÃO CẤP TẠI TRUNG TÂM ĐỘT QUỴ,
BỆNH VIỆN BẠCH MAI
Mai Duy Tôn1,2,3, Phạm Quang Thọ1,
Nguyễn Lê Ngọc1, Đào Việt Phương1,2,3
TÓM TẮT50
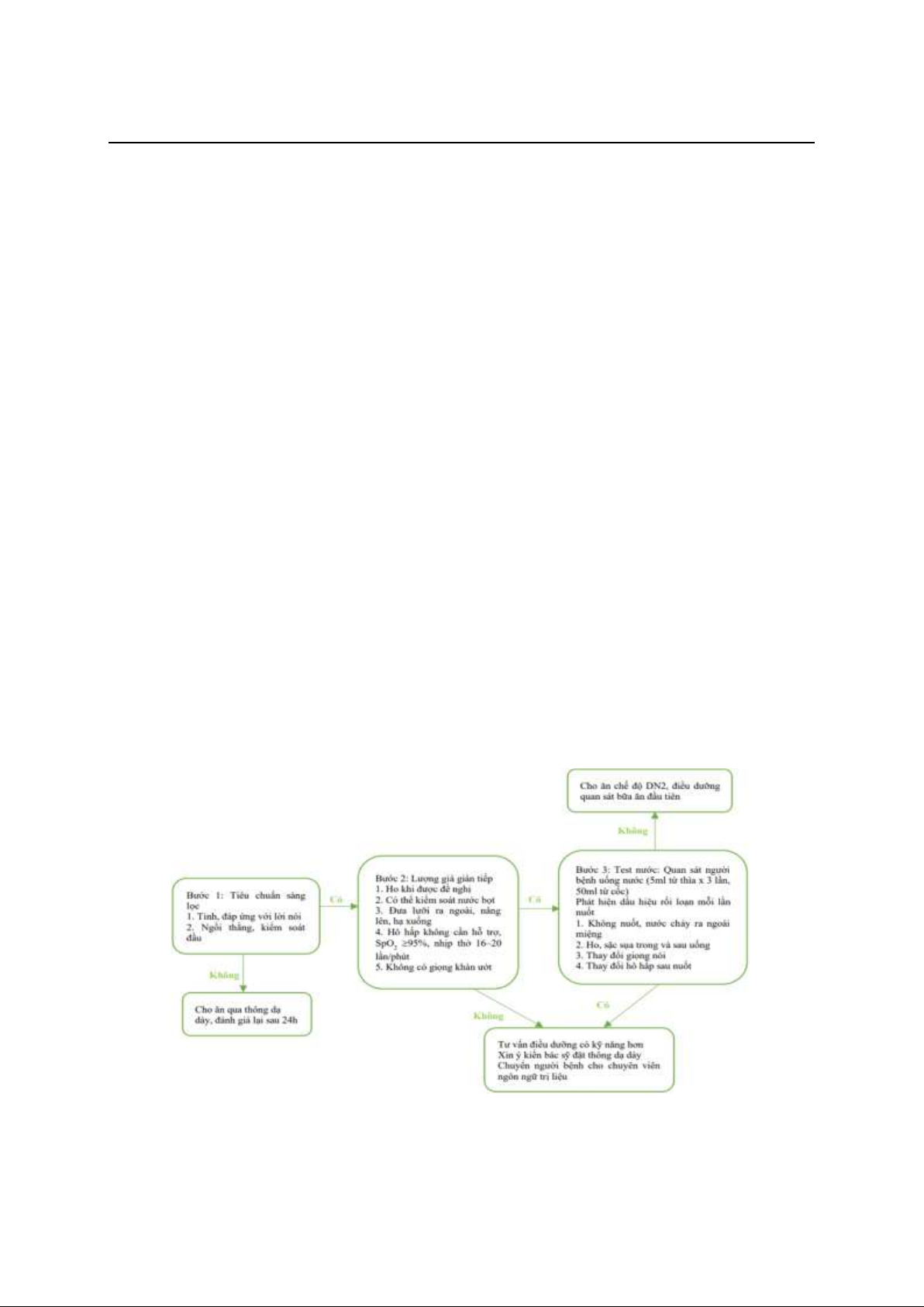
Mục tiêu: Đánh giá tình trạng rối loạn nuốt
(RLN) bằng bộ công cụ SSA và một số yếu tố
liên quan ở bệnh nhân (BN) nhồi máu não
(NMN) cấp tại trung tâm Đột quỵ Bạch Mai. Đối
tượng và phương pháp: Nghiên cứu quan sát
mô tả các BN chẩn đoán NMN cấp điều trị tại
trung tâm Đột quỵ Bạch Mai từ 01/01/2024-
31/03/2024, được đánh giá sàng lọc RLN bằng
công cụ SSA. Kết quả: 1068 BN được thu tuyển
vào nghiên cứu. Tuổi trung bình (67,3±12,3)
tuổi, nam giới (62,8%), tăng huyết áp là bệnh lý
đồng mắc phổ biến nhất. Trong nghiên cứu, điểm
Glasgow và NIHSS trung bình lần lượt là 15 và 7
điểm. RLN (16,7%). Các yếu tố liên quan tình
trạng RLN gồm: tuổi >55, tiền sử đột quỵ não cũ,
NIHSS >10, tắc động mạch lớn, nhồi máu vùng
thân não và biến chứng chuyển dạng chảy máu.
Kết luận: Rối loạn nuốt là tình trạng khá phổ
biến ở BN NMN cấp. Việc xác định các yếu tố
nguy cơ RLN giúp dự đoán, từ đó có kế hoạch dự
phòng và điều trị BN tốt hơn.
Từ khóa: Nhồi máu não cấp, Rối loạn nuốt.
1Trung tâm Đột quỵ BV Bạch Mai
2Bộ môn Đột quỵ và Bệnh lý mạch máu não Đại
học Y Dược, Đại học Quốc gia Hà Nội
3Đại học y Hà nội
Chịu trách nhiệm chính: Mai Duy Tôn
ĐT: 0983668829
Email: tonresident@gmail.com
Ngày nhận bài: 19/8/2024
Ngày gửi phản biện: 21/8/2024
Ngày duyệt bài: 4/9/2024
SUMMARY
TO EVALUATE DYSPHASIA RATE
AND SOME PREDICTIVE FACTORS
AMONG ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
PATIENTS AT BACH MAI STROKE
CENTER
Aims: To evaluate dysphagia rate and some
predictive factors among acute ischemic stroke
patients at Bach Mai Stroke Center. Subject and
methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out
among acute ischemic stroke patients treated at
Bach Mai Stroke Center from January 1, 2024, to
March 31, 2024. They were screened for
swallowing disorders using the SSA tool.
Results: 1068 patients were recruited into the
study. The mean age was 67.3 ± 12.3 years,
62.8% were male. Hypertension was the most
common comorbidity. In the study, the average
Glasgow and NIHSS scores were 15 and 7
points, respectively. Swallowing disorders
occurred in 16.7% of patients. Factors associated
with swallowing disorders include age >55,
history of previous stroke, NIHSS >10, large
artery occlusion, brainstem infarction, and
hemorrhagic transformation. Conclusion:
Dysphagia is quite common in patients with
acute ischemic stroke. Identifying risk factors for
swallowing disorders helps predict, thereby
planning better prevention and treatment of
patients.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke,
Swallowing disorders.