
UBND QUẬN HÀ ĐÔNG
TRƯỜNG THCS DƯƠNG NỘI
--------------------------
ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP GIỮA KỲ I
NĂM HỌC 2023-2024
MÔN: TIẾNG ANH 9
A. COMPLEX SENTENCES:
1. Adverb Clause of Time: Adverb clauses of time are introduced by the subordinating
conjunctions whenever, while, after, before, since, as, etc.
When you have finished your work you may leave.
Don’t talk loud while she is singing.
As soon as he heard the news he wrote to me.
No sooner did he see us than he disappeared
2. Adverb Clause of Place: Adverb Clauses of Place are introduced by the
subordinating conjunctions where and whereas,
I have put it where I can find again.
They can stay where they are.
3. Adverb Clause of Purpose: Adverb clauses of purpose are introduced by the
subordinating conjunctions so that, in order that, and lest.
I will give you a map so that you can find the way.
We eat so that we may live.
4. Adverb Clause of Cause or Reason: Adverb clauses of cause or reason are
introduced by the subordinating conjunctions because, as, since, that.
I am glad that you like it.
Since you are so clever you will be able to explain this.
Because I like you, I shall help you.
5. Adverb Clause of Condition:
+ Adverb clauses of condition are introduced by the subordinating conjunctions if,
whether, unless.
If it rains we shall stay at home.
Unless you work harder you will fail.
+ Sometimes the subordinating conjunction is omitted in adverb clauses of condition;
as,
Had I not seen this from my own eyes I would not have believed it.
Were an angel to tell me such a thing of you, I would not believe it.
What would you answer did I ask you such a question?
+ Adverb clauses of condition are sometimes introduced by a relative pronoun, or
adjective, or adverb (without any antecedent); as,
Whichever road we take we shall be too late.

2
6. Adverb Clause of Result: Adverb clauses of result or consequence are introduced by
the subordinating conjunction that. Frequently so or such precedes it in the principal
clause.
He is such a good man that all respect him.
The Romans built in such a way that their walls are still standing.
7. Adverb Clause of Comparison : Adverb clauses of comparison of degree are
introduced by the subordinating conjunction than, or by the relative adverb as; as,
He is older than he looks.
He is as stupid as he is lazy
He is not so clever as you think.
8. Adverb Clauses of Supposition or Concession: Adverb Clauses Supposition or
Concession are introduced by the Subordinating Conjunctions though, although, even if.
Though I am poor I am honest.
Although troops had marched all day they fought bravely all night.
Even if he is old he is able to do a great deal of work.
I would not do it even if you paid me.
B.PHRASAL VERBS:
1. set up: khởi nghiệp, xây dựng sự nghiệp
2. bring out: xuất bản, phát hành
3. look through: đọc
4. keep up with: bắt kịp với
5. run out of: hết
6. pass down: chuyển giao
7. close down: đóng cửa, dừng (kinh doanh)
8. get on with: thân thiết với
9. turn down: phản đối, từ chối
10. set off: khởi hành
11. pass down: chuyển giao
12. turn up: xuất hiện, đến
13. work out: kết thúc
14. take over: đảm đương, đảm nhận
15: find out: tìm thông tin
16. bring out: = publish : xuất bản
17. Look through: nhìn
18. Keep up with = stay equal with:
19. Run out of = short of: cạn kiệt, hết
20. Pass down: phá sản, phá vỡ
21. Live on: sống nhờ vào

3
22. Deal with : giải quyết
23. Look over: xem xét, kiểm tra
24. face up to (with) = deal with : đồng ý, đối mặt
25. Turn down: phản đối, từ chối
26. splitup: vỡ ra, tách ra
27. rustleup: vội vàng, hối hả
28. tuck into: ăn ngon lành
29: put off: trì hoãn
30: get on (well) with: có mối quan hệ tốt
B. COMPARISION
1.Equality(So sánh bằng)
S + V + as + adj/adv + as + N/pronoun
S + V + not + so/as + adj/adv + N/Pronoun
Ex:
+She is as stupid as I/me
+This boy is as tall as that one
2.Comparative(So sánh hơn)
Short Adj:S + V + adj + er + than + N/pronoun
Long Adj: S + V + more + adj + than + N/pronoun
Ex:
She is taller than I/me
This boy is more intelligent than that one.
Dạng khác:S + V + less + adj + than + N/pronoun.(ít hơn)
3. Superlative(So sánh nhất)
Short adj:S + V + the + adj + est + N/pronoun
Long adj:S + V + the most + adj + N/pronoun.
Ex:
She is the tallest girl in the village.
He is the most gellant boy in class.
Dạng khác:S + V + the least + adj + N/pronoun(ít nhất)
Các tính từ so sánh bất quy tắc thì học thuộc lòng
good/better/the best bad/worse/the worst many(much)/more/the most
little/less/the least far/farther(further)/the farthest(the furthest)
4.Double comparison(So sánh kép)
Same adj:
Short adj:S + V + adj + er + and + adj + er

4
Long adj:S + V + more and more + adj
Ex:
The weather gets colder and colder.
His daughter becomes more and more intelligent.
Different adj:
The + comparative + S + V the + comparative + S + V.
Ex:
The richer she is the more selfish she becomes.
The more intelligent he is the lazier he becomes.
Dạng khác(càng...càng...)
The + S + V + the + comparative + S + V
Ex: the more we study the more stupid we feel.
5. Comparison (So sánh gấp nhiều lần)
S + V + multiple numbers + as + much/many/adj/adv + (N) + as + N/pronoun.
Ex: She types twice as fast as I.
B.PHRASAL VERBS ( cont)
1. Set up : khởi nghiệp
2. take off: cởi bỏ, cất cánh
3. grow up: lớn lên
4. show smb around: đưa ai đi dạo
5. pull down: kéo sập
6. turn off: tắt
7: go over: kiểm tra
8. go on with: tiếp tục
C.INDIRECT SPEECH (REPORTED SPEECH)
A.STATEMENTS IN REPORTED SPEECH
1. Direct Speech (Lời nói trực tiếp)
- Thuật lại nguyên vẹn lời của người nói, không sửa đổi lời văn.
Ex: He says: “I am very hungry”
- Lời nói trực tiếp được đặt trong ngoặc kép, sau V tường thuật say (said) , tell (told)…
và sau dấu hai chấm.
2. Indirect speech / Reported speech (Lời nói gián tiếp)
- Thuật lại lời của người nói bằng lời văn của mình và thực hiện những sự thay đổi cần
thiết.
Ex : He says : “ I am very hungry” (trực tiếp)
→ He says (that ) he is very hungry. (gián tiếp)
- Lời nói gián tiếp không có dấu hai chấm và dấu ngoặc kép.
3. Cách chuyển từ câu trần thuật trực tiếp sang câu trần thuật gián tiếp.
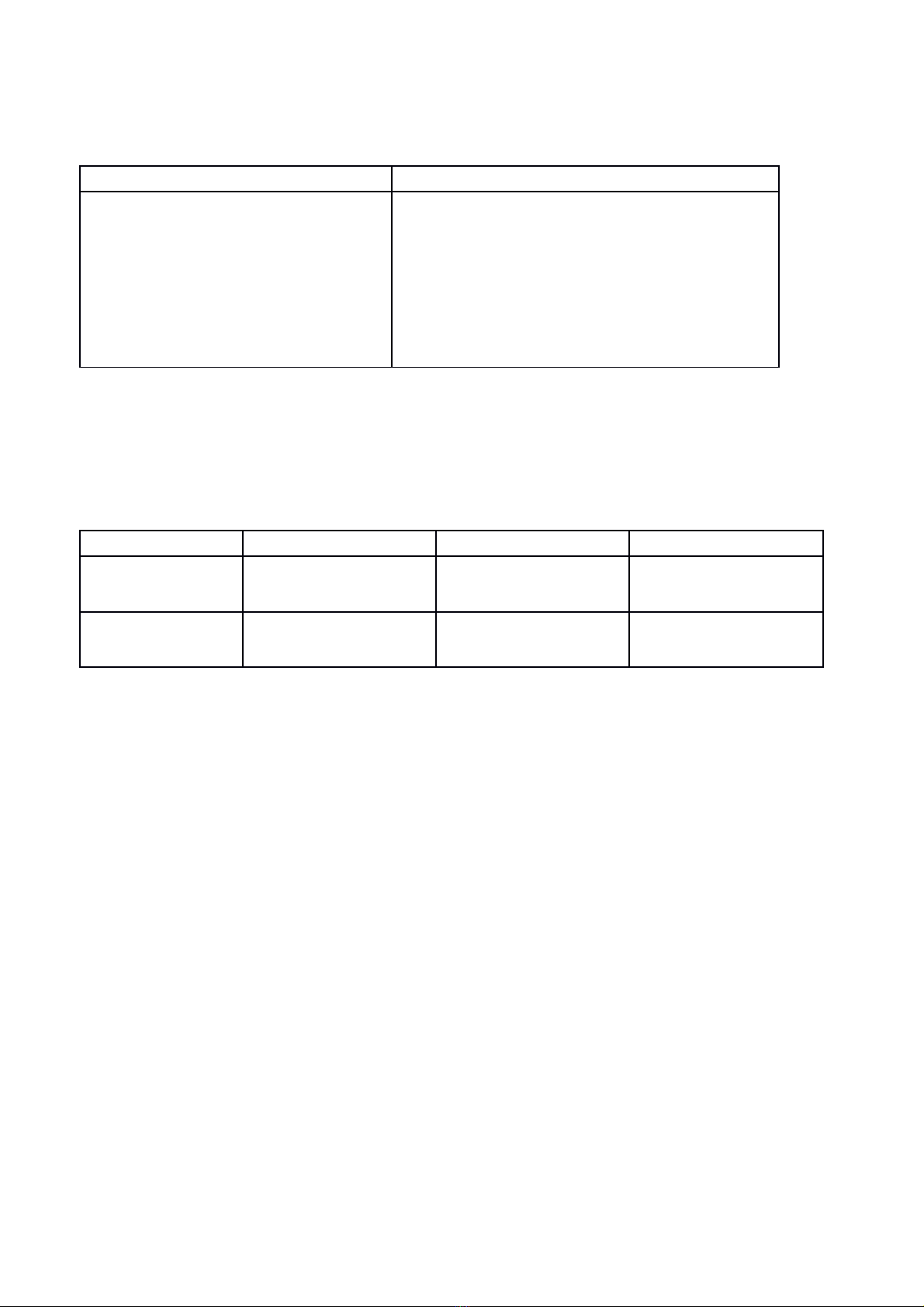
5
* Khi chuyển từ câu trần thuật trực tiếp sang gián tiếp ta áp dụng những sự thay đổi sau
đây :
1. Đổi V tường thuật.
Trực tiếp Gián tiếp
Say
Said
Tell
Told
Say to
Said to
Say / say that
Said / said that
Tell (that)
Told (that)
Tell
Told
Ex: He said to me: “She is in the room”
→ He told me (that) she was in the room.
2. Thay đổi S (đại từ nhân xưng làm chủ ngữ) , O (tân ngữ) , Possessive Adjectives
(tính từ sở hữu) cho phù hợp .
* Cách chuyển đổi S, O, Tính từ sở hữu như sau :
S O P.ADJ (TTSH) Cách chuyển
Ngôi 1 : I , We Me , us My , our - Chuyển theo ngôi
người nói
Ngôi 2 :You You Your - Chuyển theo ngôi
người nghe
3. Đổi đại từ chỉ định , trạng từ thời gian và nơi chốn. (nếu V tường thuật ở quá
khứ)




![Bài tập so sánh hơn và so sánh nhất của tính từ [kèm đáp án/mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250808/nhatlinhluong27@gmail.com/135x160/77671754900604.jpg)
![Tài liệu tham khảo Tiếng Anh lớp 8 [mới nhất/hay nhất/chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250806/anhvan.knndl.htc@gmail.com/135x160/54311754535084.jpg)




![Tài liệu Lý thuyết và Bài tập Tiếng Anh lớp 6 [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250802/hoihoangdang@gmail.com/135x160/18041754292798.jpg)





