
21/11/15
21/11/15 Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing
Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing 1
1
Digital Image Processing
Image Enhancement
Image Enhancement

21/11/15
21/11/15 Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing
Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing 2
2
Image Enhancement
Image Enhancement
To process an image so that output is “visually better”
To process an image so that output is “visually better”
than the input, for a specific application.
than the input, for a specific application.
Enhancement is therefore, very much dependent on
Enhancement is therefore, very much dependent on
the particular problem/image at hand.
the particular problem/image at hand.
Enhancement can be done in either:
Enhancement can be done in either:
–Spatial domain: operate on the original image
Spatial domain: operate on the original image
g
g(
(m
m,
,n
n) =
) = T
T[
[f
f(
(m
m,
,n
n)]
)]
–Frequency domain: operate on the DFT of the original image
Frequency domain: operate on the DFT of the original image
G(u,v)
G(u,v) =
= T
T[
[F(u,v)
F(u,v)], where
], where
F(u,v)
F(u,v) =
= F
F[
[f(m,n)
f(m,n)], and
], and G(u,v)
G(u,v) =
= F
F [
[g(m,n)
g(m,n)],
],

21/11/15
21/11/15 Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing
Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing 3
3
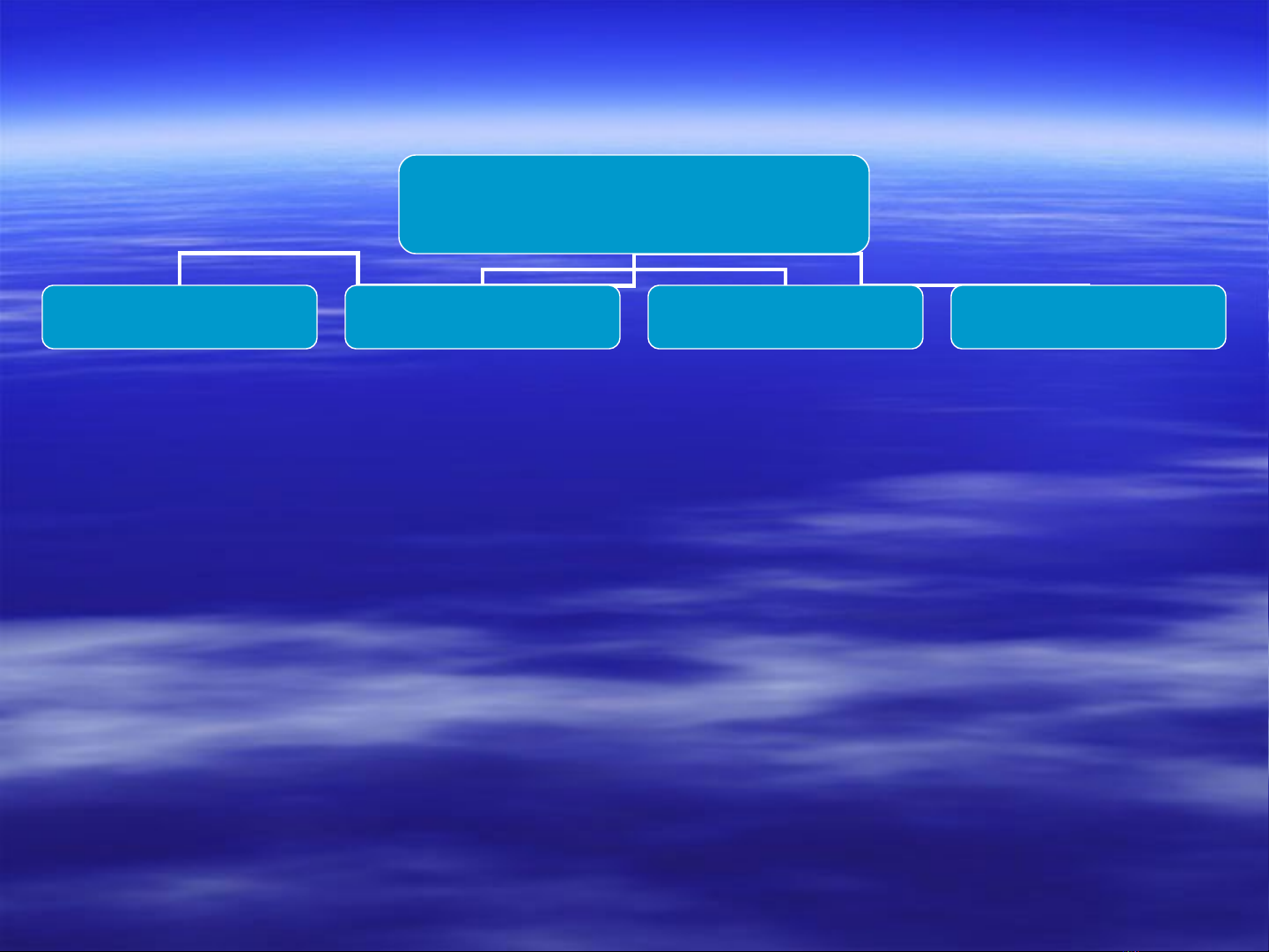
Image Enhancement Techniques
Image Enhancement Techniques
Point Operations Mask Operations Transform Operations Coloring Operations
•Image Negative
•Contrast
Stretching
•Compression of
dynamic range
•Graylevel slicing
•Image
Subtraction
•Image Averaging
•Histogram
operations
•Smoothing
operations
•Median Filtering
•Sharpening
operations
•Derivative
operations
•Histogram
operations
•Low pass
Filtering
•Hi pass Filtering
•Band pass
Filtering
•Homomorphic
Filtering
•Histogram
operations
•False Coloring
•Full color
Processing
21/11/15
21/11/15 Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing
Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing 4
4
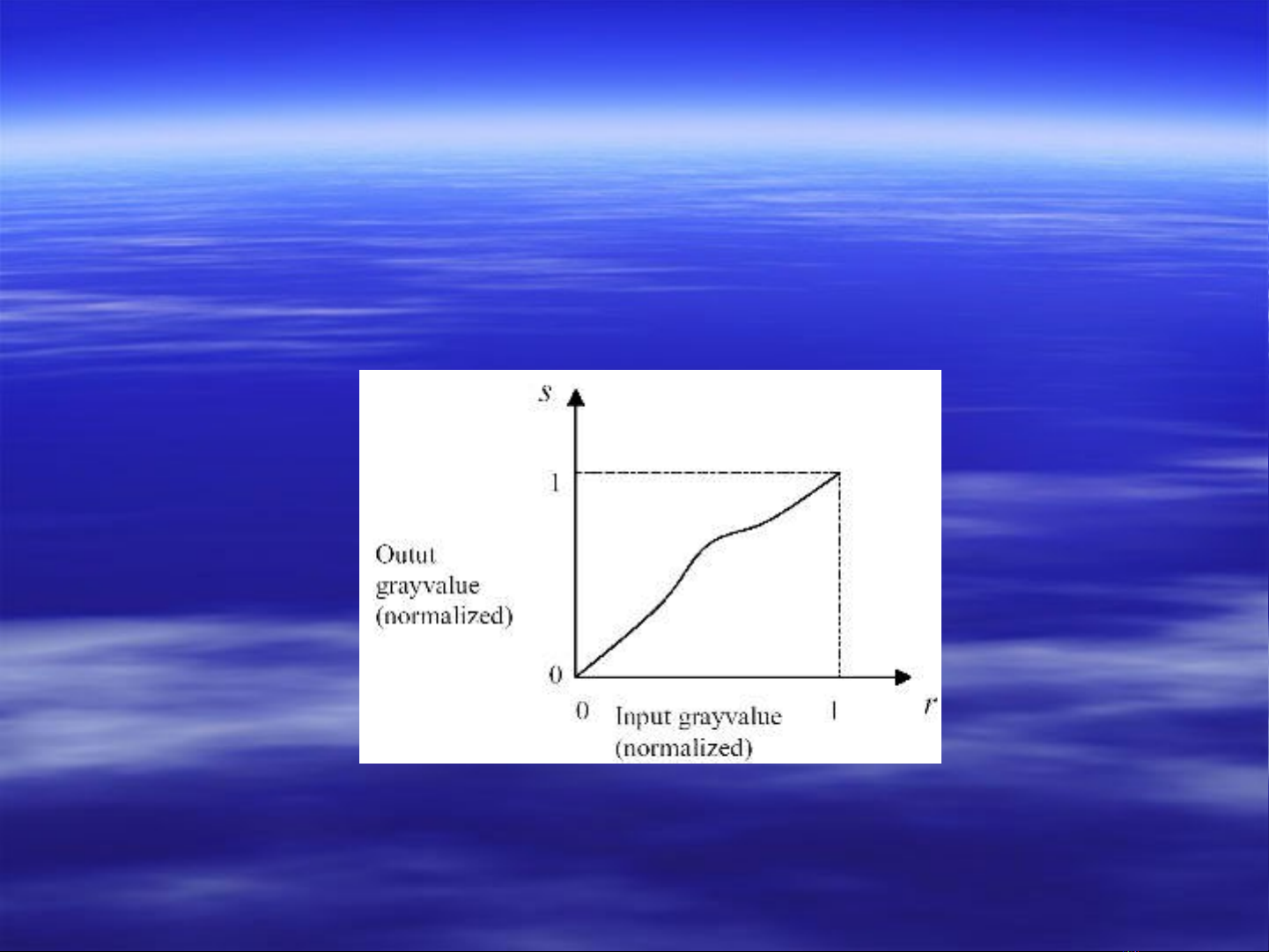
Point Operations
Point Operations
Output pixel value
Output pixel value g
g(
(m
m,
, n
n) at pixel (
) at pixel (m
m,
, n
n) depends only on the input
) depends only on the input
pixel value at
pixel value at f
f(
(m
m,
, n
n) at (
) at (m
m,
, n
n) (and not on the neighboring pixel
) (and not on the neighboring pixel
values).
values).
We normally write
We normally write s
s =
= T
T(
(r
r), where
), where s
s is the output pixel value and
is the output pixel value and r
r is the
is the
input pixel value.
input pixel value.
T
T is any increasing function that maps [0,1] into [0,1].
is any increasing function that maps [0,1] into [0,1].
21/11/15
21/11/15 Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing
Duong Anh Duc - Digital Image Processing 5
5
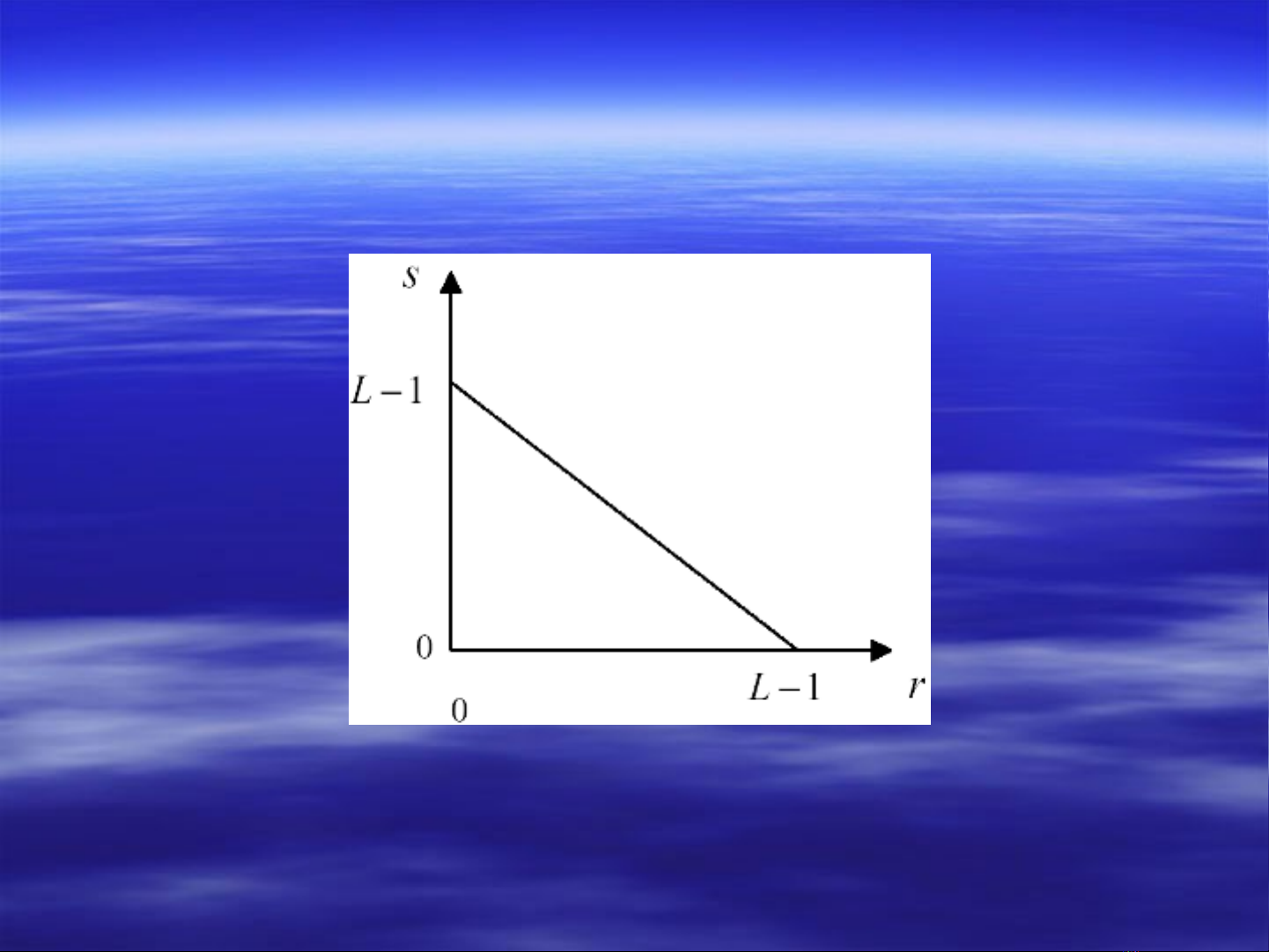
Image Negative
Image Negative
T(r) = s = L-1-r, L: max grayvalue


























