
Các thì trong ti ng Anh ế
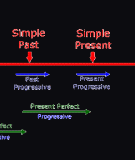
1- Thì Hi n t i đ n , Hi n t i ti p di n (Present, Present continuous) ệ ạ ơ ệ ạ ế ễ
2- Thì Hi n t i hoàn thành, Hi n t i ti p di n (Present perfect, Present Perfectệ ạ ệ ạ ế ễ
continuous)
3- Thì Quá kh đ n, Quá kh ti p di n (Past perfect, Past Perfect continuous) ứ ơ ứ ế ễ
4- Thì Quá kh hoàn thành, Quá kh hoàn thành ti p di n (Past perfect, Past Perfectứ ứ ế ễ
continuous)
5- Thì T ng lai, T ng lai ti p di n (Future, Future continuous) ươ ươ ế ễ
6- Thì T ng lai hoàn thành, T ng lai hoàn thành ti p di n (Future perfect, Futureươ ươ ế ễ
perfect continuous)
1- HI N T I Đ N - HI N T I Đ N TI P DI N Ệ Ạ Ơ Ệ Ạ Ơ Ế Ễ
A- THÌ HI N T I Đ N Ệ Ạ Ơ
Thì hi n t i đ n gi n di n t hành đ ng có th t trong quá kh , hi n t i, và t ng lai.ệ ạ ơ ả ễ ả ộ ậ ứ ệ ạ ươ
Thì hi n t i đ n gi n cũng di n t thói quen và ho t đ ng hàng ngày. ệ ạ ơ ả ễ ả ạ ộ
CH T + Đ NG T Ủ Ừ Ộ Ừ
(đ ng t thì hi n t i, đ ng t thêm "S" hay "ES" n u ch t là ngôi 3 s ít: She, he,ộ ừ ở ệ ạ ộ ừ ế ủ ừ ố
it, Mary, John)
Thì hi n t i đ n gi n có th di n t th i gian trong t ng lai khi ý nghĩ đó thu c vệ ạ ơ ả ể ễ ả ờ ươ ộ ề
th i khóa bi u. ờ ể
ex:
The English alphabet consists of 26 letters.
The sun rises in the east.
She goes to school every day.
The boy always wakes up at 8 every morning.
SAI:
They are always trying to help him.

We are studying every day.
ĐÚNG:
They always try to help him.
We study every day.
The game starts in ten minutes.
My class finishes next month.
C m t và t ng ch th i gian: Always, usually, often, sometimes etc., (a fact, habit, orụ ừ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
repeated action), every time, as a rule, every day (every other day), once (a month), once
in a while
B- THÌ HI N T I TI P DI N Ệ Ạ Ế Ễ
Thì hi n t i ti p di n di n t hành đ ng đang x y ra. ệ ạ ế ễ ễ ả ộ ả
CH T + IS/ARE/AM + Đ NG T THÊM -ING Ủ Ừ Ộ Ừ
M t hành đ ng gì đó đang x y ra tu n này, tháng này, ho c năm này. ộ ộ ả ầ ặ
Thì hi n t i ti p di n có th di n t th i gian trong t ng lai khi ý nghĩ đó là 1 s đ nhệ ạ ế ễ ể ễ ả ờ ươ ự ị
s n. ẵ
ex:
I"m typing right now.
It is raining at the moment.
Shhh! The baby is sleeping.
She is taking ESL 107 this semester.
Tammy is writing a letter to her mom tomorrow.
Jack is visiting his relatives tomorrow.
SAI: It is raining tomorrow. (Rain không th là 1 s d đ nh tr c) ể ự ự ị ướ
C m và t ng ch th i gian: Right now, at the moment, at present, now, shhh!, listen!,ụ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
look!, this semester.

2- HI N T I HOÀN THÀNH - HI N T I HOÀN THÀNH TI P DI N Ệ Ạ Ệ Ạ Ế Ễ
A- THÌ HI N T I HOÀN THÀNH Ệ Ạ
CH T + HAVE/ HAS + QUÁ KH PHÂN T (PAST PARTICIPLE) Ủ Ừ Ứ Ừ
Thì hi n t i hoàn thành di n t hành đ ng đã x y ra ho c ch a bao gi x y ra 1 th iệ ạ ễ ả ộ ả ặ ư ờ ả ở ờ
gian không xác đ nh trong quá kh . ị ứ
Thì hi n t i hoàn thành cũng di n t s l p đi l p l i c a 1 hành đ ng trong quá kh . ệ ạ ễ ả ự ậ ậ ạ ủ ộ ứ
Thì hi n t i hoàn thành cũng đ c dùng v i i since và for. ệ ạ ượ ớ
Since + th i gian b t đ u (1995, I was young, this morning etc.) Khi ng i nói dùngờ ắ ầ ườ
since, ng i nghe ph i tính th i gian là bao lâu. ườ ả ờ
For + kho ng th i gian (t lúc đ u t i bây gi ) Khi ng i nói dùng for, ng i nói ph iả ờ ừ ầ ớ ờ ườ ườ ả
tính th i gian là bao lâu. ờ
ex:
She has never seen snow.
I have gone to Disneyland several times.
We have been here since 1995.
They have known me for five years.
C m và t ng ch th i gian: Never, ever, in the last fifty years, this semester, since, for,ụ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
so far, up to now, up until now, up to the present, yet, recently, lately, in recent years,
many times, once, twice, and in his/her whole life
B- THÌ HI N T I HOÀN THÀNH TI P DI N Ệ Ạ Ế Ễ
Thì hi n t i hoàn thành ti p di n nh n m nh kho ng th i gian c a 1 hành đ ng đãệ ạ ế ễ ấ ạ ả ờ ủ ộ
x y ra trong quá kh và ti p t c t i hi n t i (có th t i t ng lai). ả ứ ế ụ ớ ệ ạ ể ớ ươ
CH T + HAVE/HAS + BEEN + Đ NG T THÊM -ING Ủ Ừ Ộ Ừ
I have been waiting for you about 20 minutes.
The child has been sleeping all afternoon.
C m và t ng ch th i gian: All day, all week, since, for, for a long time, almost everyụ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
day this week, recently, lately, in the past week, in recent years, up until now, and so far

3- QUÁ KH - QUÁ KH TI P DI N Ứ Ứ Ế Ễ
A- THÌ QUÁ KH Đ N Ứ Ơ
Thì quá kh đ n di n t hành đ ng đã x y ra và k t thúc trong quá kh v i th i gianứ ơ ễ ả ộ ả ế ứ ớ ờ
xác đ nh. ị
CH T + Đ NG T QUÁ KH Ủ Ừ Ộ Ừ Ứ
When + thì quá kh đ n (simple past) ứ ơ
When + hành đ ng th nh t ộ ứ ấ
I went to the library last night.
She came to the U.S. five years ago.
He met me in 1999.
When they saw the accident, they called the police.
C m và t ng ch th i gian: last night, last year, last time, etc., ago, in 1999, today,ụ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
yesterday, then = at that time, in the 1800"s, in the 19th century, when, and for
Today đôi khi đ c dùng thì hi n t i ti p di n và t ng lai đ n. For đôi khi đ cượ ở ệ ạ ế ễ ươ ơ ượ
dùng thì hi n t i hoàn thành (present perfect). ở ệ ạ
B- THÌ QUÁ KH TI P DI N Ứ Ế Ễ
In (a), 2 hành đ ng đã x y ra cùng lúc. Nh ng hành đ ng th nh t đã x y ra s m h nộ ả ư ộ ứ ấ ả ớ ơ
và đã đang ti p t c x y ra thì hành đ ng th hai x y ra. ế ụ ả ộ ứ ả
CH T + WERE/WAS + Đ NG TÙ THÊM -ING Ủ Ừ Ộ
While + thì quá kh ti p di n (past progressive) ứ ế ễ
In (b), 2 hành đ ng đã x y ra cùng m t lúc. ộ ả ộ
a. What were you doing when I called you last night?
b. He was watching TV while his wife was cleaning the bedroom.
C m và t ng ch th i gian: While, at that very moment, at 10:00 last night, and thisụ ừ ữ ỉ ờ
morning (afternoon)
4- QUÁ KH HOÀN THÀNH - QUÁ KH HOÀN THÀNH TI P DI N Ứ Ứ Ế Ễ

A- THÌ QUÁ KH HOÀN THÀNH Ứ
Thì quá kh hoàn thành di n t 1 hành đ ng đã x y ra và k t thúc trong quá kh tr cứ ễ ả ộ ả ế ứ ướ
1 hành đ ng khác cũng x y ra và k t thúc trong quá kh . ộ ả ế ứ
CH T + HAD + QUÁ KH PHÂN T Ủ Ừ Ứ Ừ
I had just finished watering the lawn when it began to rain.
She had studied English before she came to the U.S.
After he had eaten breakfast, he went to school.
B- THÌ QUÁ KH HOÀN THÀNH TI P DI N Ứ Ế Ễ
Thì quá kh hoàn thành ti p di n nh n m nh kho ng th i gian c a 1 hành đ ng đãứ ế ễ ấ ạ ả ờ ủ ộ
đang x y ra trong quá kh và k t thúc tr c 1 hành đ ng khác x y ra và cũng k t thúcả ứ ế ướ ộ ả ế
trong quá kh . ứ
CH T + HAD + BEEN + Đ NG T THÊM -ING Ủ Ừ Ộ Ừ
We had been living in Santa Ana for 2 years before we moved to Garden Grove. C m vàụ
t ng ch th i gian: Until then, by the time, prior to that time, before, after ừ ữ ỉ ờ
Dùng thì quá kh hoàn thành cho hành đ ng th nh t. Dùng thì quá kh cho hành đ ngứ ộ ứ ấ ứ ộ
th hai. ứ
M o: Quí v có th nh theo cách này. ẹ ị ể ớ
Ch cái ti ng Anh A B C....... ữ ế
"A" đ ng v trí th nh t và "A" là ch cái đ u tiên c a ch "After". Cho nên After +ứ ị ứ ấ ữ ầ ủ ữ
hành đ ng th nh t. ộ ứ ấ
Tr c tiên: Alex had gone to bed. ướ
Sau đó": He couldn"t sleep.
After Alex had gone to bed, he couldn"t sleep.
Tr c tiên: Jessica had cooked dinner. ướ
Sau đó": Her boyfriend came.
Jessica"s boyfriend came after she had cooked dinner.







![Bài tập thì hiện tại hoàn thành [kèm đáp án chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251106/thuthao27062004/135x160/41601762420911.jpg)






![Tài liệu ôn tập Ngữ pháp tiếng Anh [chuẩn/mới nhất/tổng hợp]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250821/vuongdinhlinh1412@gmail.com/135x160/933_tai-lieu-on-tap-ngu-phap-tieng-anh.jpg)




