
REVIEW ARTICLE
Models and mechanisms of O-O bond activation by cytochrome P450
A critical assessment of the potential role of multiple active intermediates
in oxidative catalysis
Peter Hlavica
Walther-Straub-Institut fu
¨r Pharmakologie und Toxikologie der LMU, Mu
¨nchen, Germany
Cytochrome P450 enzymes promote a number of oxidative
biotransformations including the hydroxylation of unacti-
vated hydrocarbons. Whereas the long-standing consensus
view of the P450 mechanism implicates a high-valent iron-
oxene species as the predominant oxidant in the radicalar
hydrogen abstraction/oxygen rebound pathway, more
recent studies on isotope partitioning, product rearrange-
ments with Ôradical clocksÕ, and the impact of threonine
mutagenesis in P450s on hydroxylation rates support the
notion of the nucleophilic and/or electrophilic (hydro)
peroxo-iron intermediate(s) to be operative in P450 catalysis
in addition to the electrophilic oxenoid-iron entity; this may
contribute to the remarkable versatility of P450s in substrate
modification. Precedent to this mechanistic concept is given
by studies with natural and synthetic P450 biomimics. While
the concept of an alternative electrophilic oxidant necessi-
tates C-H hydroxylation to be brought about by a cationic
insertion process, recent calculations employing density
functional theory favour a Ôtwo-state reactivityÕscenario,
implicating the usual ferryl-dependent oxygen rebound
pathway to proceed via two spin states (doublet and quar-
tet); state crossing is thought to be associated with either an
insertion or a radicalar mechanism. Hence, challenge to
future strategies should be to fold the disparate and some-
times contradictory data into a harmonized overall picture.
Keywords: (hydro)peroxo-iron; iron-oxene; O
2
-activation;
P450 biomimics; P450.
Introduction
Cytochrome P450 (P450 or CYP) enzymes (EC 1.14.14.1),
a superfamily of b-type hemoproteins found in organisms
from all domains of life [1], are major catalysts in the
oxidative biotransformation of a structural diversity of
endogenous and exogenous compounds [2]. While the
general chemistry of substrate hydroxylation has been
assessed on a broad basis, the specific problem of dioxygen
activation during P450 cycling is still the most important
and intriguing one in the area of P450 research. Here, the
need for an active oxidant capable of insertion into
unactivated C-H bonds in hydrocarbons and related
compounds has extensively captured the imagination of
biochemists owing to the unfavourable thermodynamics of
the dissociation event [3]. Early views of such a mechanism
focused on an oxygen insertion pathway promoted by an
electrophilic, high-valent iron-oxo species (compound I) [4].
This hypothesis was soon supplanted by the Ôhydrogen
abstraction/oxygen reboundÕconcept implicating the exist-
ence of radical intermediates, as developed on the basis of
the well-known chemical properties of peroxidases and
porphyrin model systems [5,6]. The mechanistic details of
oxygen transfer have been addressed elsewhere [7,8].
Mounting evidence provided during the past decade
suggests that hydroxylation reactions are more complex
than previously anticipated, and are not compatible with
the idea of a single reaction pathway. The picture began to
cloud when the application of ultrafast Ôradical clocksÕ
to time the oxygen-rebound step disclosed the amounts of
rearranged products not to correlate with the radical
rearrangement rate constants [9]. Moreover, the use of a
probe that could distinguish between radical and cationic
species hinted at the interference of cationic rearrangements,
predicting the hydroxylation to occur via an insertion
reaction in place of abstraction and recombination [9]. The
former process thus necessitated the insertion into a C-H
bond of the elements of OH
+
, implying that the ultimate
electrophilic oxidant was either hydroperoxo-iron or iron-
complexed hydrogen peroxide [10]. In addition, examina-
tion of the oxidative deformylation of cyclic aldehydes as a
model for the demethylation reaction mediated by steroido-
genic P450s strongly favoured nucleophilic attack on the
Correspondence to P. Hlavica, Walther-Straub-Institut fu
¨r Pharmak-
ologie und Toxikologie, Goethestr. 33, D-80336 Mu
¨nchen, Germany.
Fax: +49 89 218075701, Tel.: +49 89 218075706,
E-mail: hlavica@lrz.uni-muenchen.de
Abbreviations: TSR, two-state reactivity; KIE, kinetic isotope effects;
Hb, haemoglobin; Mb, myoglobin; HO, heme oxygenase; PDO,
phthalate dioxygenase; TDO, toluene dioxygenase; NDO, naphtha-
lene 1,2-dioxygenase; PMO, putidamonooxin; BLM, bleomycin;
NOS, nitric oxide synthases.
Enzymes: Cytochrome P450 (EC 1.14.14.1); NADPH-cytochrome
P450 oxidoreductase (EC 1.6.2.4); heme oxygenase (EC 1.14.99.3);
phthalate oxygenase reductase (EC 1.18.1); phthalate dioxygenase
(EC 1.14.12.7); toluene dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.11); naphthalene
1,2-dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.12); putidamonooxin (EC 1.14.99.15);
nitric oxide synthases (EC 1.14.13.39).
(Received 29 July 2004, revised 27 September 2004,
accepted 28 September 2004)
Eur. J. Biochem. 271, 4335–4360 (2004) FEBS 2004 doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04380.x
substrates by an iron-peroxo intermediate [11]. The sum of
these findings points at the involvement of more than one
active oxidant in the diverse types of P450-catalyzed
substrate processing [12–15].
The goal of the present perspective is to provide a critical
update of several aspects of the current state of biochemistry
relating to the apparently complex machinery of dioxygen
activation, which is considered to possibly implicate mul-
tiple oxygenating species in P450 catalysis. Emphasis will be
put on the evaluation of comparative studies with non-P450
hemoproteins, nonheme metalloenzymes as well as bio-
mimetic model systems to discuss the Ômultiple oxidantÕvs.
the Ôtwo-state reactivityÕtheory.
Iron-oxene acting as an electrophilic oxidant
in P450-catalyzed hydroxylations
The consensus mechanism for hydrocarbon hydroxylation
by P450 enzymes involves hydrogen atom abstraction from
the hydrocarbon by a high-valent iron-oxo species, best
described as an O ¼Fe(IV) porphyrin p-cation radical,
followed by homolytic substitution of the alkyl radical thus
formed in the so-called Ôoxygen reboundÕstep [5–8]
(Scheme 1). Using CYP2B isoforms as the catalysts, radical
collaps was demonstrated to occur at highly variable rates
exceeding those of the gross molecular motions of many
enzyme-bound substrates and depending on the stereo-
chemical specificities of the compounds to be acted upon
[16,17]. Reduction of ferric P450 to the ferrous state sets the
stage for dioxygen binding, the event that commits the
hemoprotein to the step-by-step production of the active
oxidant (Scheme 2). Association of dioxygen with ferrous
microsomal CYP1A2 [18], certain CYP2B isoforms [19–21],
and CYP2C3 [18] to yield hexacoordinate low-spin com-
plexes has been shown to be characterized by absorption
bands around 420 and 557 nm in the absolute spectra and
broad maxima at about 440 and 590 nm in the difference
spectra. Similar optical perturbations were also observed
upon O
2
binding to so-called class I P450s, comprising
mitochondrial and bacterial isozymes such as CYP11A1
[22–24] and CYP101 [25,26], respectively. The rapid initial
step in molecular oxygen activation by both class I and class
II P450s, as measured at varying temperatures, usually
exhibits monophasic kinetic behaviour, with the second-
order rate constants ranging from 0.58 to 8.41 ·10
6
M
)1
Æs
)1
[18,20,24,25]. Interestingly, the presence of certain substrates
such as aromatic amines appears to favour homotropic
cooperativity in dioxygen binding to P450s: using liver
microsomal samples from untreated rabbits, the O
2
satura-
tion kinetics for acetanilide 4-hydroxylation have been
reported to bear sigmoidal character corresponding to a Hill
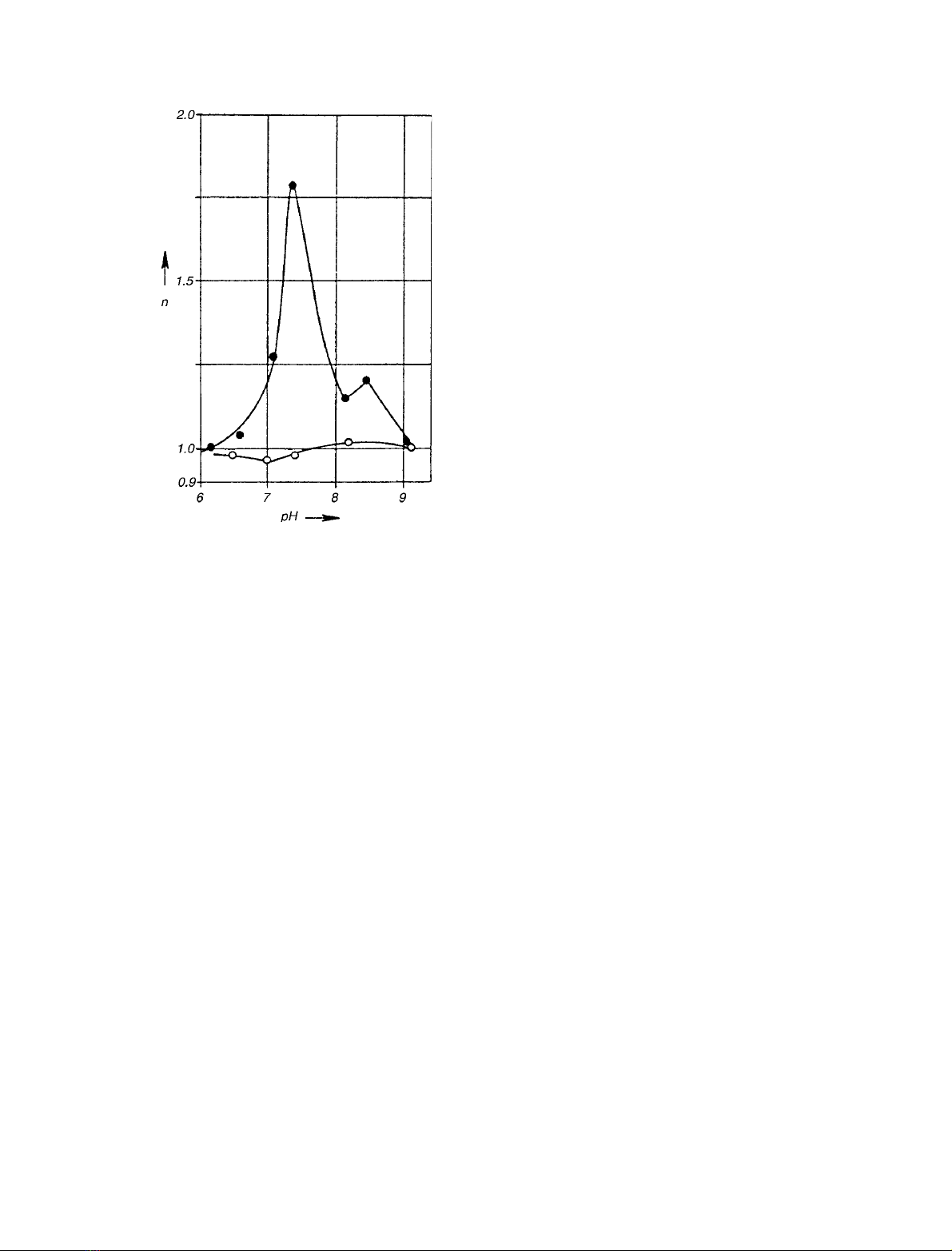
interaction coefficient, n, of 2.2 [27]. Similar experiments
with N-alkyl arylamines gave concave upward double-
reciprocal plots of velocity vs. O
2
concentration, from which
ncould be calculated to have a value of 2.0–2.1 [28,29].
Apparent cooperativity in dioxygen association was found
to be highly sensitive to changes in hydrogen ion concen-
tration and was most pronounced at physiological pH,
whereas CO, acting as a positive effector, abolished
autoactivation at all pH values examined (Fig. 1) [30]. In
view of the well-known microheterogeneity of several rabbit
liver P450s [31], the amine-induced cooperativity in O
2
complexation has been argued to involve the equilibrium
between multiple, kinetically distinct protein conformations
[32]. Alternatively, the oligomeric nature of P450 [33] might
offer the possibility of substrate–specific subunit inter-
actions, as has been proposed for the fractional saturation
of hemoglobin by dioxygen [34].
Results from resonance Raman spectroscopy [35] and
Mo
¨ssbauer studies [36] with microbial CYP101 indicate that
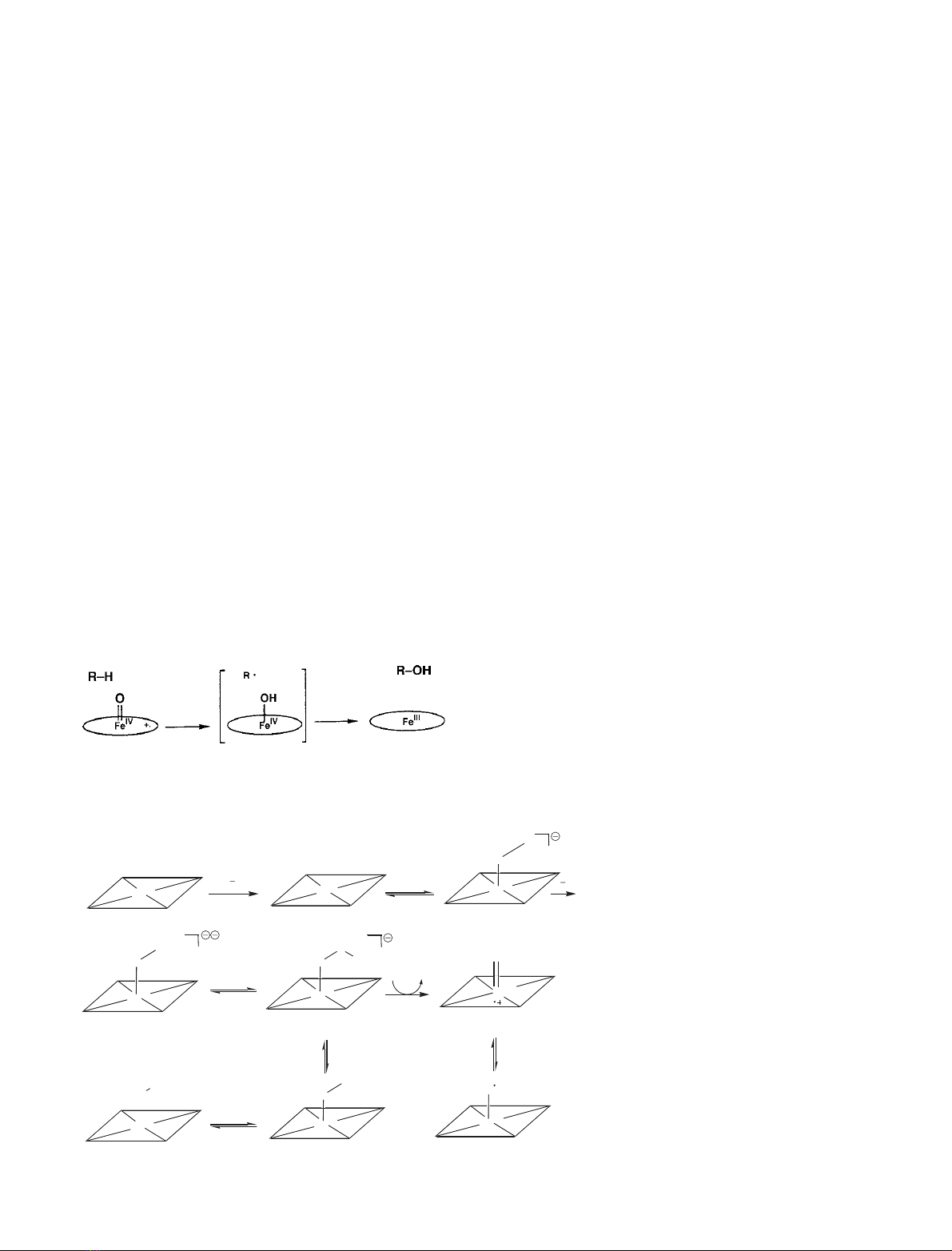
Scheme 1. Rebound mechanism for P450-catalyzed hydroxylations.
Reproduced from [6] with permission.
Fe(III) Fe(II) Fe(III)
O
O
Fe(III)
O
O
Fe(III)
O
O
H
Fe(IV)
O
Fe(III) Fe(III)
HO
OH
Fe(IV)
O
HO OH
+ H+
+ H+ + H+ H2O
O2
peroxo-iron
nucleophilic oxidant
hydroperoxy-iron
(inserts OH+?)
oxo-ion, low spin
(inserts O)
spin inversion
iron-complexed hydrogen peroxide
(inserts OH+?)
oxo-ion, high spin
(abstracts H+)
ee
Scheme 2. The putative iron-oxygen inter-
mediates in P450 and their possible roles as
oxidants. Data collated from [10,15] with
permission.
4336 P. Hlavica (Eur. J. Biochem. 271)FEBS 2004
the ÔoxyÕintermediate of P450 most likely exists in the low-
spin ferric-superoxide form, with the sixth 3d electron
largely transferred to O
2
in an autoxidative process
(Scheme 2). Spontaneous autodecomposition of oxy-cyto-
chrome 2B4 to release ferric pigment and superoxide [37]
has been shown to occur in a biphasic [21,38] or even
triphasic [39] fashion, while monophasic first-order kinetics
were observed for autoxidation of substrate-bound adreno-
cortical CYP11A1 [23,24] and bacterial CYPs 101 and 102
[25,26,40], as measured above 0 C or at subzero temper-
atures. Abortive decay of oxygenated P450 is retarded in the
presence of hydroxylatable substrate [23,26,38], preserving
the complex for arrival of the second electron, and is
inversely proportional to the coupling efficiency of the
system [41]. Moreover, the steady-state level of oxyferrous
P450 has been recognized to be governed by the hydrogen
ion concentration and ionic strength of the reaction medium
[21,24,25]. In view of the strategic importance of the
oxyferro intermediate in the process of dioxygen activation,
the influence of the physiological redox partner, cytochrome
b
5
, on its autoxidative breakdown has been examined in
detail: though increasing the rate of regeneration of ferric
enzyme from oxygenated CYP2B4 by a factor of about 8,
reduced donor protein added to the assay mixtures failed to
undergo substantial reoxidation, suggesting the electron
carrier to act as an allosteric effector in this reaction [38,42].
In accord with this, both apocytochrome b
5
and aporubre-
doxin reportedly stimulate autoxidative transformation of
oxy CYP101 to the ferric state [43]. Superoxide departing
from regenerated P450 has been found to serve as a source
of hydrogen peroxide usually generated during NADPH/O
2
consumption [44].
Addition of an electron to oxyferrous P450 (Scheme 2)
results in the formation of an optimized species,
37 kcalÆmol
)1
higher in energy, with elongated Fe-O
distance but unchanged O-O bond characteristics [45].
Significant O-O bond weakening occurs upon protonation,
the calculated proton affinity being )442.1 kcalÆmol
)1
[45].
The proton-delivering machinery has been recognized to
involve a highly conserved active-site threonine residue
[46,47] working in tandem with an essential aspartate [48–
50]. The residue pair has been ascribed a critical role in
orchestrating the dynamic organization of active-site water
molecules [46], forming a hydrogen-bonded network
capable of pumping protons to the reduced FeO unit [51]
to generate the hydroperoxo-iron derivative (compound O;
Scheme 2). Intermediacy of the end-on Fe(III)-OOH species
has been unequivocally proven by electronic absorption,
EPR and ENDOR spectroscopic techniques upon cryo-
radiolytic reduction of oxy CYP101 [52–55] and CYP119
[56] at 77 K. The same intermediate was also obtained by
reacting ferrous CYP101 with KO
2
[57] or bioreduction of
oxyferrous CYP101 with putidaredoxin [58].
Unless the protonated peroxide complex decays in a
nonproductive mode to liberate ferric enzyme and H
2
O
2
[18], conversion to the actual oxidant proceeds with a
significant energy release of 50 kcalÆmol
)1
[59]. While
acylation of the distal oxygen to make it a better leaving
group prior to Fenton-type homolytic O-O bond rupture
has been vitiated owing to discrepancies between theory and
measured data [60], the most favoured activation pathway is
heterolytic O-O bond scission to formally produce a
[FeO]
3+
species (Scheme 2) [6,8], having a midpoint poten-
tial of 1.5–2.0 V [61]. The so-called ÔpushÕeffect of the
thiolate ligand in P450s has been shown to promote
heterolytic cleavage of heme-bonded dioxygen by increasing
electron density at the iron atom [62–66]. The electron-
donating properties of the active-site thiolate of CYP101
have been demonstrated to be enhanced by putidaredoxin-
induced alterations in enzyme conformation [50–67].
Attempts were made to characterize the P450 reactive
oxygen intermediate. Thus, iodosylbenzene, a single-oxygen
donor [68], as well as peroxides and peracids, acting as
versatile O
2
surrogates in oxidative reactions [69–71], have
been revealed to elecit spectral perturbations with P450s
closely resembling those of the green, high-valent FeOPor•
+
species (compound I) of peroxidases, including the thiolate-
ligated, P450-like chloroperoxidase enzyme [72–75]. These
findings lent credit to the notion, that an analogous key
oxidant might be operative in P450-catalyzed monooxy-
genations, too, albeit there is a significant difference between
P450 and peroxidase models regarding the displacement of
the iron atom from the porphyrin plane, resulting in longer
Fe-O bond in the P450 active intermediate [76]. Density
functional studies demonstrate that both enzyme systems,
though looking very similar, behave like chemical chame-
leons, in which small alterations in the environment can
cause drastic changes in the reactivity of the active species
[76]. Further support in favour of the idea of the involve-
ment of a high-valent iron-oxene in P450 catalysis came
from experiments with metalloporphyrin models [5,6,77]. Of
particular importance, a green oxo-ferrylporphyrin p-cation
radical intermediate could be isolated and spectrophoto-
metrically and chemically characterized, that was capable of
Fig. 1. Effect of hydrogen ion concentration on the Hill interaction
coefficient nfor oxygen binding. Rabbit liver microsomal N-oxide for-
mation from N,N-dimethylaniline was measured in the absence (d)and
presence (s)of490l
M
CO. Reproduced from [30] with permission.
FEBS 2004 O-O Bond activation by cytochrome P450 (Eur. J. Biochem. 271) 4337

oxygen transfer reactions [78]. Nevertheless, identification
of the [FeO]
3+
adduct by UV-visible spectroscopic analysis
of CYP119 [79] or transient X-ray crystallography using
CYP101 [80] appears to be quite tentative.
The proportion of the putative iron-oxene species not
used for monooxygenations undergoes uncoupling to
generate ferric P450 and water [81] in a 4-electron reductive
process [82], uncoupling being controlled by substrate
accessibility [83]. In fact, the presence of substrate has been
shown to stabilize the active oxy complex produced with
CYP2B4 and organic hydroperoxide, and the protective
effect is intensified by cytochrome b
5
binding [84,85]. Active
oxidant thus preserved is thought to promote hydrogen
transfer from substrate to initiate monooxygenation
(Scheme 1); this step, which proceeds with a remarkable
low free–energy barrier, has been suggested to be governed
by peripheral heme substituents in the P450 molecule [86].
Firm evidence for the nonconcerted hydrogen abstraction/
oxygen rebound chemistry presented in Scheme 1 is provi-
ded by a plethora of experimental observations such as (a)
the stereochemical scrambling in norbornane [87] and
camphor [88] hydroxylation (b) the allylic rearrangements
found in the hydroxylation of unsaturated hydrocarbons
[89] (c) the correlation of susceptibility toward oxidative
attack with C-H bond strength [90] (d) the large kinetic
isotope effects (KIE; k
H
/k
D
11) for C-H activation using
norbornane [87], diphenylpropane [91] or difluorocamphor
[92] as the hydroxylatable substrates and (e) the results from
investigations with Ôradical clockÕprobes such as bicyclo-
pentane, having highly strained carbocyclic structures to
permit the unmasking of radical intermediates that rear-
range at a rate faster than that of the recombination step
[16,93].
Despite the apparent predominance of the hydrogen
transfer mechanism as the initial step in substrate hydroxy-
lation, electron transfer to generate a carbocation, followed
by capture of a hydroxyl anion has been discussed as an
alternative oxygenating principle [94,95]. The net outcome
would be oxidation of an otherwise unactivated C-C single
bond. Although cations may be the logic precursor for
certain substrates with low oxidation potentials, such a
pathway cannot be reconciled with the large KIE and
stereochemical scrambling detailed above. To quantitatively
assess the significance of electron transfer in the transition
states of hydroxylation reactions, studies on the regioselec-
tivity of nitroacenaphthene oxygenation were conducted
with various oxometalloporphyrins; hydrogen abstract-
ion was shown to be the preferred route for all models
examined [96].
Hydroperoxo-iron acting as an alternative
electrophilic oxidant in P450-catalyzed
hydroxylations
Evidence from kinetic analysis of P450 function
Studies on the oxidative transformation of 1-methyl-2-
phenylcyclopropane and its mono-, di-, and trideuterio-
methyl congeners by microsomal CYP2B1 and CYP2E1
suggested that, judging from the large magnitudes of the
combined primary and secondary KIEs for hydrogen
abstraction, rotation in the enzyme pocket was faster than
its relatively slow reaction (< 10
6
Æs
)1
) with the putative
iron-oxene species [97], while the lifetimes of carbon-centred
radicals derived from a diverse set of substrates are on the
order of about 10
)10
s [98]. Moreover, the randomness of
the apparent intramolecular KIEs for unrearranged and
rearranged alcohol products generated from enantiomeric
dideuteriomethyl substrate forms implicated that more than
one reaction channel existed [99]. This concept was
reinforced when the KIEs for NADPH-and cumene
hydroperoxide-driven N-demethylation of amitryptiline by
CYP2D6 were found to be severely discrepant [100].
Examination of the competitive intermolecular KIE for
sulfoxidation/N-dealkylation reactions mediated by bacter-
ial CYP102 hinted at the involvement of two distinct
electrophilic oxidizing species [101], as was also concluded
from the intermolecular noncompetitive KIEs for a-and
b-hydroxylation of fatty acids by CYP152 peroxygenase
isozymes [102].
Probing of the metabolism of norcarane by CYP2B4
revealed the formation of a cation-derived rearrangement
product not compatible with the hydrogen abstraction
mechanism [103]. The latter was also challenged by the
finding that evaluation of the metabolic transformation of a
series of cyclopropane derivatives by CYP2B4 gave unrea-
sonably high rate constants for oxygen rebound (k
OH
)
ranging from 1.5 to 7 ·10
12
s
)1
; this disparate result was
rationalized by possible steric effects in the enzyme’s active
site causing overestimation of the k
OH
values [17]. However,
experiments on the CYP2B1-catalyzed hydroxylation of a
new constrained substrate, that would be less likely to be
subject to steric constraint, also yielded an incredibly high
apparent k
OH
value of 1.4 ·10
13
s
)1
[104]. Moreover, the
plot of the ratio of rearranged to unrearranged alcohol
products vs. the rate constant for rearrangement of the
putative radical intermediate (k
r
) revealed a lack of corre-
lation between these parameters [104]. In addition, hyper-
sensitive radical probe studies with four P450 isozymes gave
consistently small amounts of rearranged products, ham-
pered radical ring opening on steric grounds being unlikely
[105]. The sum of these findings thus suggested that there
was either an error in the kinetic scale for fast radical
reactions or the mechanistic paradigm of P450-mediated
hydroxylations was incomplete. To solve this problem,
further hypersensitive radical probe substrates were intro-
duced, that could distinguish between radical and carbo-
cation intermediates on the basis of the identity of the
rearranged products [9,106,107]. Oxidation of these probes
with several members of the CYP2 family gave cation-
derived rearrangement products, disproving the assumption
that such rearrangements arose exclusively from radical
species. Variable partitioning between the radical and
carbocation mechanisms thus was concluded to explain
thewiderangeofk
OH
values described above [106]. From
the small amounts of radical rearrangement products
generated from the hypersensitive probes, the radical
lifetimes in the P450-catalyzed reactions could be calculated
to range from 70 to 200 fs [106,107], which are too short for
true radical intermediates, but rather correspond to vibra-
tional lifetimes or the lifetimes of transition states. Hence,
the cationic intermediates observed could be ruled out to
originate from oxidation of such transient radicals, so that
their occurrence necessitated another mechanistic enigma.
4338 P. Hlavica (Eur. J. Biochem. 271)FEBS 2004

In this regard, the most plausible premise is insertion of
OH
+
into a C-H bond to generate protonated alcohol
species that can undergo solvolysis-type reactions to yield
cationic rearrangement products [9,107]. This route requires
heterolytic O-O bond fission of the hydroperoxo-iron state
of P450 (Scheme 3A) to release OH
+
and [FeO]
+
[106,107].
However, density functional analysis of mechanisms
involved in ethylene epoxidation by a Fe(III)–OOH model
disclosed barriers for the various pathways of 37–53 kcalÆ
mol
)1
[108]. This was taken to indicate that hydroperoxo-
iron, as such, could not be the ultimate oxidant, in line with
its significant basicity and poor electron-accepting capabil-
ities [108]. Moreover, molecular orbital calculations carried
out with a similar model system unveiled nonrepulsive
potential curves only for peroxo-iron, but not for hydro-
peroxo-iron as the catalytic intermediate in the turnover of
aniline and fluorobenzene [109]. Comparative investigations
on the NADPH/O
2
- and iodosylbenzene-dependent meta-
bolism of lauric acid by CYP2B4 favoured the Fe(III)-H
2
O
2
complex (Scheme 3B) as acting as an alternative electro-
philic oxidant [110]. This postulate is in accord with data
from measurements with hypersensitive radical clocks
[9,106], albeit there is some objection to this idea: protona-
tion of the proximal oxygen in the reduced ferrous dioxygen
unit is usually thought to trigger Fe-O bond weaking
followed by uncoupling of monooxygenation reactions
[111]. On the other hand, stable end-on iron(III)-hydrogen
peroxide complexes have been shown to incur in the
catalytic cycle of cytochrome cperoxidase [112], horseradish
peroxidase [113] and chloroperoxidase [114], but their
immediate participation in monooxygenation processes
has not been established. Finally, molecular dynamics
simulations employing the CYP101 crystal structure pro-
posed the diprotonated species displayed in Scheme 3C to
be an oxidant far superior to compound I [115]. As can be
readily seen, the question of the nature of the alternative
oxygenating intermediate remains inherently elusive.
The functional importance of hydroperoxo-iron or iron-
coordinated hydrogen peroxide as the putative second
oxidant in P450 catalysis is also corroborated by studies on
heteroatom oxidation. Thus, comparative investigations
on the NADPH/O
2
- and cumene hydroperoxide-driven
N-hydroxylation of 4-chloroaniline by CYP2B4 indicated
discrepancies in the positions of the Soret maxima in the
absolute spectra of the individual oxy complexes [116].
Noteworthy, transformation of P450 to the denatured P420
form through treatment with either p-chloromercuribenzo-
ate or deoxycholate rendered the hemoprotein a more
powerful peroxygenase [116], but disrupted NADPH-linked
monooxygenase activity [117]. Hence, resonanace stabiliza-
tion via the thiolate Ôpush effectÕ(see above) did not appear
to be obligatory when peroxide substituted for reduced
cofactor and dioxygen. While N-(4-chlorophenyl) hydroxy-
lamine was found to be the major metabolic product under
mixed-function conditions, a marked change to the prepon-
derant formation of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene was observed
when organic hydroperoxide served as the oxygen donor
[116]. Involvement in the N-oxidative process of CmO•
(CmOÆ
2) radicals could be safely ruled out owing to
insensitivity of the reaction toward radical scavengers,
whereas blockage of turnover by cyanide hinted at an
iron-based mechanism [116]. The sum of these findings
raised serious questions as to the commonness of the
oxygenating species operative in the NADPH- and hydro-
peroxide-sustained hydroxylations. In fact, evidence has
been provided for the existence of fairly stable Fe(III)-OOR
intermediates generated by reacting organic hydroperoxides
with mononuclear iron catalysts [118–120] or intact
CYP2C11 [121], and their ability to transfer oxygen to
substrates prior to heterolytic cleavage at low temperatures
has been ascertained [122–124]. As N-hydroxylation of
4-chloroaniline by the putative Fe(III)-OOR species must
compete not only with conversion of the intermediate to
[FeO]
3+
, but also with self-destructive oxidation of the heme
moiety of P450 [125], it seems worth mentioning that the
rate of cumene hydroperoxide-induced loss of CO-reactive
CYP2B4 [85] could be demonstrated to be far below that of
release of N-oxy product from the ternary complex [116].
There is also reason to envisage iron-bound hydro-
peroxide as a potential oxidant in NADPH-promoted
N-oxygenation of N,N-dimethylaniline by CYP2B4: the
presence of superoxide dismutase inhibits the reaction by
75%, whereas catalase or mannitol leave N-oxide formation
unaffected, dismissing free H
2
O
2
or OH•radicals to act as
catalysts [126]. Notably, investigations with a superoxide-
generating system ruled out O
2
•
)
itself to function as the
active intermediate, so that superoxide was invoked to serve
as a source for production of the ultimate oxygenating
species, presumably Fe(III)-OOH, catalyzing attack on the
electron-rich nitrogen centre of the tertiary arylamine
[126–128]. The active oxidant thus was anticipated to arise
from interaction, in the presence of protons, of newly
generated O
2
•
)
with either ferrous or oxyferrous [Fe(III)-
O
2
•
)
] P450, as given in Eqns 1 and 2 [129–132]. That Fe(III)-
OOH generated in this way would only serve as a precursor
in the transformation to:
FeðIIÞþOÆ
2þHþ!½FeðIIIÞOOHð1Þ
½FeðIIIÞOÆ
2þOÆ
2þHþ!½FeðIIIÞOOHþO2
ð2Þ
iron-oxene as the actual catalyst could be discounted
on kinetic grounds. As an example, the reaction
sequence given in Eqn 2 follows second-order kinetics
with a rate constant of 4 ·10
3
M
)1
Æs
)1
[133], while
injection into Fe(II)-O
2
of the ÔsecondÕelectron to
produce compound I during regular catalytic cycling is
a diffusion-controlled process characterized by a rate
constant of 4 ·10
10
M
)1
Æs
)1
[134]. Comparison of these
data no doubt precludes the major portion of ferryl
material required for efficient substrate turnover to
originate from the dismutation-type bypass reaction. As
Fe3+
O
SCys
OH
Fe3+
O
SCys
O
H
Fe3+
O
SCys
OH
H
Fe3+
O
SCys
OH
H
H
ABC
Scheme 3. Potential Ôsecond oxidantÕspecies in P450 catalysis. Data
adapted from [108] with permission.
FEBS 2004 O-O Bond activation by cytochrome P450 (Eur. J. Biochem. 271) 4339
















