1
Chuyên đê: M ng truy n d n quangạ ề ẫ
Bài 4: IP Over WDM Integration
Mechanisms
TS. Võ Viết Minh Nhật
Khoa Du Lịch – Đại học Huế
vominhnhat@yahoo.com

2
M c tiêuụ
oBài này nhằm cung cấp cho học viên các kiến thức và kỹ năng về:
Yêu cầu về viêc tích hợp IP over WDM
Tích hợp IP over WDM dựa trên quan đi m Data Planeể
•IP Over ATM Over SDH for WDM Transmission
•IP Over ATM Directly on WDM
•IP Over SDH; Packet Over SONET
•IP Over SDL Directly Over WDM
•IP Over GbE Over WDM
Tích hợp IP over WDM dựa trên quan đi m Control Planeể
GMPLS trong việc tích hợp IP over WDM

3
N i dung trình bàyộ
4.1. Introduction
4.2. IP Over WDM—The Data Plane Perspective
4.2.1. IP Over ATM Over SDH for WDM Transmission
4.2.2. IP Over ATM Directly on WDM
4.2.3. IP Over SDH; Packet Over SONET
4.2.4. IP Over SDL Directly Over WDM
4.2.5. IP Over GbE Over WDM
4.3. Control Plane Integration
4.4. GMPLS

4
4.1. Introduction
oDifferent approaches have been proposed for the smooth, fast, and reliable
provisioning and management of Internet services over the optical layer.
oThe approaches can be categorized in three main areas:
ones using the control plane only,
ones using the management plane only, and
ones combing the management and control plane approaches.
oMost of the research efforts are trying to benefit from the control and
signaling mechanisms of the control plane approach in the optical layer,
leaving the management functions in a supportive/secondary role.
5
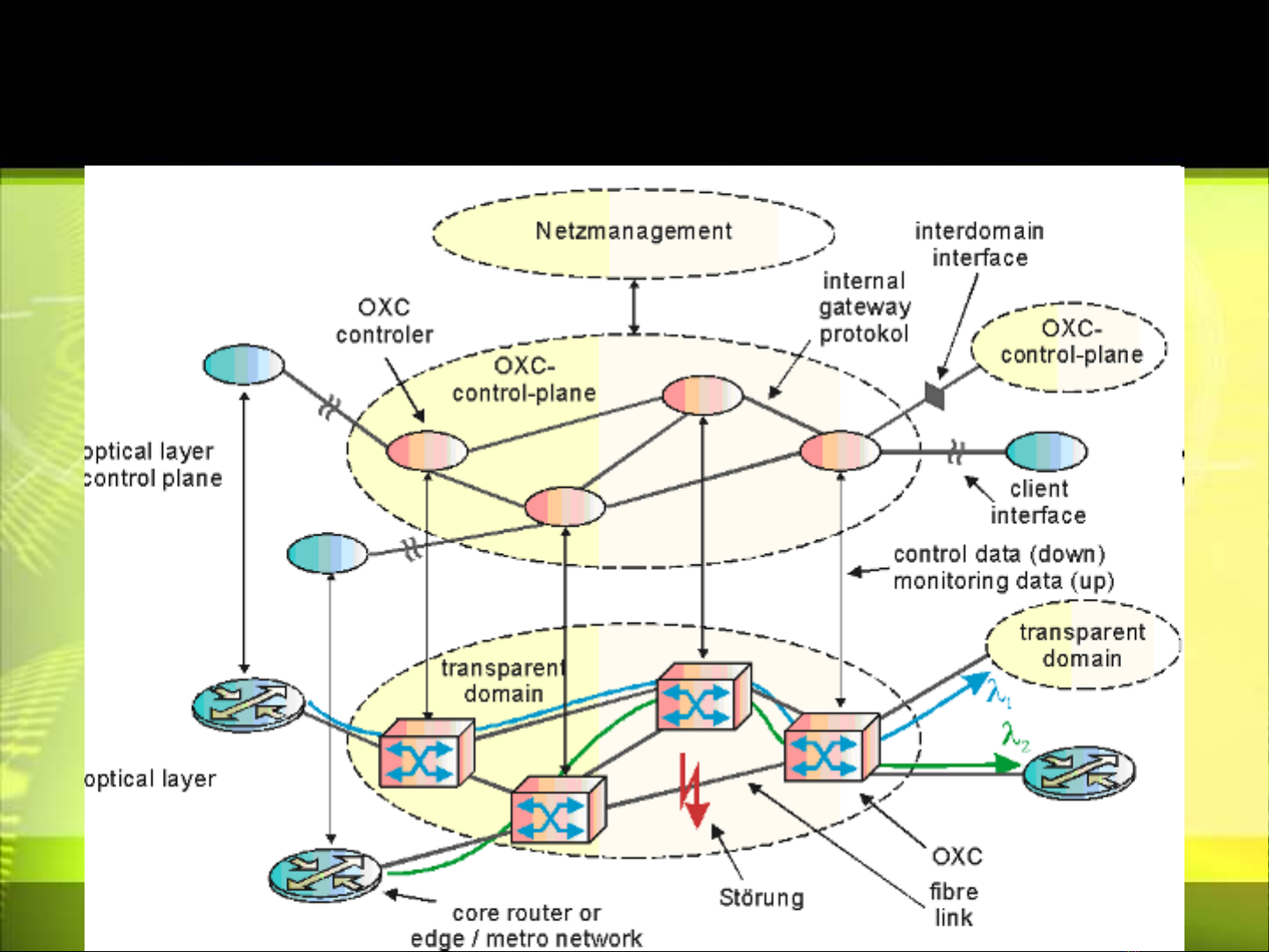
Approache of C.Plane over D.Plane









![Bài giảng Cáp mạng, vật tải truyền - GV. Lê Bá Thi [Chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2016/20160409/o0tchya0o/135x160/4531460212639.jpg)



![Trắc nghiệm Mạch điện: Tổng hợp câu hỏi và bài tập [năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251118/trungkiendt9/135x160/61371763448593.jpg)












