
Dynamic Equivalence Problem
We will use a tree to represent each set,
since each element in a tree has the same
root.
The root can be used to name the set.
There will be a collection of trees, each
tree representing one set. A collection of
trees is called a forest.

Lecture No.35
Data Structure
Dr. Sohail Aslam

Dynamic Equivalence Problem
The trees we will use are not necessarily
binary.
To perform union of two sets, we merge
the two trees by making the root of one
point to the root of the other.
A find(x) on element x is performed by
returning the root of the tree containing x.
Dynamic Equivalence Problem
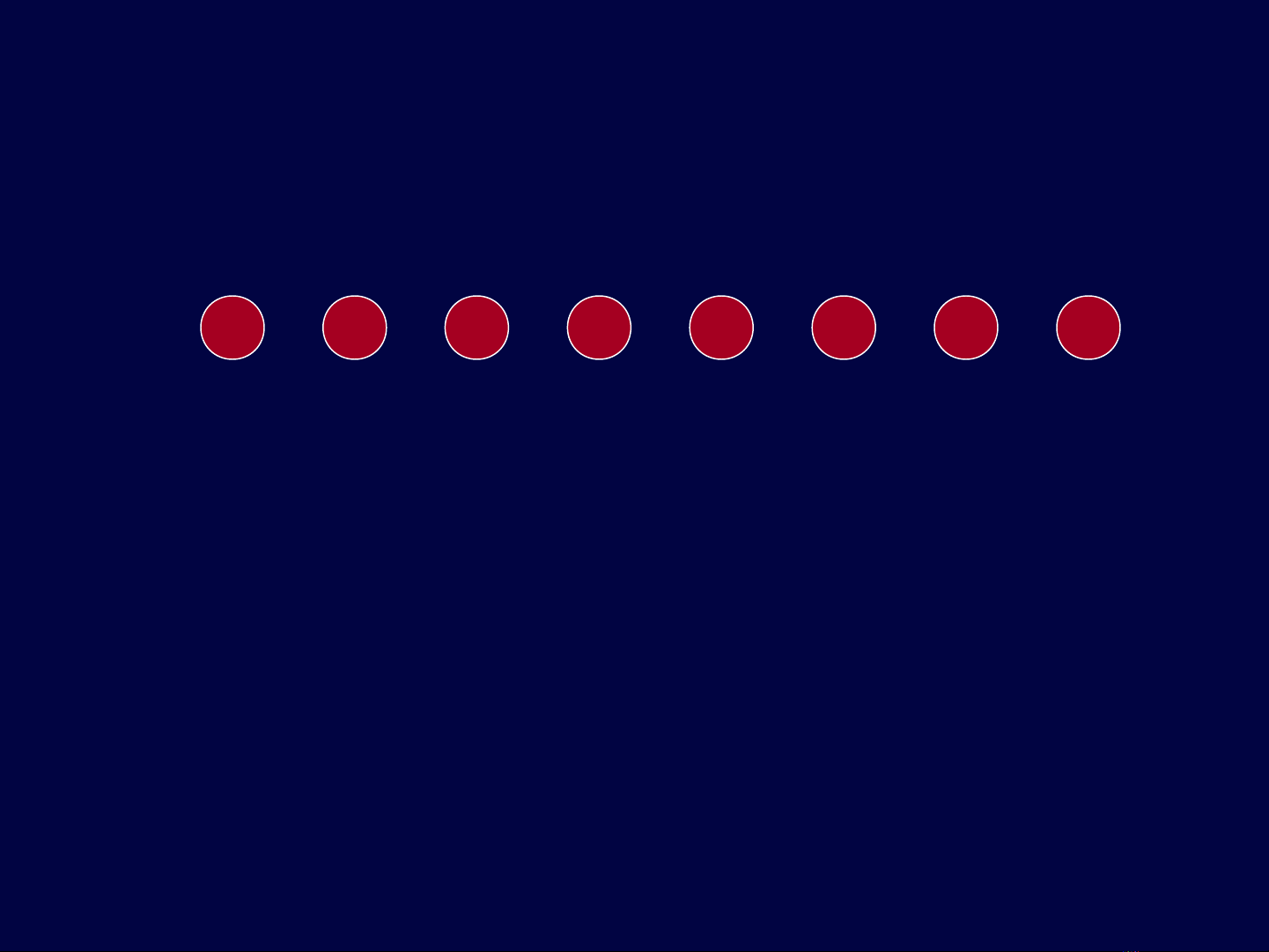
Eight elements, initially in different sets.
12345678
Dynamic Equivalence Problem
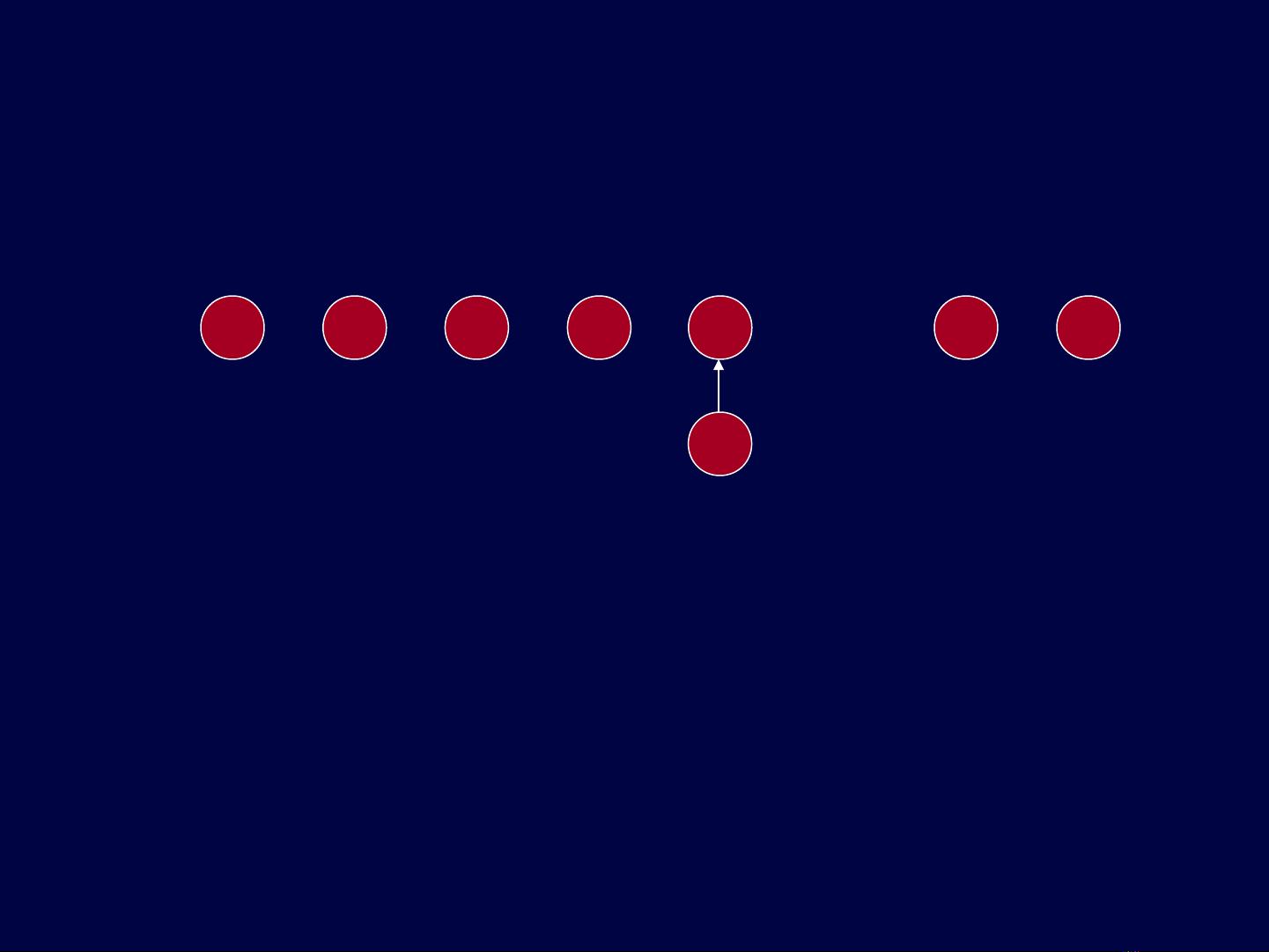
After union(5,6)
1 2 3 4 5
6
7 8



















![Bài giảng Phân tích thiết kế hệ thống [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250811/vijiraiya/135x160/642_bai-giang-phan-tich-thiet-ke-he-thong.jpg)






