Tài li u ielts – Đ Minh Quangệ ỗ
KHUNG T DUY 6 T NG CHO IELTS WRITING TASK 2 – ÁP D NG M I CH ĐƯ Ầ Ụ Ọ Ủ Ề
Tài li u này giúp b n n m v ng cách t duy ph n bi n theo mô hình 6 t ng đ x lý b t kỳ đ bài nào trong ệ ạ ắ ữ ư ả ệ ầ ể ử ấ ề
IELTS Writing Task 2. M i t ng đ u kèm theo các câu h i vàng giúp b n phát tri n ý sâu s c, m ch l c, d đ t ỗ ầ ề ỏ ạ ể ắ ạ ạ ễ ạ
band cao. Ph n cu i sẽ có m u đo n văn và bài vi t s d ng mô hình này.ầ ố ẫ ạ ế ử ụ
1. PH N 1: MÔ HÌNH T DUY 6 T NG & CÁC CÂU H I VÀNGẦ Ư Ầ Ỏ
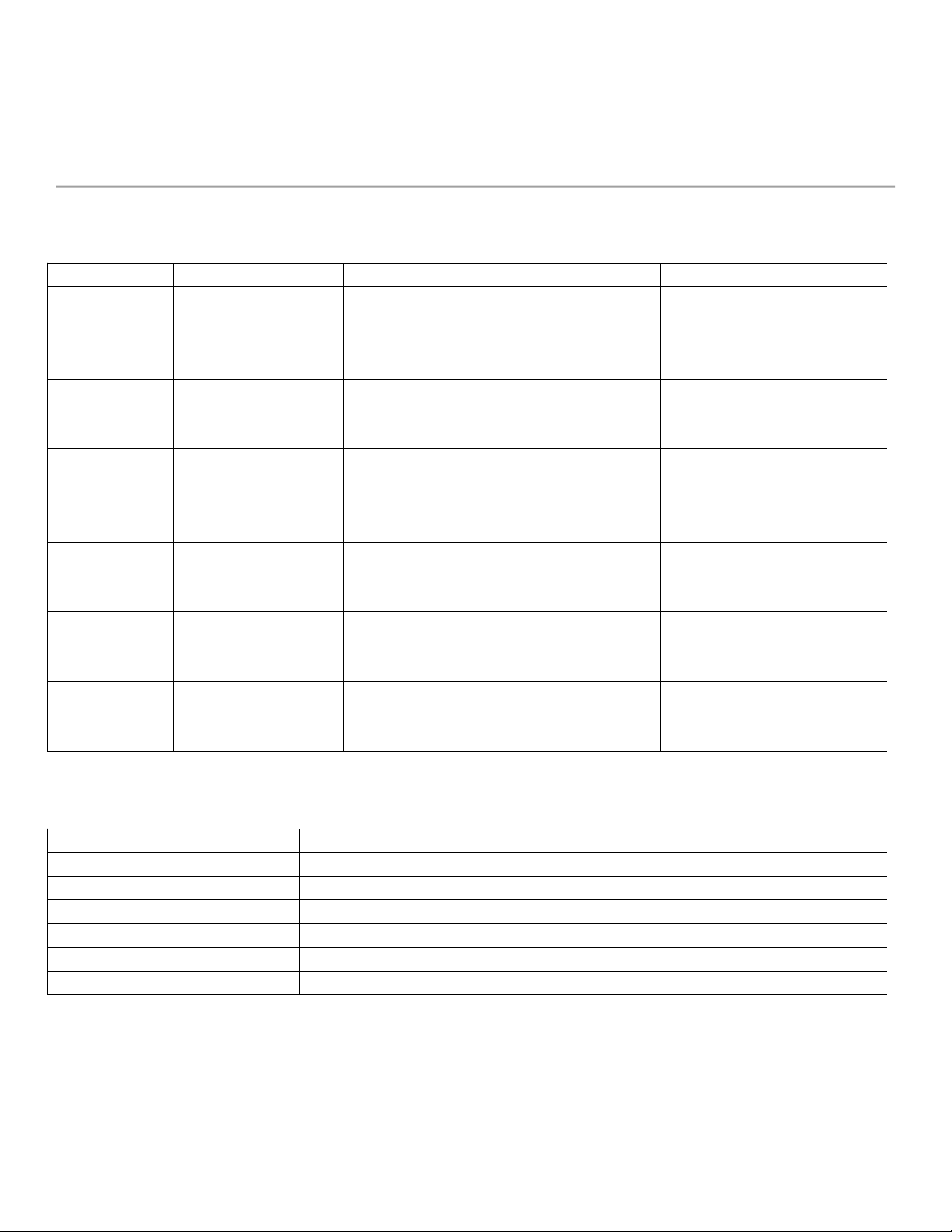
T ng t duyầ ư Ch c năng t duyứ ư Câu h i vàng đ t duyỏ ể ư Ví d ng nụ ắ
1. Hi n ệ
t ng (B ượ ề
m t)ặ
Xác đ nh rõ v n ị ấ
đ /mâu ề
thu n/hành vi ph ẫ ổ
bi nế
What is happening?What is the problem
everyone sees?What is the current
trend?
Plastic waste is increasing
rapidly.
2. Nguyên
nhân g n ầ
(Tr c ti p)ự ế
Lý do c th , hành ụ ể
vi tr c ti pự ế
Why is this happening right now?Who is
doing it and how?What action causes
this directly?
People use disposable
plastic for convenience.
3. Nguyên
nhân sâu
(G c r t ố ễ ư
duy)
Ni m tin, t duy ề ư
ho c giá tr sai l chặ ị ệ
What belief or mindset allows this to
continue?What systems or values are
behind the behavior?
A consumerist mindset
encourages convenience
over sustainability.
4. H qu ệ ả
(H u qu đa ậ ả
t ng)ầ
Tác đ ng t cá nhân ộ ừ
đ n xã h i, t ng laiế ộ ươ
So what?What are the consequences?
Who suffers and how?
This harms marine
ecosystems and threatens
food chains.
5. Gi i pháp ả
(C p hành ấ
đ ng)ộ
H ng gi i quy t ướ ả ế
kh thiả
What should be done?Who should take
responsibility?What is the first practical
step?
Governments should ban
single-use plastics.
6. Giá tr g c ị ố
(C p th gi i ấ ế ớ
quan)
Thay đ i t duy, ổ ư
nâng c p giá tr c t ấ ị ố
lõi
What core value needs to change?What
mindset should replace the old one?
We need to promote long-
term thinking and
environmental respect.
TÓM T T NHANH – B NG H C THU CẮ Ả Ọ Ộ
T ngầT khóa nhừ ớ T duyư
1 Hi n t ngệ ượ Có gì đang x y ra? ả(What?)
2 Nguyên nhân g nầVì sao l i x y ra? ạ ả (Why – surface?)
3 Nguyên nhân sâu T duy/l i s ng nào d n t i đi u đó? ư ố ố ẫ ớ ề (Why – deeper?)
4 H u quậ ả Ai b nh h ng và th nào? ị ả ưở ế (So what?)
5 Gi i phápảAi nên làm gì? B t đ u t đâu?ắ ầ ừ
6 Giá tr g cị ố Ni m tin/t duy nào c n thay đ i?ề ư ầ ổ
2. PH N 2: CÔNG TH C S P X P Ý T NG VÀ VI T BÀI LU NẦ Ứ Ắ Ế ƯỞ Ế Ậ
a) C u trúc bài lu n tiêu chu n:ấ ậ ẩ
M bài (Introduction)ở
oGi i thi u ch đớ ệ ủ ề
oDi n đ t l i đ bàiễ ạ ạ ề
1

Tài li u ielts – Đ Minh Quangệ ỗ
oNêu rõ quan đi m (n u d ng opinion)ể ế ạ
Thân bài 1 (Body Paragraph 1): Lu n đi m chính 1 (theo 6 t ng)ậ ể ầ
Thân bài 2 (Body Paragraph 2): Lu n đi m chính 2 (theo 6 t ng)ậ ể ầ
K t bài (Conclusion)ế: Tóm l c và nh n m nh l i quan đi mượ ấ ạ ạ ể
b) Công th c đo n văn Body: ứ ạ [Topic Sentence] → [Gi i thích] → [Ví d ] → [K t n i & m r ng]ả ụ ế ố ở ộ
c) G i ý câu chuy n m ch:ợ ể ạ
M đ u ý chínhở ầ : Firstly / To begin with / One major reason is that…
Gi i thích sâuả: This means that / In other words / This is due to…
Đ a ví dư ụ: For example / For instance / A case in point is…
M r ng và k t lu n đo nở ộ ế ậ ạ : As a result / Consequently / Therefore / This highlights that…
3. PH N 3: VÍ D PHÂN TÍCH KHUNG T DUYẦ Ụ Ư
- Đ bài:ề
Some people think that the best way to reduce crime is to give longer prison sentences. Others, however,
believe there are better ways to reduce crime. Discuss both views and give your opinion.
- Phân tích b ng 6 t ng – Ý 1: Tăng án tùằ ầ
1. Hi n t ngệ ượ : Crime rates remain high in many cities.
2. Nguyên nhân g nầ: Criminals often reoffend after release.
3. Nguyên nhân sâu: Lack of fear of short sentences; belief that jail is not a real deterrent.
4. H u quậ ả: Victims suffer; society feels unsafe; jails overcrowded.
5. Gi i phápả: Harsher sentences might deter some crimes.
6. Giá tr g cị ố : T duy “tr ng ph t là cách duy nh t đ răn đe”.ư ừ ạ ấ ể
- Phân tích b ng 6 t ng – Ý 2: H ng giáo d c/phòng ng aằ ầ ướ ụ ừ
1. Hi n t ngệ ượ : Young offenders involved in petty crime.
2. Nguyên nhân g nầ: Lack of education, poverty, peer pressure.
3. Nguyên nhân sâu: T duy thi u c h i, h th ng xã h i b t công.ư ế ơ ộ ệ ố ộ ấ
4. H u quậ ả: Tái ph m cao, gánh n ng xã h i.ạ ặ ộ
5. Gi i phápả: Đ u t giáo d c, đào t o kỹ năng, ph c h i c ng đ ng.ầ ư ụ ạ ụ ồ ộ ồ
6. Giá tr g cị ố : Tin vào c h i th hai và phòng ng a h n tr ng ph t.ơ ộ ứ ừ ơ ừ ạ
4. PH N 4: M U ĐO N VĂN & BÀI VI T HOÀN CH NH ÁP D NG 6 T NGẦ Ẫ Ạ Ế Ỉ Ụ Ầ
- M u đo n văn (Band 7.0+)ẫ ạ
Topic Sentence: One major reason why crime persists is that short prison sentences fail to deter offenders.
Gi i thíchả: This means that when criminals are given lenient punishments, they do not fear the
consequences of reoffending.
Ví dụ: For instance, many petty thieves in urban areas are arrested and released within weeks, only to
return to criminal behavior shortly after.
M r ngở ộ : Consequently, society suffers repeated offenses, and prisons become overcrowded without
resolving the core issue.
- M u bài lu n hoàn ch nh (Band 7.0–7.5)ẫ ậ ỉ
2

Tài li u ielts – Đ Minh Quangệ ỗ
Introduction: Crime remains a serious concern in many societies today. While some believe that increasing prison
sentences is the most effective way to curb crime, others argue for alternative approaches. This essay will discuss
both perspectives and explain why I believe that education and rehabilitation offer more sustainable results.
Body 1 – Longer prison sentences: One reason people support harsher punishments is that they believe fear of
long-term imprisonment can deter crime. Short sentences may be perceived as insignificant by repeat offenders.
For example, a thief who knows they will only serve a short term might not think twice before reoffending. As a
result, victims feel unprotected, and the justice system appears ineffective. However, relying solely on punishment
overlooks deeper social issues.
Body 2 – Alternative methods: Conversely, many experts advocate preventive methods such as education, job
training, and social support. Young people, especially from disadvantaged backgrounds, often turn to crime due to
lack of opportunities. Addressing these root causes helps break the cycle of criminal behavior. For instance, youth
programs in Norway have significantly reduced juvenile crime rates. Such approaches focus on long-term
transformation rather than short-term control.
Conclusion: In conclusion, while longer prison sentences might offer temporary relief, they fail to address the
underlying factors that lead to crime. Investing in education and preventive strategies is a more humane and
effective solution in the long run.
5. PH N 5: BÍ KÍP COHESION & COHERENCE + NG PHÁP HAYẦ Ữ
Linking words theo t ng b c:ừ ướ
Gi i thi u lu n đi mớ ệ ậ ể : Firstly / It is often argued that / One view is that
Chuy n ý/đ i l pể ố ậ : On the other hand / However / By contrast
Gi i thích thêmả: This shows that / In fact / This implies that
K t lu n đo n/bàiế ậ ạ : Therefore / In conclusion / For these reasons
C u trúc ng pháp nâng cao:ấ ữ
Câu đi u ki nề ệ : If young people are educated properly, they are less likely to commit crimes.
M nh đ quan hệ ề ệ: Those who lack support are more vulnerable to criminal influence.
Rút g n m nh đọ ệ ề: Given limited education, many youths fall into crime.
Câu b đ ngị ộ : Opportunities should be created for at-risk communities.
6. PH N 6: M O T DUY VÀ X LÝ M I D NG ĐẦ Ẹ Ư Ử Ọ Ạ Ề
- M o m r ng ý t ng:ẹ ở ộ ưở
Luôn t h i: “T i sao?”, “Ai h ng l i/h i?”, “Ni m tin nào đ ng sau?”ự ỏ ạ ưở ợ ạ ề ứ
Đ t mình vào vai ng i khác: n n nhân, chính ph , doanh nghi p, h c sinh...ặ ườ ạ ủ ệ ọ
So sánh qu c gia phát tri n và đang phát tri n đ m r ng t m nhìnố ể ể ể ở ộ ầ
- X lý các d ng đ :ử ạ ề
Opinion (Agree/Disagree): Dùng 2 thân bài theo 2 lu n đi m ng h quan đi mậ ể ủ ộ ể
Discuss both views: Phân tích đ u 2 bên + nêu rõ quan đi mề ể
Problem & Solution: Dùng t ng 1–4 cho ph n “Problem”, t ng 5–6 cho ph n “Solution”ầ ầ ầ ầ
3

Tài li u ielts – Đ Minh Quangệ ỗ
Advantages/Disadvantages: M i thân bài t p trung vào m t khía c nh t t/x u, nh ng v n đào sâu theo ỗ ậ ộ ạ ố ấ ư ẫ
t ng t duyầ ư
4













![Tài liệu luyện thi TOEIC cấp tốc trong 10 ngày [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251029/kimphuong1001/135x160/99661761725822.jpg)
![Tài liệu Phá đảo TOEIC 900+ từ mất gốc trong 30 ngày [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251029/kimphuong1001/135x160/2101761720956.jpg)











