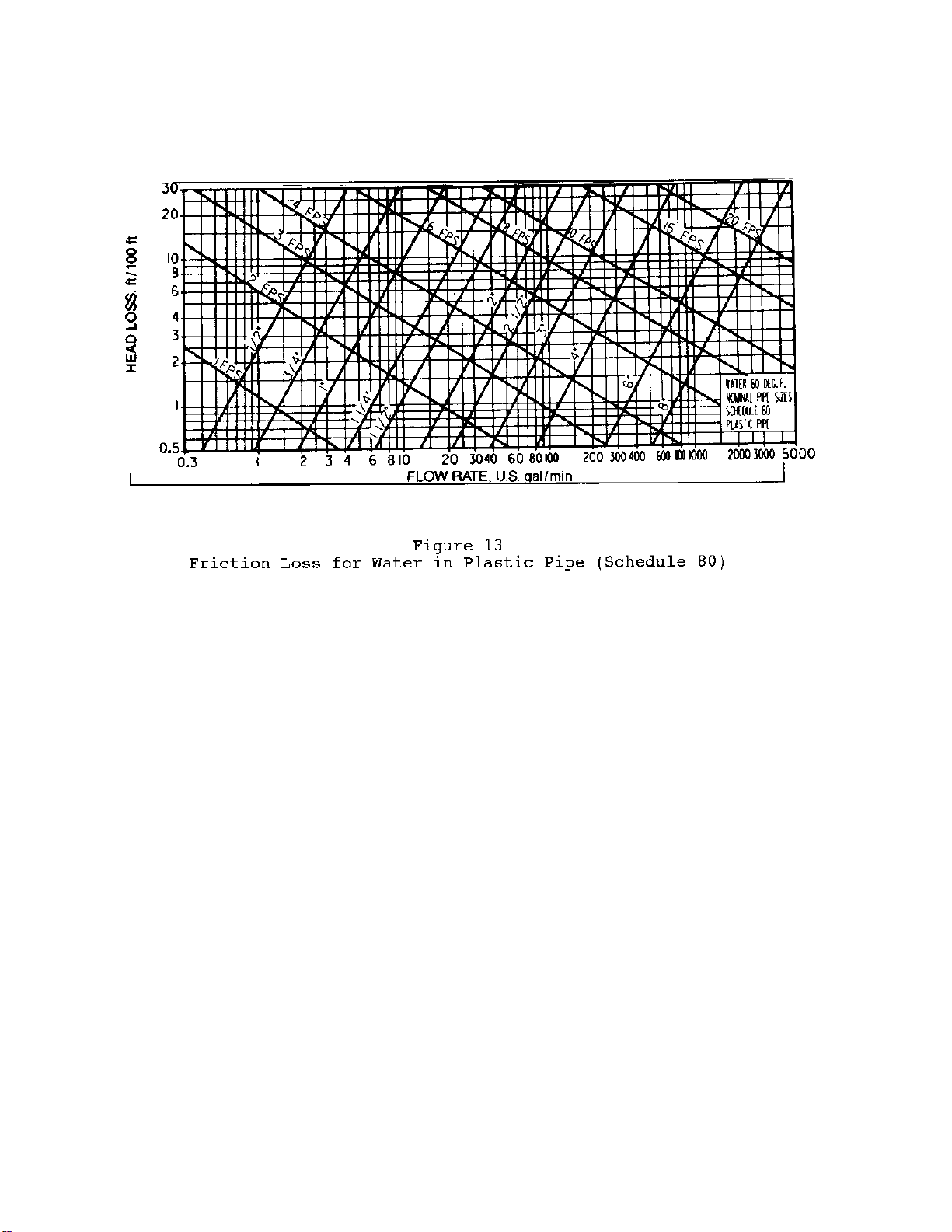
MIL-HDBK-1003/3
Reprinted by permission of ASHRAE, from ASHRAE Handbook, Fundamentals.
a) Hot Water Piping to Coil. Water coils will not perform if there
is air in the piping. Ensure that the piping from the main, to the coil, and
to the return main is appropriately sloped up and vented to eliminate
entrained air that can air lock the flow.
b) Hot Water Coil Selection. Consult the manufacturer's catalog
data to decide the best selection, number of rows, parallel or counter flow,
turbulators or serpentines, and other selection information. Using the
appropriate type, make the coil selection:
(1) Capacity required
(2) Water temperature in and out
(3) Air temperature in and out
(4) Airflow
(5) Water flow
(6) Air pressure drop
72
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://www.simpopdf.com

MIL-HDBK-1003/3
(7) Water pressure drop
(8) Coil face velocity
(9) Any special requirements
After the coil selection has been made and documented
in the design analysis, be sure to provide the above data in the
coil schedule on drawings. This will ensure a good bidding
climate, with equipment manufacturers knowing what to bid, and
what to submit in the shop drawings phase.
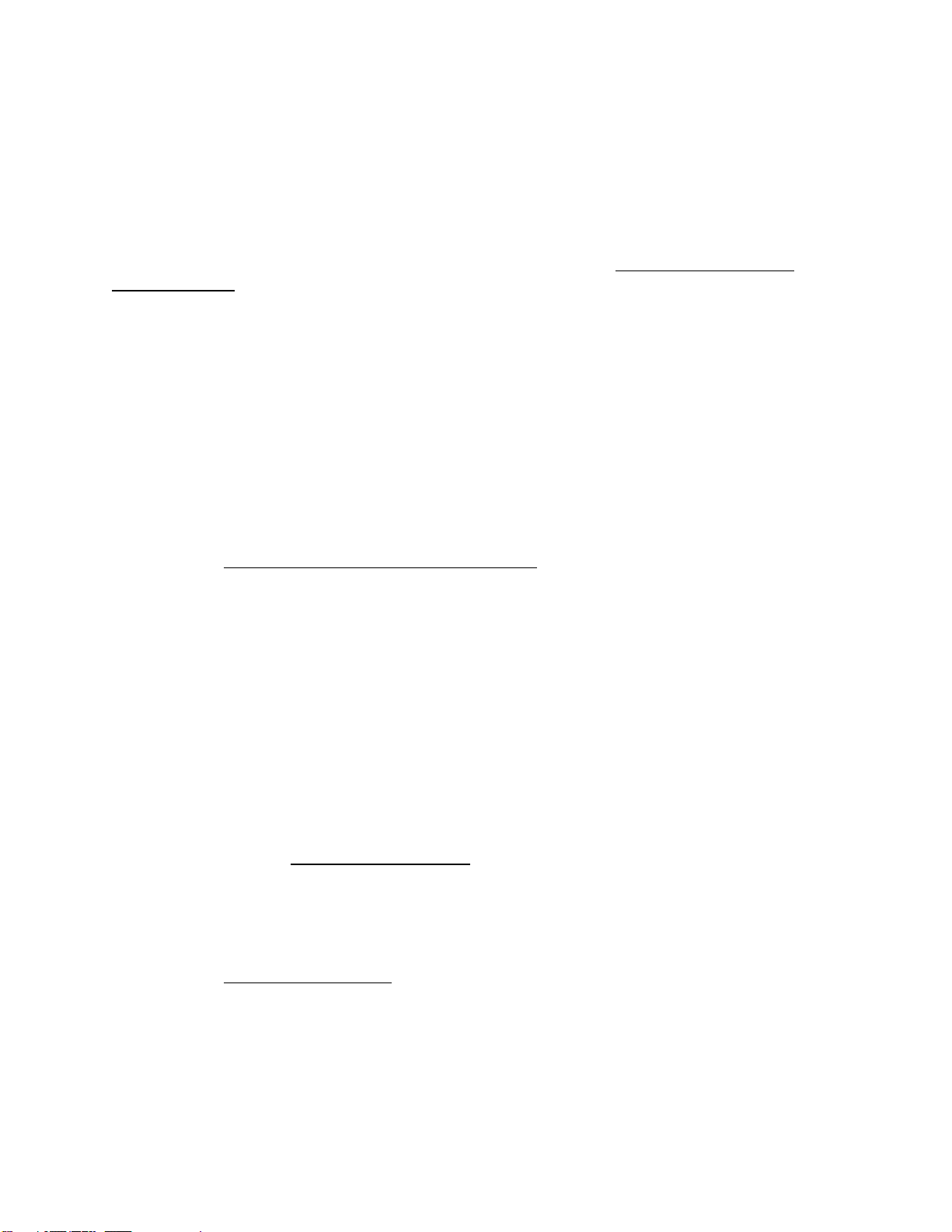
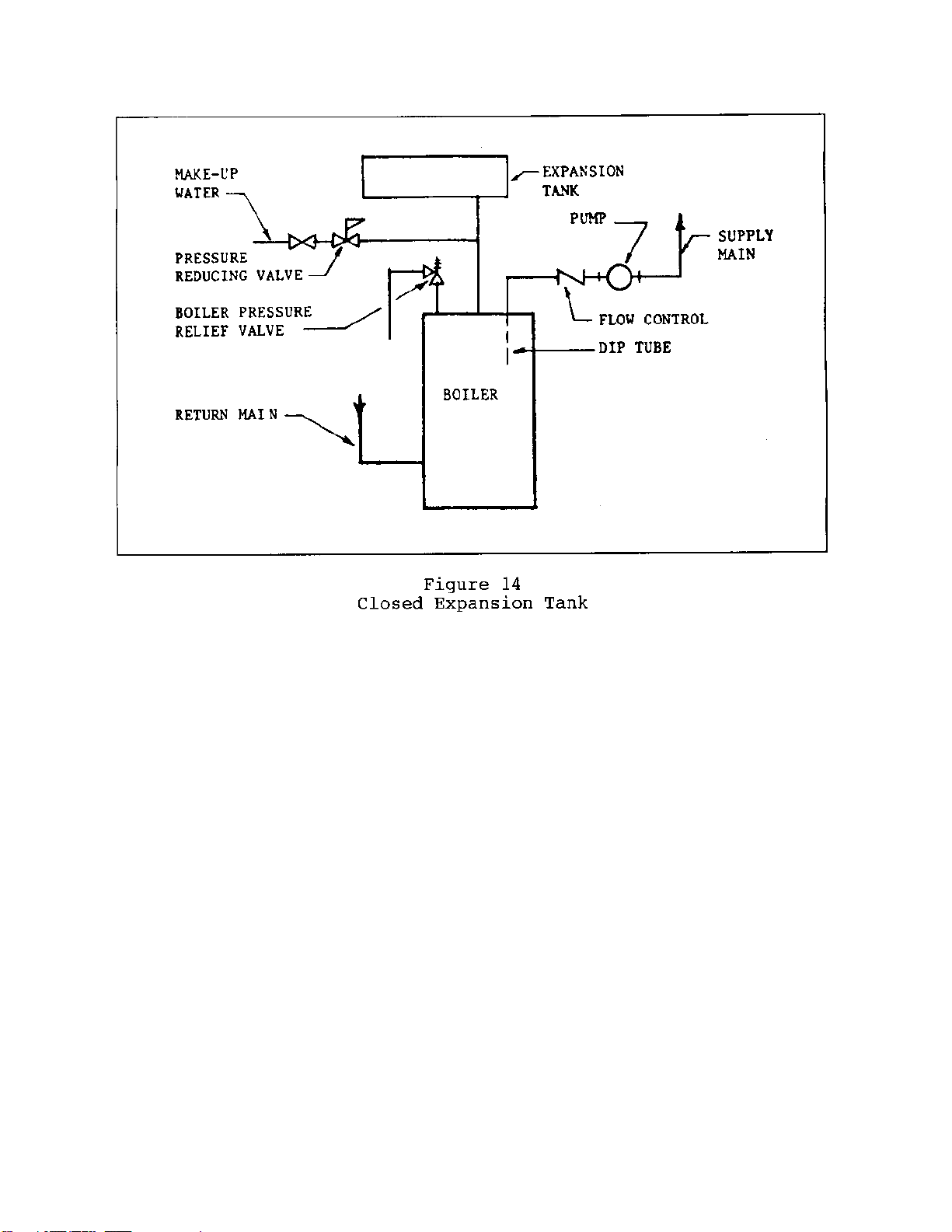
7.2.2.3 Expansion Tanks and Air Separator
a) Expansion Tanks General. When water in a hot water
heating system is heated, water expands and occupies more volume.
System pressure control is needed to:
(1) Limit pressure in all parts of the system to
the allowable working pressure.
(2) Maintain minimum pressure in the system to
prevent pump cavitation and to prevent boiling of system water.
(3) Minimize addition of makeup water.
b) Expansion Tank With Air Separator. An expansion
tank with an air separator performs these system pressure control
functions. Since this section does not address medium
temperature hot water system (250 to 350 degrees F) or high
temperature hot water system (above 350 degrees F); discussion
will be limited to the following types of tanks:
(1) Closed expansion tanks with an air cushion.
See Figure 14.
(2) Diaphragm (or bladder) type closed expansion
tanks. See Figure 15.
Open expansion tanks located at the system high point
will also work on low temperature hot water systems, but are not
generally used on Navy building projects.
c) Expansion Tanks. Some specifics regarding
expansion tanks are as follows:
(1) Expansion tanks are required on chilled water
and hot water systems.
73
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://www.simpopdf.com
MIL-HDBK-1003/3
(2) Locate the tank on the suction side of the
system pump so that system pressure is always positive with
respect to atmospheric pressure.
(3) Do not install a shutoff valve between the
heat source and the expansion tank.
(4) Refer to ASHRAE Handbook, HVAC Systems and
Application or manufacturer's literature for tank sizing.
(5) See Figure 14 for closed expansion tank
placement.
(6) See Figure 15 for diaphragm expansion tank
placement.
(7) Do not use a gage glass on the expansion tank.
A gage glass on a steam boiler is permitted since the wet steam
vapor keeps the upper glass packing tight. With an expansion
tank, the air will dry out the upper gage glass packing and cause
air leaks.
7.2.2.4 Domestic Hot Water Generator. An interface occurs
between the heating system and the plumbing system when boiler
steam or boiler hot water is used to heat water for plumbing
fixtures. Some points to consider in heating domestic hot water
are as follows:
a) Domestic water can be heated by the boiler (steam
or hot water) or a separate hot water generator, if the heating
source is available during the summer. If heated by the space
heating boiler, evaluate boiler efficiency for summer operation.
b) If the space heating boiler provides hot water,
evaluate if it should be an instantaneous heater, a semi-
instantaneous heater, or a storage type hot water generator. The
selection will affect the boiler capacity specified. Refer to
NAVFAC DM-3.01, Plumbing Systems for domestic hot water system
design.
With these decisions made, select the hot water system
and equipment. See Figure 16 and Figure 17.
7.2.2.5 Heat Exchangers. Heat exchangers are used for steam to
heat water. One medium flows through the shell, and the other
medium flows through the tubes in the tube bundle. Include the
following in the equipment schedule:
a) Water flow
74
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://www.simpopdf.com
MIL-HDBK-1003/3
75
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://www.simpopdf.com
MIL-HDBK-1003/3
76
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://www.simpopdf.com

![Hệ thống HVAC và Dehumidifying: Tổng quan [Năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_14_8134.jpg)
![Hệ thống HVAC và Dehumidifying: Tổng quan [Năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_13_3651.jpg)
![Hệ thống HVAC và Dehumidifying: [Thêm từ mô tả/định tính để tăng CTR]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_12_8041.jpg)
![Hệ thống HVAC và Dehumidifying: [Thông tin chi tiết/Hướng dẫn/Lựa chọn]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_11_4149.jpg)
![Hệ thống HVAC và hệ thống hút ẩm: [Thông tin chi tiết/Hướng dẫn/Lựa chọn tốt nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_10_7992.jpg)
![HVAC và Hệ thống Hút Ẩm: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_9_3668.jpg)

![HVAC và Dehumidifying Systems: Hệ thống điều hòa không khí và hút ẩm [chuẩn SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_7_2859.jpg)
![Hệ thống HVAC và Dehumidifying: [Thông tin chi tiết/Hướng dẫn/Lựa chọn]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_5_3816.jpg)
![HVAC và Dehumidifying Systems: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2012/20120202/luly_meo1/135x160/hvac_and_dehumidifiying_systems_b_split_4_7836.jpg)








![Ngân hàng trắc nghiệm Kỹ thuật lạnh ứng dụng: Đề cương [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251007/kimphuong1001/135x160/25391759827353.jpg)






