TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(01): 24 - 31
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 24 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
CLONING AND DETERMINATION GENE SEQUENCES OF OUTER
MEMBRANE PROTEINS OmpK AND OmpU in Vibrio parahaemolyticus N9
Ngo Thi Huyen1, Dong Van Quyen1, Tran Ngoc Kien2, Pham Thi Tam3, Ngo Duc Manh4,
Le Thi Tuoi5, Vu Thi Bich Huyen5*
1Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, 2Vinschool The Harmony
3Hanoi Open University, 4University of Science - Vietnam National University,
5Hanoi National University of Education
ARTICLE INFO
ABSTRACT
Received:
02/8/2024
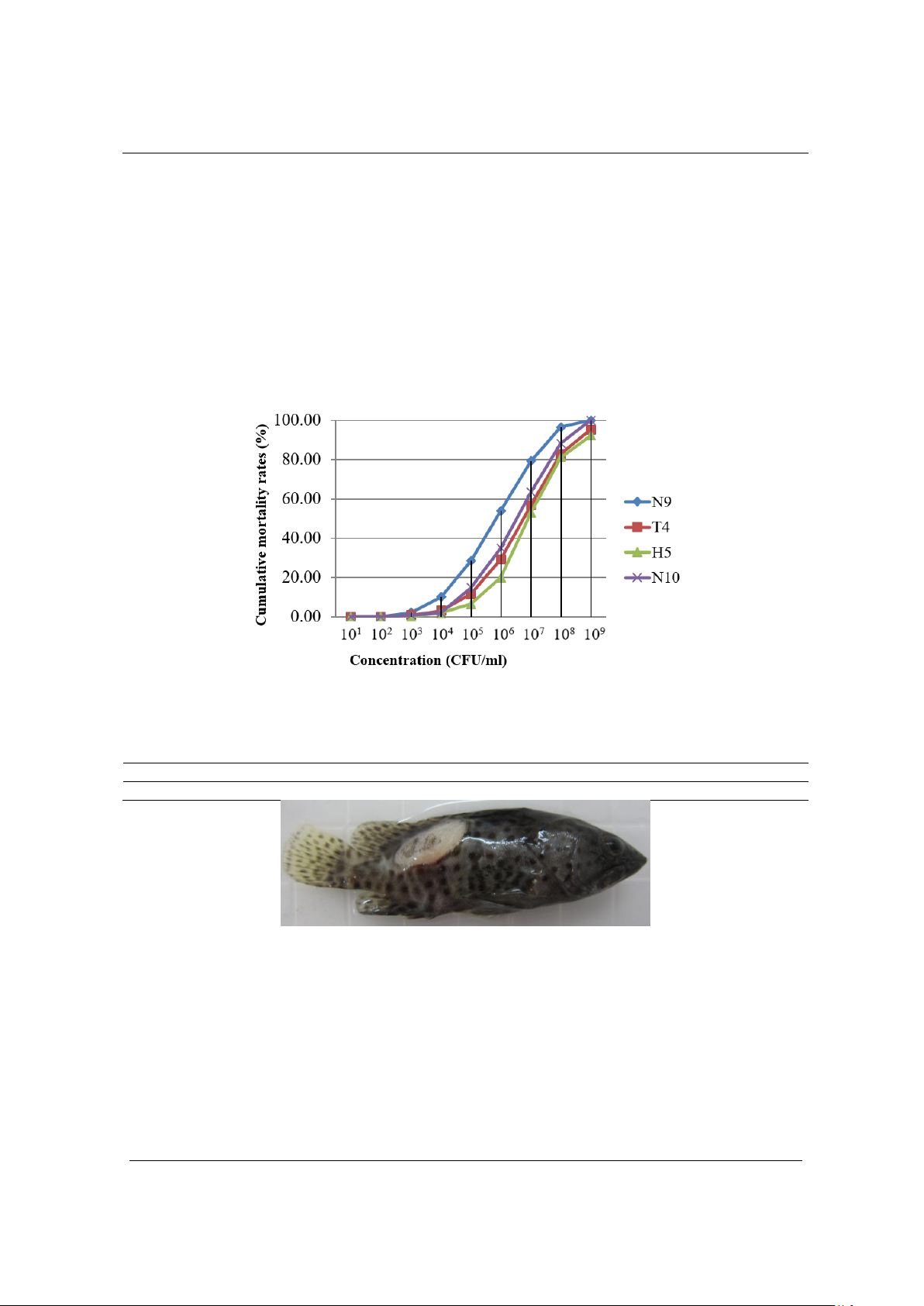
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is one of the dangerous pathogens of aquatic
animals, including fish. The outer membrane proteins play an
essential role in bacterial virulence and are potential candidates for
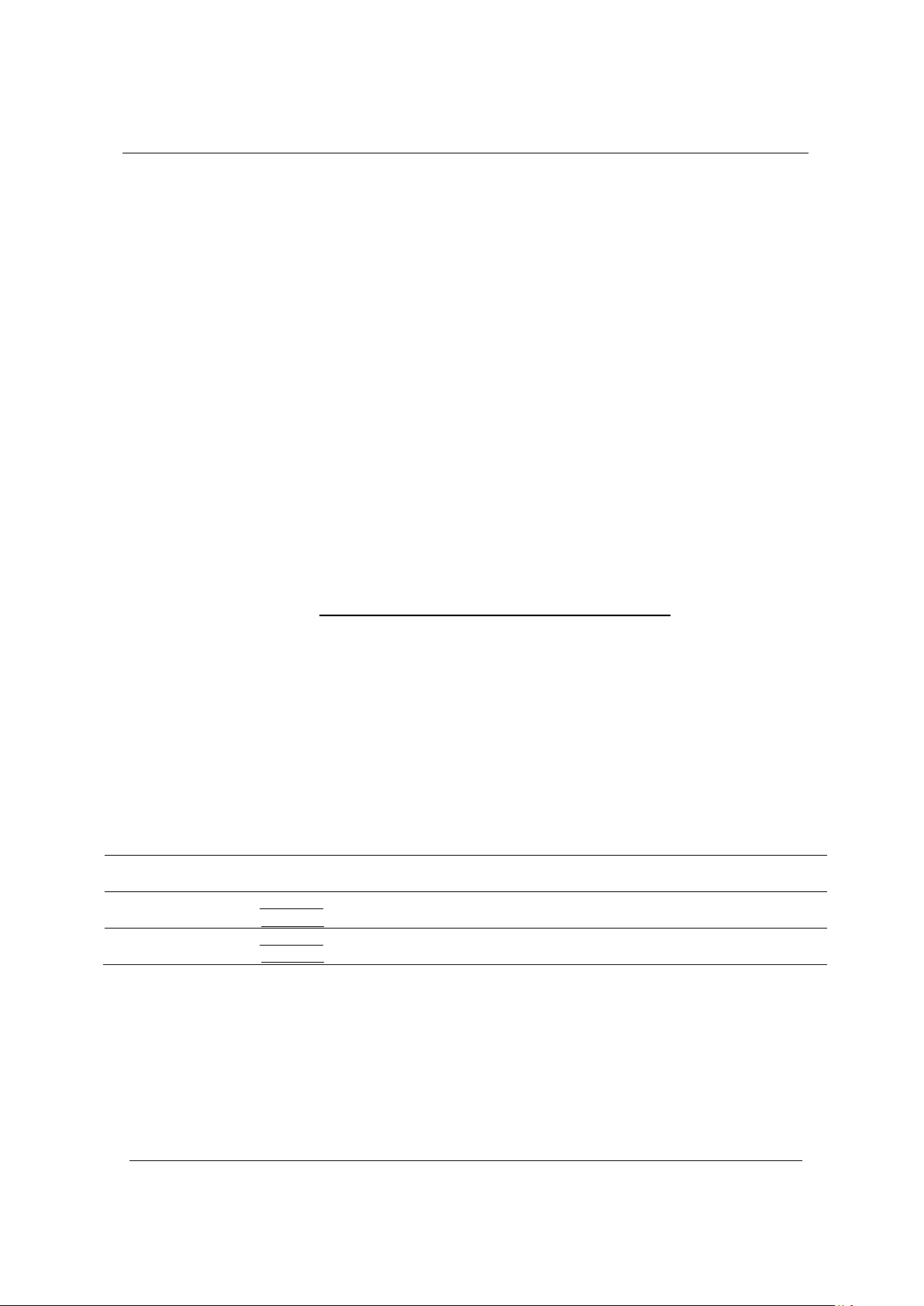
vaccine development. In this study, the virulence of four V.
parahaemolyticus strains was studied, and the result was that strain.
The V. parahaemolyticus N9 has the strongest virulence with an LD50
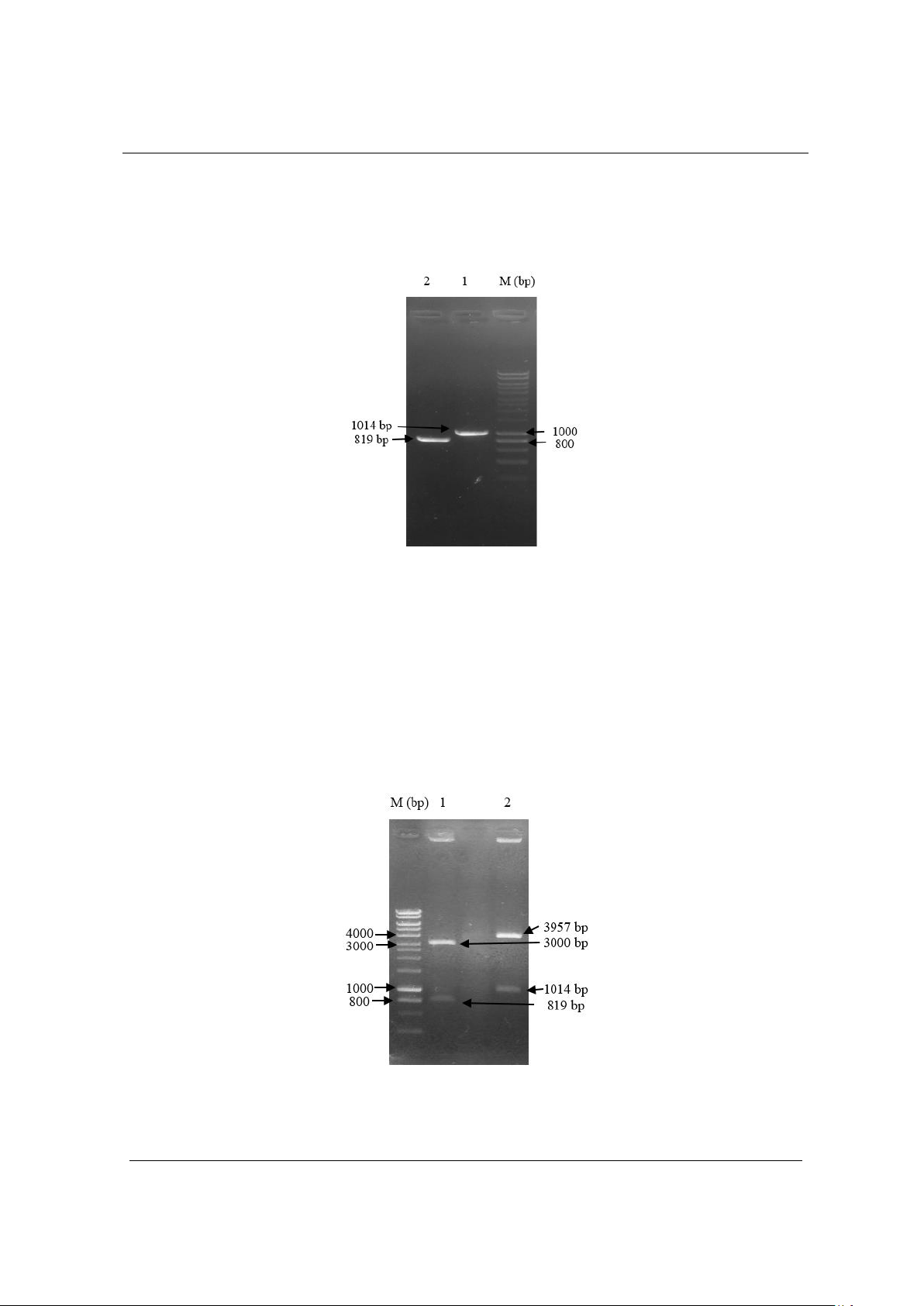
of 106.15 CFU/mL. OmpK and OmpU genes from V. parahaemolyticus
N9 strain, which are coding for two outer membrane proteins. Two
genes were determined the sequence of the open reading frame (ORF)
with sizes of 819 bp (OmpK gene) and 1014 bp (OmpU gene),
respectively. In addition, we also successfully cloned these two
antigen genes OmpK and OmpU into pGEM-T and pCE2 TA vectors,
respectively. This is the first step in studying vaccine development
against diseases caused by V. parahaemolyticus in some marine fish
species.
Revised:
16/10/2024
Published:
17/10/2024
KEYWORDS
OmpK
OmpU
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Cloning
Antigen
TÁCH DÒNG VÀ XÁC ĐỊNH VÙNG TRÌNH TỰ GENE KHÁNG NGUYÊN
MÃ HÓA PROTEIN MÀNG NGOÀI CỦA Vibrio parahaemolyticus N9
Ngô Thị Huyền1, Đồng Văn Quyền1, Trần Ngọc Kiên2, Phạm Thị Tâm3, Ngô Đức Mạnh4,
Lê Thị Tươi5, Vũ Thị Bích Huyền5*
1Viện Hàn lâm Khoa học và Công nghệ Việt Nam, 2Vinschool The Harmony,
3Trường Đại học Mở Hà Nội, 4Trường Đại học khoa học tự nhiên - ĐH Quốc gia Hà Nội,
5Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội
THÔNG TIN BÀI BÁO
TÓM TẮT
Ngày nhận bài:
02/8/2024
Vibrio parahaemolyticus là một trong những tác nhân gây bệnh nguy
hiểm cho động vật thủy sản, trong đó có cá. Các protein màng ngoài
đóng vai trò quan trọng trong độc lực của vi khuẩn và là ứng cử viên
tiềm năng để phát triển vaccine. Trong nghiên cứu này, độc lực của
bốn chủng V. parahaemolyticus được nghiên cứu cho kết quả là
chủng V. parahaemolyticus N9 có độc lực mạnh nhất với LD50 là
106,15 CFU/ml. Gene OmpK và OmpU của chủng V.
parahaemolyticus N9 mã hóa các protein màng ngoài đã được xác
định trình tự khung đọc mở (ORF) có kích thước lần lượt là 819 bp
và 1014 bp. Ngoài ra, hai gene mã hóa kháng nguyên OmpK và
OmpU đã tách dòng thành công lần lượt trong vector pGEM-T và
pCE2 TA. Đây là bước đầu nghiên cứu phát triển vaccine phòng
bệnh do V. parahaemolyticus gây ra ở một số loài cá biển.
Ngày hoàn thiện:
16/10/2024
Ngày đăng:
17/10/2024
TỪ KHÓA
OmpK
OmpU
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Tách dòng
Kháng nguyên
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.10621
* Corresponding author. Email: huyenvtb@hnue.edu.vn