Giới thiệu tài liệu
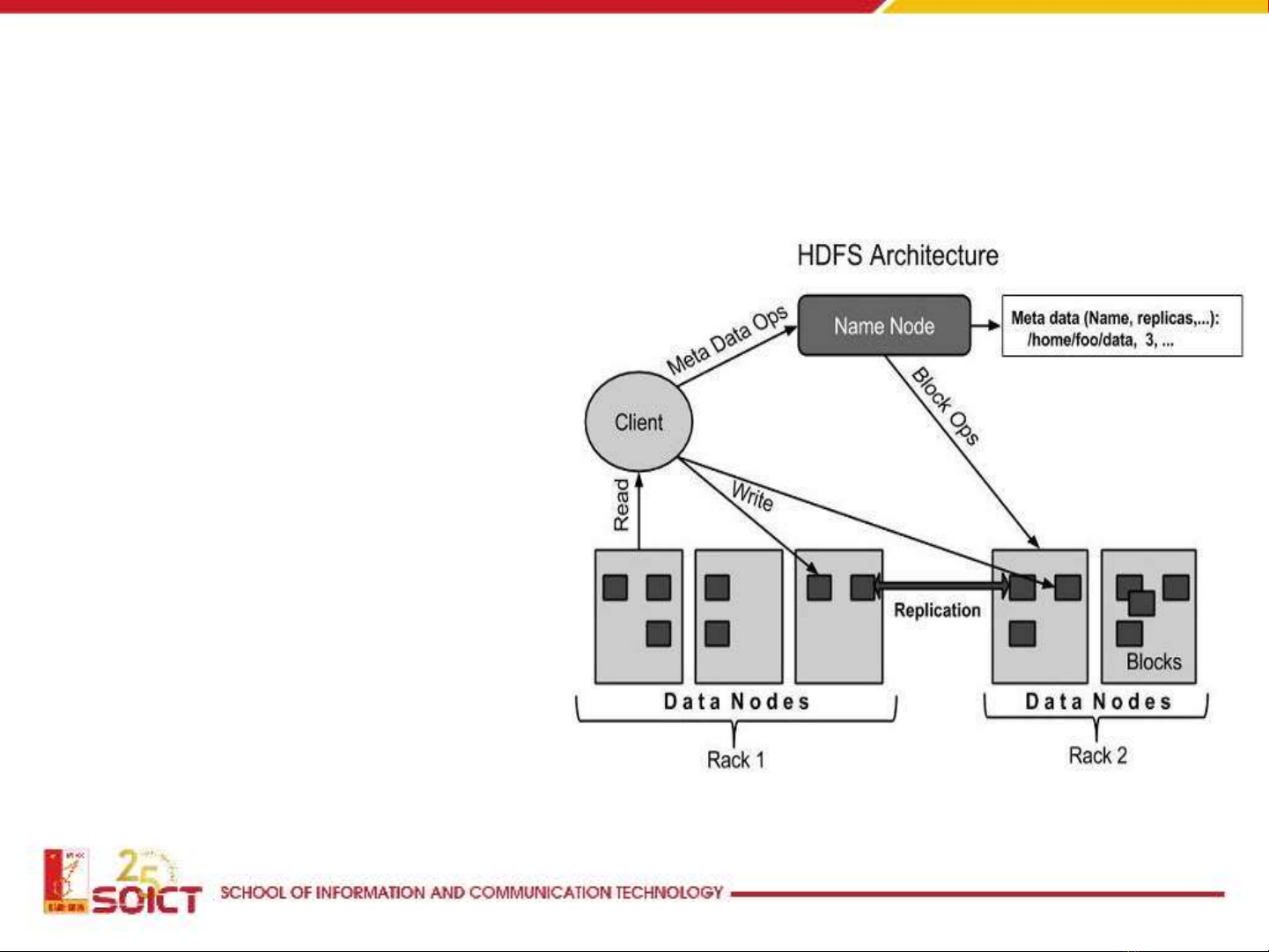
Lecture 'Administration and visualization: Chapter 2.2 - Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS)' offers students an in-depth understanding of HDFS, its main design principles, architecture, functions of a namenode, and more. This lecture covers the overview of HDFS, including its cost-effective and reliable storage for large amounts of data; designed for large files (100 MB to several TB); written once, read multiple times; runs on commercial hardware; uses UNIX-style file system; and has UNIX file and permission systems. The document provides a detailed explanation of HDFS's design principles, architecture, namenode functions, and data replication strategies.
Đối tượng sử dụng
Students, researchers, data engineers, and professionals interested in understanding the design principles, architecture, and functions of Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS)
Nội dung tóm tắt
The lecture 'Administration and visualization: Chapter 2.2 - Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS)' delves into the details of this powerful file system. It begins with an overview of HDFS, which offers cost-effective and reliable storage for large amounts of data, designed for files larger than 100 MB to several TB. The lecture explains that HDFS operates on a write-once, read-many principle and runs on commercial hardware while using a UNIX-style file system with UNIX file and permission systems. It provides a detailed explanation of the design principles of HDFS, including input/output model, data distribution model, chunking, and replication. The lecture also covers the architecture of HDFS, which consists of a master namenode and slave datanodes. The namenode manages the namespace and metadata, while datanodes store actual files (chunks). The lecture outlines the functions of a namenode, including managing the namespace, mapping file names to chunks, mapping chunks to data nodes, and configuring the cluster. Metadata stored by the namenode includes lists of files, lists of chunks for each file, lists of data nodes for each chunk, and file properties such as creation time and replication factor. Datanodes are responsible for storing data in local filesystems (e.g., ext3) and providing both data and metadata to clients. HDFS uses a data replication strategy to ensure data redundancy and reliability. Chunk placement is one such strategy, where one copy is stored on the local node, another copy is stored on a remote rack, and a third copy is stored on the same remote rack. The lecture concludes with an explanation of how HDFS can balance disk space and network traffic through data replication.