
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 782 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET)
Volume 10, Issue 03, March 2019, pp. 782-792. Article ID: IJMET_10_03_082
Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?JType=IJMET&VType=10&IType=3
ISSN Print: 0976-6340 and ISSN Online: 0976-6359
© IAEME Publication Scopus Indexed
INFORMATION SYSTEM OF CUSTOMER
RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT PT HASRAT
ABADI MERAUKE REGENCY
Stanly Hence Dolfi Loppies
Department of Information Systems, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Musamus, Merauke,
Indonesia
Fransiskus Xaverius Manggau
Informatics Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Musamus,
Merauke, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
Customer relationship management (CRM) is defined as a clear business strategy
and is a combination of a range of functions, skills, processes, and technologies that
together allow companies to better manage profits with customers as real assets. PT
Hasrat Abadi is the official distributor for Toyota and Yamaha vehicles in five regions
in Eastern Indonesia. However, PT Hasrat Abadi does not have software that can
manage company relationships with customers, and provide fast information to
customers for customer satisfaction and increase profits from the company. Making
this application uses the RUP (Rational Unified Process) methodology which is
gradual with upward progress and iterative (repetitive) to get the appropriate results.
Applications can help companies in making a new breakthrough to market their goods
and services by reading customer behavior through questionnaires, polling and
recording customer activity, this application can help companies to promote the latest
products to customers online so they can keep customers even new customers.
Keywords: CRM, RUP, online
Cite this Article Stanly Hence Dolfi Loppies and Fransiskus Xaverius Manggau,
Information System of Customer Relationship Management Pt Hasrat Abadi Merauke
Regency, International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 10(3),
2019, pp. 782-792.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/issues.asp?JType=IJMET&VType=10&IType=3
1. INTRODUCTION
Customer satisfaction is defined as the level of fulfillment of a number of needs, desires,
goals, or something that culminates in the pleasure of an exchange transaction between the
consumer and the company through the performance of a product used (Sunder, 2009)

Information System of Customer Relationship Management Pt Hasrat Abadi Merauke Regency
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 783 editor@iaeme.com
Customer relationship management (CRM) is defined as a clear business strategy and is a
combination of a range of functions, skills, processes, and technologies that together allow
companies to better manage profits with customers as tangible assets (Baran et al, 2008)
Marketing is defined as a function of the company and a series of processes to create,
communicate, and provide value to customers and manage customer relationships that provide
benefits to the company and interested parties (Istijanto, 2007)
PT. Abadi Hasrat belongs to the Strategic CRM component and uses service automation
contained in operational CRM. This is because business processes in Strategic CRM focus on
customers as the main target of product marketing, creating customer satisfaction and
retaining customers. While service automation in operational CRM aims to make it easier for
companies to communicate with their customers, through today's rapidly developing
technologies such as telephone and company websites stored in good database management.
(Kadir A, 2010).
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a method of software engineering by focusing on
developing models using the Unified Modeling Language (UML) with special characteristics
in particular are use-case driven for business needs (Latief, M et al. 2017).
At present, PT Hasrat Abadi Merauke Regency does not yet have software that can
facilitate and accelerate officers in serving maintenance processes, vehicle repairs, ordering
services online. Online services are considered to be able to improve the quality of service of
an agency or organization (Maulany, G.J and Loppies, S.H.D, 2018). Because the internet is a
vast collection of large and small computer networks that are interconnected using
communication (tele) networks that exist throughout the world (Darynto, 2004)
In this study, the resulting solution is a customer relationship management information
system that can record customer activity with the company through the system, so that
customer behavior and customer needs can be known to facilitate the sales and marketing
process of the company's products, and facilitate the provision of information to customers.
2. THEORETICAL BASIS
2.1. Customer Relationship Management
The definition of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) can be grouped as (Baran et al.
2008):
1. CRM is the same as a software package, process, system, or technology
2. CRM is the same as focusing on data storage and analysis
3. CRM is the same as the cultural change in the company from customer-centric
transactions (the main focus here is to have a dialogue with each customer in a one-to-one
manner so that the company knows the customer's needs to penetrate the market)
4. CRM is the same as the important concept of "managing demand"
5. CRM is the same as new customer-focused strategies today (identification, selection,
acquiring, developing, cross-selling and up-selling, managing migration and win back)
6. So if it is concluded CRM is a core business strategy that combines internal processes and
functions, external networks to create and deliver value to customers for profit. CRM is
based on quality customer data that is made possible by the existence of information
technology (Shanmugasundaram, S, 2008).
Components of CRM (Buttle, 2007) which is also a CRM architecture are divided into
three components, namely:

Stanly Hence Dolfi Loppies and Fransiskus Xaverius Manggau
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 784 editor@iaeme.com
2.2. Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating the ways a company deals with customers. CRM
software applications allow marketing, sales, and service functionality to run automatically.
Examples of operational CRM applications include:
a. Automation of marketing Automation Marketing automation (Marketing Automation-
MA) is the use of technology in marketing processes.
b. Automation of Sales-Sales Force Automation (SFA) Fleet
This system applies technology in managing various sales activities of the company.
c. Service Automation
With the support of service automation, companies can carry out service functions to
customers automatically, either through the call center or contact center they have, or through
company website facilities, or through face-to-face meetings between service officers and
consumers in the field.
2.3. Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM is used to exploit consumer and company data to increase its value. This
system is developed based on information about consumers. Customer data can be obtained
from information centers or data banks owned by each relevant company, namely sales data
(history of purchases of goods or services by customers), financial data (payment history or
credit score), marketing data (consumer responses to advertising campaigns, product loyalty
scale data), and service data. Furthermore, internal data can be supplemented with external
data, such as geodemographic data and data on consumer lifestyles provided by business
intelligence organizations. By using data mining tools, companies can interrogate the data.
2.4. Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM is focused on efforts to develop customer-centric business types. This culture
is intended to win the hearts of consumers and maintain their loyalty by creating and
providing value to customers who outperform competitors. In a customer-oriented culture, all
resources will be allocated to support all steps that can increase company value in the eyes of
customers, as well as reward systems that can enhance positive behavior of employees that
lead to customer satisfaction, as well as improving collection systems, dissemination, and
application of information about customers to support various company activities. There are
three most important business orientations, namely; products, production and sales.
2.5. Marketing
Marketing is a social and and managerial process in which there are individuals and groups to
get what they want through the process of creating, offering, and exchanging valuable
products (Hartono, et al, 2012). Marketing can also be interpreted as a function of the
company and a series of processes to create, communicate, and provide value to customers
and manage customer relationships that provide benefits to the company and interested
parties. Efficiency in carrying out the marketing concept can have an impact on the
development of the company in achieving the expected benefits (Leclercq, A, 2015).
2.6. Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is defined as the level of fulfillment of a number of needs, desires,
goals, or something that culminates in the pleasure of an exchange transaction between a

Information System of Customer Relationship Management Pt Hasrat Abadi Merauke Regency
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 785 editor@iaeme.com
consumer and a company on the performance of a product used (Mosahab, R et al, 2010;
Samudro et al., 2011; Sedayu and Mangkoedihardjo, 2018).
2.7. Dimensions of Service Quality
There are 5 (five) main dimensions of service quality (Tjiptono, 2009):
a. Reliability
Is the ability to provide services quickly and accurately that can provide satisfaction to
consumers.
b. Response
Is the ability to provide services quickly to provide problem solving.
c. Guarantee
Includes knowledge that can provide trust in service.
d. Attention
Includes understanding in service to all desirable needs
e. Physical Evidence
Includes physical facilities, employees and means of communication
2.8. Information system
Information System is a system in an organization that brings together daily transaction
processing needs that support managerial organizational operations functions with strategic
activities in producing the required reports by connecting several components of information
systems that interact with each other to reach the target. (Al Fatta. H, 2007).
2.9. Rational Unified Process (RUP)
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a software engineering method with a focus on developing
models using the Unified Modeling Language (UML) with special characteristics in particular
are use-case driven for business needs (Latief. M, 2016). The stages in the RUP method
include:
a) Inception: this stage is the stage of the preliminary study and data collection.
b) Elaboration: this stage is the stage of system design
c) Construction: this stage is the system design stage
d) Transition: this stage is the stage of testing and repairing the system from an error.
3. METHODOLOGY
3.1. Research procedure
The procedure of research conducted in making customer relationship management (CRM)
information systems is shown in Figure 1.
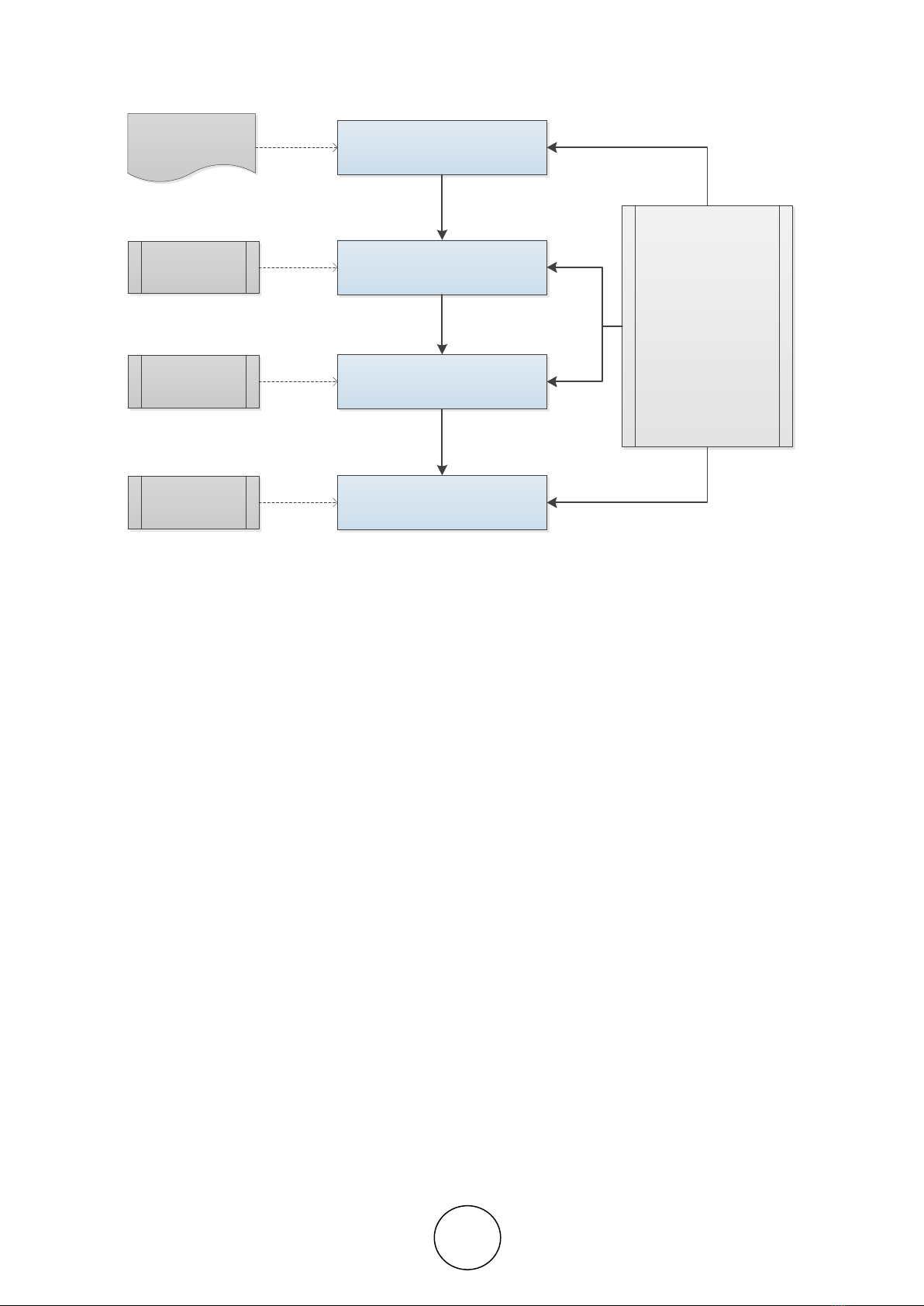
Stanly Hence Dolfi Loppies and Fransiskus Xaverius Manggau
http://www.iaeme.com/IJMET/index.asp 786 editor@iaeme.com
DATA COLLECTION
SYSTEM DESIGN
SYSTEM TESTING
SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION
1. LITERATURE STUDY
2. INTERVIEW
Rational Unified Process
1. Blackbox
2. Quistionaire
1. Coding
2. Error Fixed
1. Database Design
2. GUI Design
Figure 1. Research Procedure
3.2. System Framework
The CRM information system framework is shown through UML use-case and activity
diagram models for users (members and guests) and admin to see the business processes that
occur. use-case for the user in Figure 2 and the use case for admin in Figure 3. The user
activity diagram shown in Figure 4 and the admin activity diagram are shown in Figure 5.





![Dự án kinh doanh thương mại điện tử Shinning Together [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2018/20181014/dotuananhanh/135x160/8261539527394.jpg)




















