
Lecture 21

Recap
Script M-file
Editor/Debugger Window
Cell Mode
Chapter 3 “Built in MATLAB Function”
Using Built-in Functions
Using the HELP Feature
Window HELP Screen
Elementary Math Functions
Rounding Functions
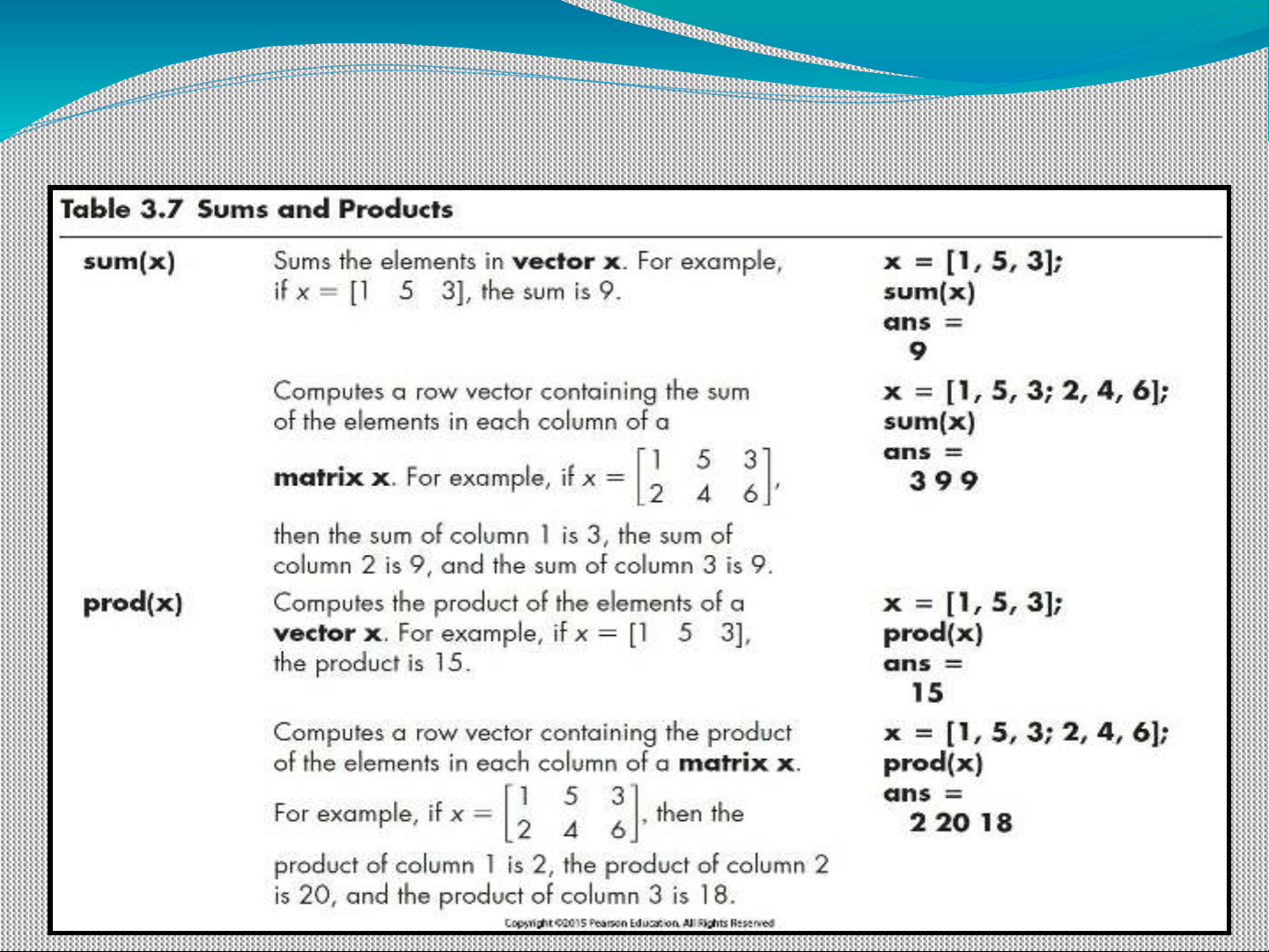
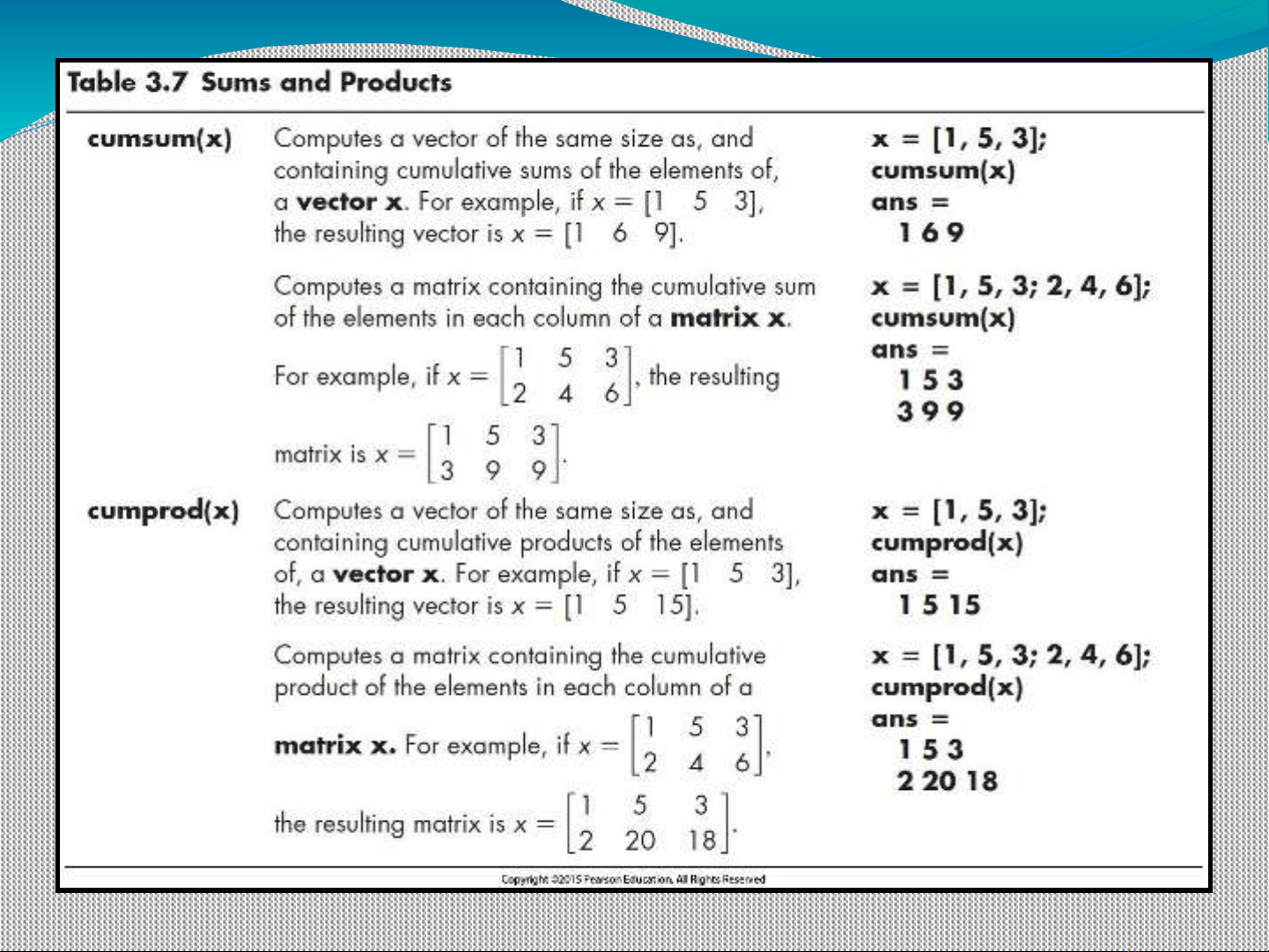
Sums and Products

Sorting Values








![[Mới nhất] Lecture note Data visualization - Chapter 28](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2020/20200723/nanhankhuoctai10/135x160/2961595506403.jpg)
![[Mới nhất] Lecture note Data visualization - Chương 27](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2020/20200723/nanhankhuoctai10/135x160/8161595506425.jpg)













![SQL: Ngôn Ngữ Truy Vấn Cấu Trúc và DDL, DML, DCL [Hướng Dẫn Chi Tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/kexauxi10/135x160/13401767990844.jpg)


