
VNU Journal of Science: Policy and Management Studies, Vol. 40, No. 3 (2024) 24-39
24
Original Article
Studying the Impact of Selected Listing on NASDAQ Stock
Exchange on Enterprise Profits: Forecasting the Case
of VinFast Manufacturing and Trading Company Limited
Tran Tu Uyen*, Hoang Thi Nhat Linh
Foreign Trade University, 91 Chua Lang, Dong Da, Hanoi, Vietnam
Received 7 June 2024
Revised 6 August 2024; Accepted 20 September 2024
Abstract: Initial Public Offering (IPO) is considered a strategic decision of utmost importance for
every business, especially companies that wish to list on the stock exchange. international. Using
the Wilcoxon non-parametric test method, the study shows that IPO activities have a positive impact
on the profits of businesses listed on the NASDAQ Global Select Market stock exchange in general
and of VinFast in particular. At the same time, the author had proposed a number of solutions to
increase the number of companies in Vietnam conducting IPOs on the international stock market as
well as policies to help increase the profits enterprises listed on the international stock market of
listed businesses.
Keywords: VinFast Company, IPO, corporate profits, NASDAQ international stock exchange.
1. Introduction*
Initial Public Offering (IPO) is one of the
most popular methods to raise capital from the
public that growing companies choose. There are
many reasons why a company wants to be listed
on stock exchanges, especially international
stock exchanges. IPOs provide cash today and
promise more money tomorrow [1]. IPO is also
an opportunity to promote the company's brand
________
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: uyentt@ftu.edu.vn
https://doi.org/10.25073/2588-1116/vnupam.4480
to more people. Listing a company on a stock
exchange can be considered a successful
marketing and public relations strategy by
increased visibility of the company in the market
through attention from the financial community
and the media. Therefore, companies can receive
a lot of free publicity, which is one of the least
expensive ways to build and strengthen a
company’s brand [2]. Furthermore, an IPO on an
international stock exchange not only positions
https://doi.org/10.25073/2588-1116/vnupam.4263

T. T. Uyen, H. T. N. Linh / VNU Journal of Science: Policy and Management Studies, Vol. 40, No. 3 (2024) 24-39
25
the corporate brand in the international market
but also enhances the position and reputation of
other businesses in the country where the
business is listed.
Rudianto pointed out that initial public
offerings change the ownership status of a
business, from a company held by a few
individuals to a public company. The author
believed that an IPO had great potential in
mobilizing capital in a relatively large amount,
which affected the performance of businesses,
including the financial performance and
financial situation of the company. The company
had also become better since then before the
IPO. In addition, the transformation from a
private company to a public company made the
decisions, strategies and activities of the
business not only affect the company itself but
also a large number of investors. Therefore, post-
IPO operating efficiency of companies is an
issue that not only businesses but also investors
are very concerned about [3].
Up to now, the impact of IPO on business
performance has always been a topic that has
attracted the attention of many authors. Typical
studies include research on the effectiveness of
IPO on initial profits and long-term operating
efficiency at issuing organizations [4-6]. A
company's performance can be assessed through
a number of financial measures such as
profitability, operating efficiency, revenue and
annual employee income. In the short term,
researchers often focus on analyzing the issue of
underpricing of stocks (IPO Underpricing),
typically in the studies of [7-9]. Meanwhile, not
only in the long term but in the short term, profit
is always one of the important factors in
evaluating company operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the performance of businesses
after an IPO is often measured by indicators such
as return on assets (ROA), return on equity
(ROE) or abnormal buy-and-retain return.
However, until now, very few scholars have
specifically researched the change in profits after
the IPO of companies, especially studies in
Vietnam. In addition, there are currently no studies
predicting profits after IPO for practical cases.
Noticed that in Vietnam recently, VinFast
Production and Trading Company Limited, one
of the subsidiaries of VinGroup Corporation
with an ownership ratio of 50.64% (According
to VinGroup's Prospectus 2023), has just
announced its listing on the international stock
exchange NASDAQ Global Select Market in
August 2023. This is a particularly important
event that not only affirms the brand value of
VinFast in the international market but also
motivates companies in Vietnam to join the
international stock market. Because up to now,
VinFast is the only company in Vietnam that has
successfully IPO'd on the NASDAQ stock
market. Therefore, research on the impact of IPO
on the profits of companies listed on
international stock exchanges in general and of
VinFast in particular is necessary.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses
2.1. Definition of Initial Public Offering
Initial Public Offering (IPO) was the first
time a private company offered common shares
on a stock exchange [10]. IPOs have often been
conducted by small-scale, or newly established
companies looking for capital to expand, but can
also be conducted by large private companies
wishing to conduct public transactions and
mobilize more capital to expand scale [11-13].
After issuing an IPO, in most cases, a company
changed from private ownership to public
ownership, and the process of issuing and offering
shares was often called "going public" [14].
Companies were divided into two main types
of businesses including private companies and
public companies. A private company has fewer
shareholders and the company's owner is not
obligated to disclose business-related
information to the outside world. Most small
businesses were privately owned (existed as
joint stock companies), and almost without
exception large companies were also privately
owned. Shares of private companies could only
be accessed through the owners and were subject
to the decisions of the company. In contrast,

T. T. Uyen, H. T. N. Linh / VNU Journal of Science: Policy and Management Studies, Vol. 40, No. 3 (2024) 24-39
26
public companies are companies that have sold
at least part of the ownership of the business to
the public and the sold shares will be traded on
stock exchanges [15].
There are many benefits for businesses after
an IPO, especially IPOs on large exchanges.
First, IPOs make it easier for companies to raise
more money in the future through secondary
offerings. Furthermore, public companies can
issue additional shares at any time the need
arises. Second, being listed on a stock exchange
makes companies more visible to the public,
thereby expanding the number of potential
customers, suppliers and employees.
Furthermore, listing on international markets
helps the company enhance its reputation and
trust from foreign investors, thereby attracting
more foreign capital from foreign individuals
and organizations. Diversifying ownership helps
businesses have large, experienced shareholders
who can contribute to the process of improving
governance quality and improving the
company's competitiveness. In addition, the
business will enhance its position and image
when listed on global stock markets. Finally,
public companies will often be more closely
monitored by the market, so these companies
will receive better interest rates when borrowing.
However, the IPO process on international
exchanges is often complicated, causing
problems for some businesses. In addition, after
the IPO, the company also faces a number of
pressures including: short-term growth pressure,
pressure to disclose information to the public,
limited company management and loss of
business. some personal advantages in business.
2.2. Profitability
Profit is one of the most important indicators
in financial analysis that shows the level of
effectiveness in cost management and revenue
growth of a business. Profit is the primary goal
of all business activities. To grow prosperously
and sustainably, a company must be profitable or
have positive profits. If it cannot make a profit,
the company will not be able to survive long
term. From an accounting perspective, some
researchers proposed using information on
financial statements to build measurement
indicators that reflect the effectiveness of profits,
for example return on assets (ROA), return on
sales (ROS), and return on equity (ROE) [16].
Return on assets (ROA) represents a
company's ability to generate profits through
effective use of economic resources and
management, and this index is used as a
dependent variable in the analysis. economic
efficiency assessment. The rate of return on
assets tends to increase, confirming the
increasingly effective use of the company's
economic resources (assets) compared to the
profits earned.
Return on sales (ROS) presents economic
efficiency from a business perspective. The
higher this index shows the more effective the
business's ability to convert net revenue into
profit. If the ROS rate increases significantly
from year to year, it proves that the company's
business activities are growing.
Return on equity (ROE) is reviewed as a
measure of a company's ability to generate net
profit per dollar of equity. This index is
considered one of the most important financial
indicators and profit measures and is applied in
financial analysis practice because it shows the
net amount of shareholders. received, thus
assisting investors in guiding strategic decisions
for the company.
2.3. Impact of IPO on Operational Efficiency
and Profits
Initial public offering (IPO) is one of the
strategic decisions in the company's
development process and is made by the owner
of the business for many different reasons. These
are benefits in terms of capital mobilization,
business promotion and a number of other
reasons. However, regardless of the reason, this
decision always has an impact on the results of
financial and accounting activities. Meanwhile,
profit is one of the most important factors
contributing to company development. The topic
related to the impacts of IPO on corporate profits
has attracted the attention of many authors.
T. T. Uyen, H. T. N. Linh / VNU Journal of Science: Policy and Management Studies, Vol. 40, No. 3 (2024) 24-39
27
Research results show that at different times in
different markets, the impact of IPO on
corporate profits is different. Table 1 states a
summary of previous studies with topics related
to the impact of IPO on corporate profits.
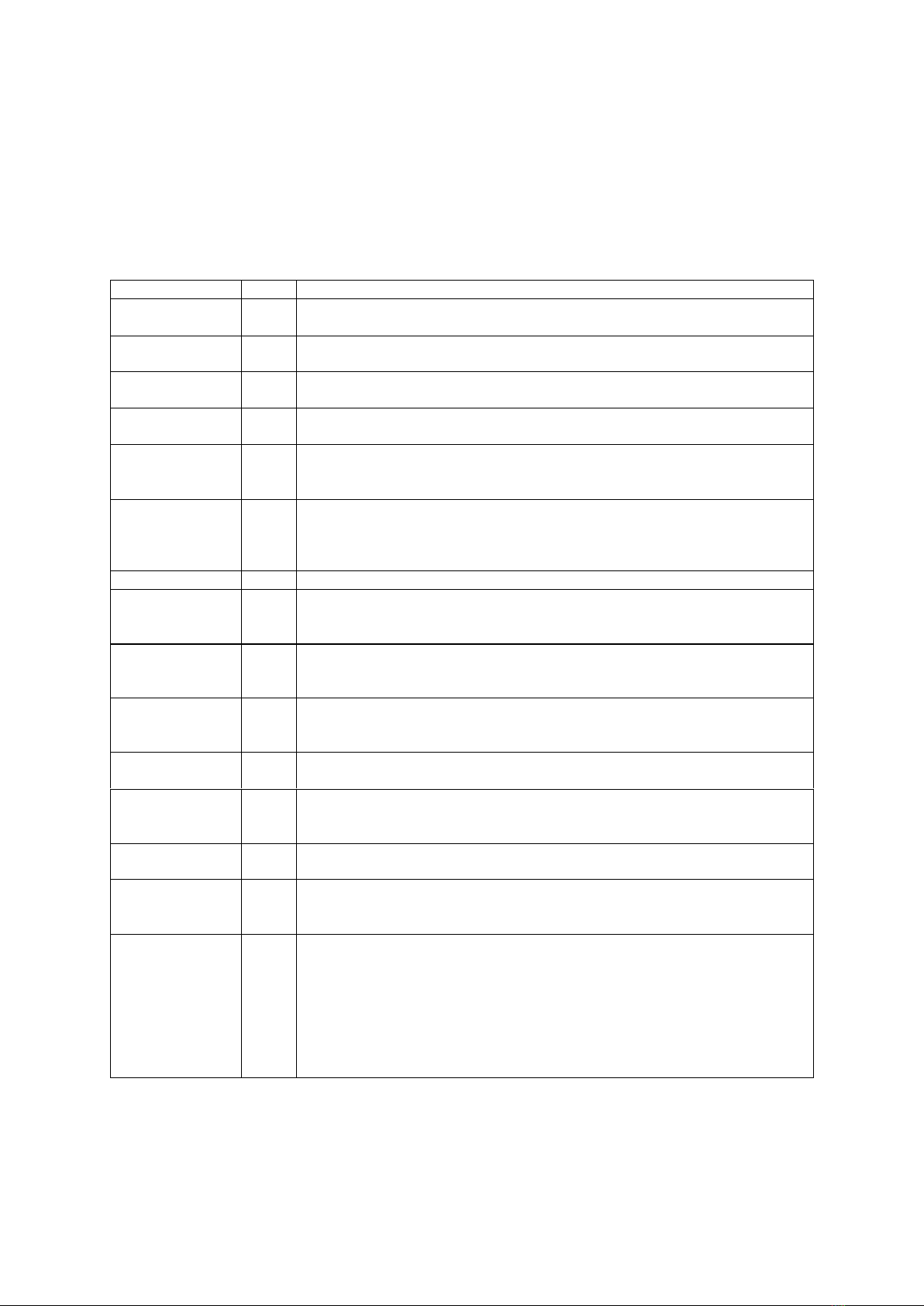
Table 1. Related Studies to the impact of IPO on corporate profits
Author
Year
Research results
Pagano et al.,
1998
Issuing shares to the public had a positive relationship with business profitability.
This positive relationship was significant across all time periods [17].
Aharony et al.,
2000
The average ROA of companies listed on Chinese stock exchanges reached its
highest level in the year of the IPO, then decreased [18].
Report by Boston
Consulting Group
2000
From the perspective of investors, after IPO, Europe's most dynamic businesses not
only increased in revenue but also rose in profit and create outstanding value [19].
Eije
2000
IPOs caused changes within the company and could contribute positively to the
company's profits [20].
Kim et al.,
2004
After the IPO, companies' operating activities were less efficient than before
entering the market. Revenue mostly increased but not enough to improve
business results after the IPO [21].
Peristani and
Hong
2004
ROA of companies participating in the US stock market was lower than the pre-
IPO period. However, the deterioration in the financial condition of companies
participating in the stock market was not a result of weaker economic conditions but
indicated that stock exchanges are facilitating companies “young” was listed [22].
Ahmad and Lim
2005
Operating performance clearly declined after the IPO in the Malaysian market [23].
Wai-yan Cheng
2005
Level Pre-listing earnings of companies did not guarantee good long-term IPO
performance, and pre-listing earnings of new issues were not an effective screen
for “poor” IPO performers [24].
Wang
2005
Through the results of analyzing more than 700 companies on the Chinese stock
market, the author concluded that there was a decline in the value of ROA of
companies after IPO [25].
Manas and Manoj
2007
Companies with large scale and high profits had a greater probability of issuing
shares to the public than for Indian companies IPOed in the period from 1999 to
2005 [26].
Ron Chuen Yeh
and Tran Tu Uyen
2009
IPO has a positive impact on the return on assets (PTBA) of listed Vietnamese
enterprises in the period 2000 – 2006 [27].
Wu et al.
2009
In general, banks in China listed on the exchange had worse results than unlisted
banks and the IPO had a significant positive impact on ROA and ROE growth at
the time before listing and during the IPO process [28].
Radosław
Pastusiak et al.,
2016
The profitability of companies one year before IPO was better than one year after
the IPO [29].
Sulaksana,
RDIZF and
Supriatna, N.
2019
There was no difference in the rate of return of companies listed on the Indonesian
market in 2014 after IPO [30].
Adiputra, A. K.,
Christmawan, P.
E. E., & Tlonaen,
A. C. A.
2023
The results of the T-test method show that there is a negative impact of ROA on
stock underpricing in companies that issue shares to the public or companies that
issue IPOs on the Indonesia Stock Exchange during the period 2010-2022. These
results show that investors always evaluate the performance of the company well
before investing and will buy shares of companies with better performance and
increase the stock price. This is because investors want to earn profits in the
future, both in the form of dividends and profits from the difference between the
selling price of shares and the buying price of shares [31].
Source: Author's own preparation.

T. T. Uyen, H. T. N. Linh / VNU Journal of Science: Policy and Management Studies, Vol. 40, No. 3 (2024) 24-39
28
In the previous period, some studies
demonstrated that IPOs had a positive impact on
the profits of companies in the United States
[4, 26, 32]. In contrast, recently, Pastusiak et al.,
found that there was a decline in post-IPO profits
in companies listed on Asian markets [29].
Another study on Indonesian companies showed
that the ratios measuring company profitability
increased after IPO, but the level of significance
when the Wilcoxon test is greater than 0.05,
meaning that the impact of IPO on corporate
profits was not statistically significant [30].
Therefore, the desire of this topic is to
conduct similar research on companies listed on
the international stock market NASDAQ Global
Select Market in the period 2019 – 2022, and
especially analyze in depth the impact of the IPO
to the profits of VinFast company. An equally
important reason is that in Vietnam this topic is
being researched deeply by very few scholars.
Based on the above documents, the study
proposes the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis H1: Return on assets (ROA) of
companies increases one year after IPO on
international stock exchanges
Hypothesis H2: Return on sales (ROS) of
companies increases one year after IPO on
international stock exchangess
Hypothesis H3: Return on equity (ROE) of
companies increases one year after IPO on
international stock exchanges
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Procedure
With the purpose of reviewing changes in
profitability ratios (ROA, ROS and ROE), the
article used quantitative methods for analysis. As
follows:
i) Descriptive statistics
Descriptive statistical methods are used to
describe the characteristics of variables. After
calculating the variables before and after the
IPO, the author used SPSS version 20 software
to calculate the minimum value (Min),
maximum value (Max), average value,
deviation. standard, median value and
interquartile ranges of the variables. Thereby,
there is an overview of the changing trends of
variables after the IPO;
ii) Wilcoxon non-parametric test
The purpose of this test is to test whether the
hypothesis about the post-IPO profit change of
the sample companies is statistically valid or not.
This method is suitable when it allows direct
examination and comparison of companies with
diverse industries across many countries and
over different time periods because it does not
require normally distributed data. Furthermore,
each company is compared to itself in previous
years, so this method is suitable because it allows
testing two different independent variables on
the same dependent variable. In fact, this method
was first used by [10] to analyze the impact of
privatization on performance. After that, a
number of other studies such as [33, 34]
continued to conduct and use the test method.
Wilcoxon determination is a key method while
evaluating company performance at the time
before and after the IPO.
3.2. Sampling Design
Research and select secondary data
collection methods to serve the research process
of the topic. The biggest advantage of this
method is that the data is collected in advance,
and has been published on the official
information pages of the enterprise, or reputable
stock forums, so the collection is easy, less
costly and less time consuming in the collection
process.
The study selected a sample of 100
businesses listed on the US stock exchange with
some sampling bases as follows:
i) The company must have complete
financial information for at least three
consecutive years, from one year before the IPO
(year -1), the year of the IPO (year 0) and one
year after the IPO (year 1). Therefore, to have
enough research data, the author chose
companies that had IPOs in the period 2019 -
2022 on the international stock exchange
NASDAQ Global Select Market;











![Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm và bài tập Thị trường chứng khoán [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260127/hoahongcam0906/135x160/57691769497618.jpg)














