Khoa Khoa học và Kỹ thuật máy tính
Bộ môn Khoa học máy tính
1
Tut 3: Stack& Queue
Assumption:
Using the stack and queue’s methods described below to solve all questions inside this
tutorial.
Stack:
bool top(<any_type>&data); // Get the value at top of stack, assign that value into
//‘data’ and return true. If stack is empty, return false;
void push(<any_type>value); // Push a value on the top of stack.
bool pop(<any_type>&data); // Remove the object at the top of this stack, assign
// value into ‘data’ variable, returns true if success and
// false otherwise.
bool isEmpty(); // Check if whether stack is empty. Return true if
// stack is empty and return false otherwise.
int size(); // Return the number of elements in stack.
Queue:
bool front(<any_type>&data); // Get the value at front of queue, assign that value into
//‘data’ and return true. If queue is empty, return false;
void enqueue(<any_type>value); // Add a value at rear of queue
bool dequeue(<any_type>&data); // Removes the object at the front of this queue, assign
// value into ‘data’ variable, returns true if success and
// false otherwise.
bool isEmpty(); // Check if whether queue is empty. Return true if
// queue is empty and return false otherwise.
int size(); // Return the number of elements in queue.
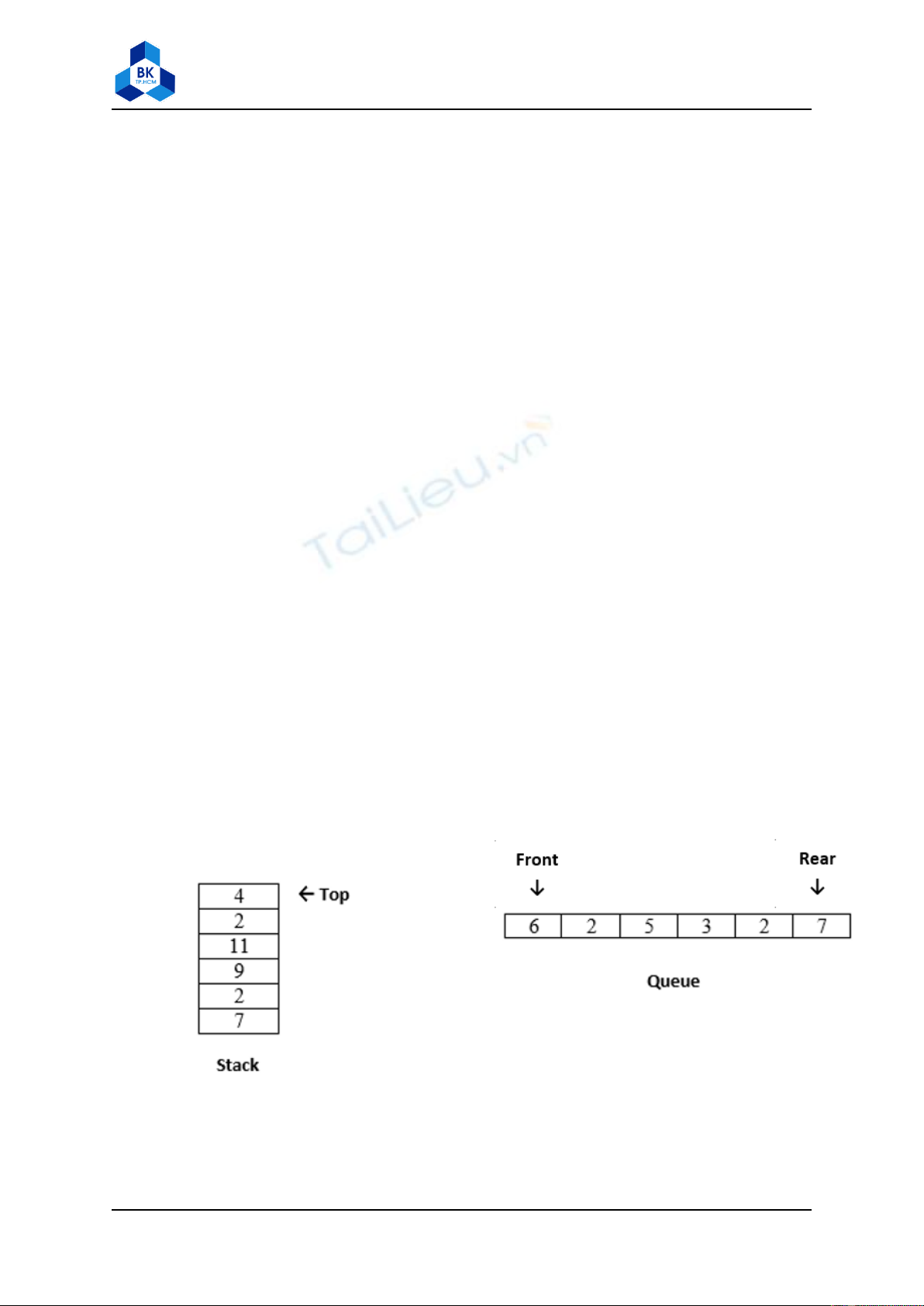
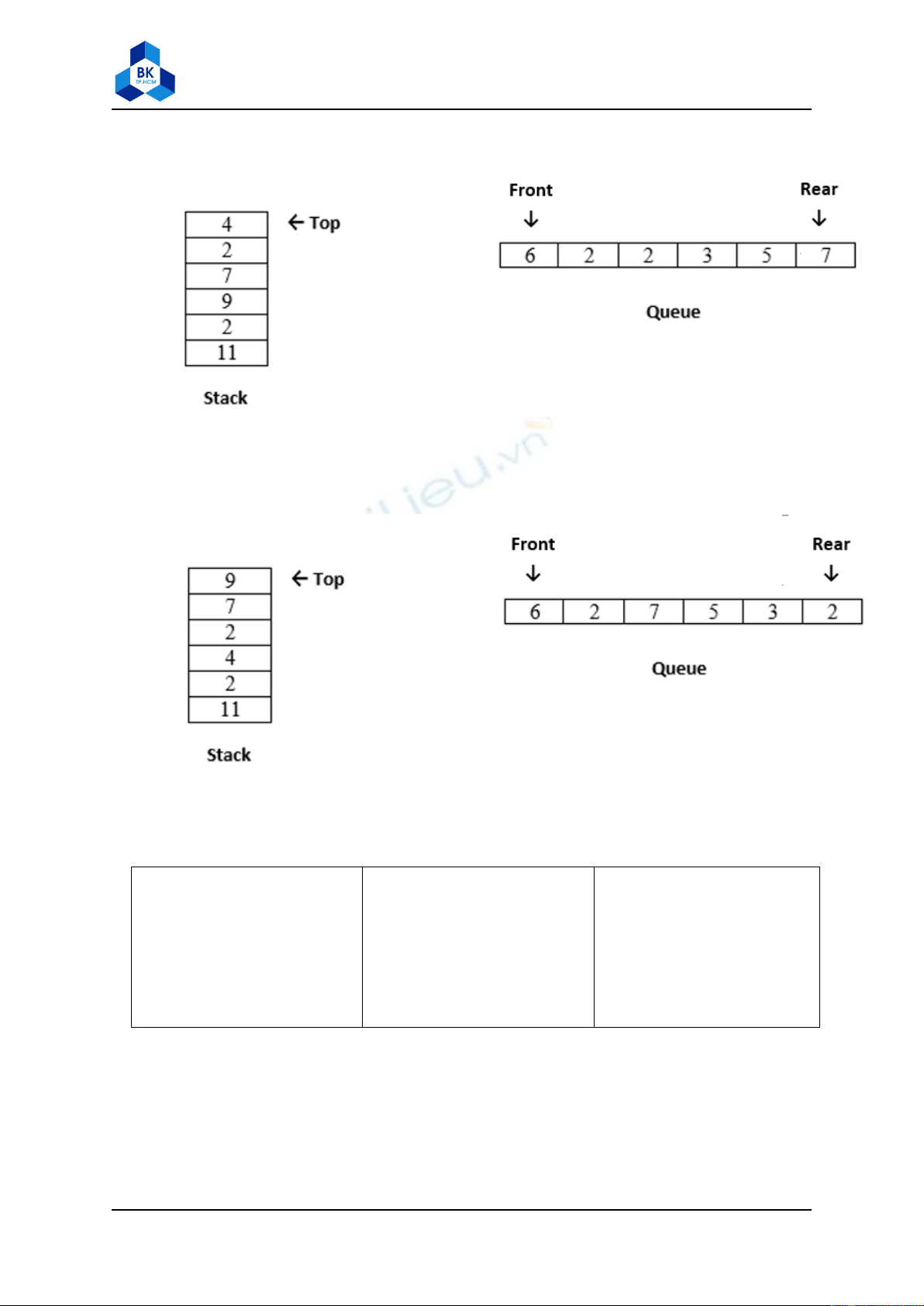
Question 1:
a) Write code to construct a stack and a queue as follow
Khoa Khoa học và Kỹ thuật máy tính
Bộ môn Khoa học máy tính
2
b) Add code to change above stack and queue in (a) to:
c) Add code to change above stack and queue in (b) to: (without using any primitive value)
e.g. push a primitive value
Stack s;
s.push(1);
Question 2: A Stacky program creates a stack and pushes following values orderly.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Stack s;
Double a;
s.push(0);
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
s.push(5);
s.push(6);
s.push(7);
s.push(8);
s.push(9);
Some pop and cout statements are inserted randomly after first push statement.
Khoa Khoa học và Kỹ thuật máy tính
Bộ môn Khoa học máy tính
3
For example:
Stack s;
Double a;
s.push(0);
s.push(1);
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
s.push(4);
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
s.push(5);
s.push(6);
s.push(7);
s.push(8);
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
s.push(9);
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
if(s.pop(a))
cout<<a<<” ”;
And the console displays:
1 3 4 8 9 7 6 5 2 0
Ask: which following results can possibly be printed by Stacky, recalling that “Some pop and
cout statements are inserted randomly after first push statement”. And write that Stacky
program to prove your answer. Write “s.pop();” instead of “if(s.pop(a)) cout<<a<<” ”;”
for short.
a) 2 4 9 8 7 5 6 3 1 0
b) 3 2 1 0 4 5 6 8 9 7
c) 0 1 4 3 7 6 8 9 5 2
Question 3: Write a program to convert and decimal number into binary number using stack
(do not use recursive).
Example:
Input: 23
Output: 10111
Question 4: Use the given methods described in Assumption, write a program to remove all
value greater than mean value of a queue.
Example:
Input queue: 1 4 6 8 1
Mean value: 4
Output queue: 1 4 1
Question 5: Write a program to sort a stack in increasing order using only one extra queue.



![Scanning Module 03: Hướng dẫn và Kinh nghiệm [Năm hiện tại]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2018/20181012/tranhanh9196/135x160/3931539335342.jpg)






















