
13
© Học viện Ngân hàng
ISSN 3030 - 4199
Tạp chí Kinh tế - Luật & Ngân hàng
Số 276- Năm thứ 27 (4)- Tháng 4. 2025
Ảnh hưởng của giao thông công cộng đến giá trị
bất động sản: Bằng chứng thực nghiệm từ mô hình
không gian tại Thành phố Thủ Đức
Ngày nhận: 22/12/2024 Ngày nhận bản sửa: 10/04/2025 Ngày duyệt đăng: 11/04/2025
Tóm tắt: Nghiên cứu này nhằm đánh giá mức độ ảnh hưởng của giao thông
công cộng đến giá trị bất động sản tại thành phố Thủ Đức (Việt Nam) trong
giai đoạn gần đây, đồng thời phân tích mối quan hệ không gian giữa các khu
vực đô thị bằng cách áp dụng các mô hình tự hồi quy không gian. Dữ liệu
nghiên cứu được thu thập từ các nguồn bất động sản trực tuyến vào tháng
12/2022 tại thành phố Thủ Đức, Việt Nam. Quá trình nghiên cứu tiến hành so
sánh các mô hình để xác định mô hình phù hợp nhất với bộ dữ liệu và các giả
định ban đầu. Kết quả phân tích cho thấy, các mô hình tự hồi quy không gian
hoạt động tốt hơn so với mô hình hồi quy tuyến tính đa biến (MLR), trong khi
MLR thể hiện sự tồn tại của tương quan không gian trong phần dư. Trong các
The impact of public transportation on property values: Empirical evidence from a spatial
econometric model in Thu Duc City, Vietnam
Abstract: This study aims to evaluate the impact of public transportation on property values in Thu Duc
City (Vietnam) in recent years, while analyzing the spatial relationships between urban areas through
the application of spatial autoregressive models. The research data was collected from various online
real estate sources in Thu Duc City, Vietnam, in December 2022. The study compares different models
to select the one that best fits the dataset and the initial assumptions. The analysis results indicate that
spatial autoregressive models outperform the multiple linear regression (MLR) model, as the MLR exhibits
spatial correlation in its residuals. Among the models evaluated, the spatial error model (SEM) with a
Queen contiguity matrix is identified as the most optimal. The findings reveal that real estate prices tend to
increase when located near public transportation routes, decrease when situated farther from commercial
centers, and experience negative impacts when in proximity to train stations. This study provides empirical
evidence regarding the spatial factors affecting the real estate market, offering valuable insights for
policymakers in making informed decisions to promote sustainable urban development.
Keywords: Hedonic pricing models, Spatial econometric models, Public transportation
Doi: 10.59276/JELB.2025.04.2853
Nguyen, Minh Hai
Email: hainm@hub.edu.vn
Organization: Faculty of Data Science in Business, Banking University of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Nguyễn Minh Hải
Khoa Khoa học dữ liệu, Trường Đại học Ngân hàng TP. Hồ Chí Minh, Việt nam

Ảnh hưởng của giao thông công cộng đến giá trị bất động sản:
Bằng chứng thực nghiệm từ mô hình không gian tại Thành phố Thủ Đức
14 Tạp chí Kinh tế - Luật & Ngân hàng- Số 276- Năm thứ 27 (4)- Tháng 4. 2025
mô hình được xem xét, mô hình SEM với ma trận Queen được đánh giá là tối
ưu nhất. Phân tích kết quả chỉ ra rằng giá bất động sản tăng lên khi gần các
tuyến giao thông công cộng, giảm khi xa trung tâm thương mại và chịu tác
động tiêu cực khi nằm gần các ga tàu. Nghiên cứu đóng góp thêm bằng chứng
thực nghiệm về tác động của các yếu tố không gian đối với thị trường bất động
sản, hỗ trợ nhà hoạch định chính sách đưa ra quyết định hiệu quả trong việc
phát triển đô thị bền vững.
Từ khóa: Mô hình giá Hedonic, Mô hình kinh tế lượng không gian, Giao thông
công cộng
1. Giới thiệu
Trong những năm qua, giá trị bất động sản
đô thị ngày càng trở thành chủ đề quan
trọng trong nghiên cứu kinh tế, đặc biệt là
trong bối cảnh đô thị hóa nhanh chóng tại
Việt Nam. Nghiên cứu này tập trung phân
tích các yếu tố không gian ảnh hưởng đến
giá trị bất động sản tại thành phố Thủ Đức,
một đô thị mới nổi và chiến lược thuộc
Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh (Việt Nam).
Lý thuyết kinh tế đô thị, được phát triển từ
các công trình của Alonso (1964) và Muth
(1969), cho rằng giá trị bất động sản chịu
ảnh hưởng bởi sự đánh đổi giữa khả năng
tiếp cận các trung tâm thương mại (TTTM)
và diện tích không gian. Theo lý thuyết
này, các bất động sản có khả năng tiếp cận
tốt hơn với các trung tâm này thường có giá
trị cao hơn, do người mua sẵn sàng chi trả
mức giá cao cho các vị trí thuận lợi. Hơn
nữa, các nghiên cứu thực nghiệm áp dụng
phương pháp Hedonics (Malpezzi, 2008)
đã chứng minh vai trò của các yếu tố không
gian, trong đó khả năng tiếp cận giao thông
là một biến số quan trọng.
Thành phố Thủ Đức, với diện tích 211,5
km² và dân số 1,2 triệu người, là khu vực
lý tưởng để nghiên cứu mối quan hệ giữa
hệ thống giao thông công cộng và giá trị
bất động sản. Được thành lập năm 2020 từ
sự sáp nhập của ba quận, Thủ Đức hiện là
trung tâm sáng tạo, công nghệ và dịch vụ
cao cấp của vùng kinh tế trọng điểm phía
Nam. Sự phát triển mạnh mẽ của các khu
đô thị như Thủ Thiêm và các dự án hạ tầng
giao thông quan trọng như tuyến Metro số
1 đã tạo ra những biến động đáng kể về giá
trị bất động sản trong khu vực này.
Để thực hiện nghiên cứu, chúng tôi sử dụng
phương pháp hồi quy Hedonics kết hợp với
các mô hình tự hồi quy không gian (SAR,
SEM, SDM). Nghiên cứu thu thập dữ liệu
từ các nguồn bất động sản trực tuyến tại
Thủ Đức vào tháng 12/2022, với các biến
số liên quan đến đặc điểm bất động sản, vị
trí địa lý và khả năng tiếp cận giao thông
công cộng. Việc áp dụng các mô hình kinh
tế lượng không gian được kỳ vọng sẽ giúp
xác định chính xác hơn tác động của các
yếu tố không gian lên giá trị bất động sản.
Bài viết được cấu trúc như sau: Phần 2 trình
bày tổng quan các nghiên cứu liên quan và
lý thuyết cơ sở. Phần 3 giới thiệu phương
pháp nghiên cứu và dữ liệu sử dụng. Phần
4 trình bày kết quả phân tích và thảo luận.
Cuối cùng, Phần 5 đưa ra kết luận và hàm ý
chính sách cho công tác quy hoạch đô thị và
phát triển thị trường bất động sản bền vững.
2. Tổng quan tài liệu
Nghiên cứu về tác động của giao thông
đến giá bất động sản chia thành hai hướng

NGUYỄN MINH HẢI
15
Số 276- Năm thứ 27 (4)- Tháng 4. 2025- Tạp chí Kinh tế - Luật & Ngân hàng
chính. Hướng thứ nhất dựa trên lý thuyết
kinh tế đô thị từ von Thünen (1826) và được
mở rộng bởi Alonso (1964), Muth (1969),
Mills (1972). Lý thuyết này tập trung vào
sự đánh đổi giữa chi phí di chuyển đến
các trung tâm thương mại (TTTM) và chi
phí không gian, thông qua hàm giá thuê.
Hướng thứ hai là các nghiên cứu thực
nghiệm áp dụng hồi quy Hedonic (Rosen,
1974) để phân tích tác động của giao thông
đến giá trị bất động sản.
Các nghiên cứu trước đây cho thấy tác
động khác nhau giữa các loại hình bất động
sản và hệ thống giao thông. Debrezion và
cộng sự (2007) xác định rằng bất động sản
thương mại tăng giá mạnh hơn bất động sản
dân cư khi gần các ga tàu, đặc biệt là các ga
ngoại ô. Tuy nhiên, Senior (2009) lại phát
hiện tuyến Metro không ảnh hưởng đáng
kể đến giá nhà tại Greater Manchester,
trong khi Ovenell (2007) ghi nhận tác động
tích cực trong phạm vi 0,5-1 km quanh
các ga tàu. Tại Đài Loan, Andersson và
cộng sự (2010) không tìm thấy ảnh hưởng
rõ ràng của đường sắt cao tốc, trái ngược
với nghiên cứu của Debrezion và cộng sự
(2006) tại Hà Lan, nơi giao thông đường
sắt thể hiện tác động rõ ràng.
Ngoài đường sắt, các nghiên cứu về hệ
thống xe buýt nhanh cũng ghi nhận các
kết quả đáng chú ý. Rodríguez và Mojica
(2009) xác định giá bất động sản tại Bogotá
tăng 13-14% sau khi hệ thống xe buýt
nhanh được đưa vào hoạt động. Munoz-
Raskin (2010) nhận thấy các bất động sản
gần trạm xe buýt nhanh có giá trị thấp hơn
4,5%, nhưng trong phạm vi đi bộ 5 phút,
giá tăng 8,7%. Cervero và Kang (2011) khi
phân tích dữ liệu tại Seoul cũng nhận thấy
giá bất động sản tăng 10% khi nằm trong
bán kính 300 m từ trạm xe buýt.
Tại Việt Nam, các nghiên cứu về tác động
của giao thông công cộng đến giá trị bất
động sản còn rất hạn chế. Hiện chưa có
nhiều nghiên cứu chuyên sâu phân tích tác
động của hệ thống giao thông công cộng
đến giá trị bất động sản trong bối cảnh đô
thị hóa nhanh chóng, đặc biệt là việc áp
dụng các mô hình không gian. Phần lớn
các nghiên cứu hiện nay tập trung vào các
yếu tố kinh tế- xã hội và các đặc điểm cấu
trúc của bất động sản mà chưa xem xét đầy
đủ tác động không gian từ các hệ thống
giao thông công cộng như tuyến Metro hay
tuyến xe buýt nhanh.
Về phương pháp nghiên cứu, phương pháp
hồi quy Hedonic gặp phải ba thách thức
chính: thiếu biến quan trọng, lựa chọn
dạng hàm và tự tương quan không gian
(Armstrong & Rodríguez, 2006). Gujarati
& Porter (2009) chỉ ra rằng thiếu biến
quan trọng có thể gây sai lệch ước lượng.
Cropper và cộng sự (1988) khuyến nghị sử
dụng dạng tuyến tính hoặc log-tuyến tính để
đạt hiệu quả tốt nhất. Vấn đề tự tương quan
không gian được nghiên cứu bởi LeSage
& Pace (2009), nhấn mạnh tầm quan trọng
của các mô hình không gian trong việc
phân tích tác động của giao thông đến giá
bất động sản.
Các mô hình không gian như SAR (Spatial
Autoregressive) và SEM (Spatial Error
Model) được Anselin (2010) phát triển
nhằm khắc phục hiện tượng tự tương
quan. Armstrong & Rodríguez (2006) áp
dụng SAR tại Massachusetts, phát hiện
giá bất động sản tăng 10% gần các trạm,
nhưng giảm khi sát đường ray. Martínez
và Viegas (2009) so sánh MLR và SAR tại
Lisbon, ghi nhận sự tồn tại của tự tương
quan không gian, song MLR được ưu tiên
nhờ khả năng dự báo tốt hơn.
Dựa trên tổng quan nghiên cứu, có thể thấy
rằng giao thông công cộng có ảnh hưởng
đáng kể đến giá trị bất động sản, song mức
độ và hướng tác động phụ thuộc vào loại
hình giao thông, loại bất động sản và đặc
điểm không gian. Tuy nhiên, khoảng trống

Ảnh hưởng của giao thông công cộng đến giá trị bất động sản:
Bằng chứng thực nghiệm từ mô hình không gian tại Thành phố Thủ Đức
16 Tạp chí Kinh tế - Luật & Ngân hàng- Số 276- Năm thứ 27 (4)- Tháng 4. 2025
nghiên cứu vẫn tồn tại, cụ thể là tác động
khác biệt giữa các loại hình giao thông công
cộng đối với các khu vực đô thị mới nổi
như thành phố Thủ Đức, Việt Nam. Việc
phân tích chi tiết hơn về tác động của tuyến
metro và tuyến xe buýt nhanh trong mối
quan hệ không gian là cần thiết để cung cấp
các bằng chứng thực nghiệm cho các chính
sách phát triển đô thị bền vững.
3. Phương pháp nghiên cứu
Để đảm bảo mô hình ước lượng hoạt động
chính xác, phần đầu tiên sẽ trình bày quy
trình xử lý dữ liệu. Tiếp theo, mô hình hồi
quy tuyến tính được giới thiệu với đầy đủ
thông tin về biến số, cấu trúc và các giả
định quan trọng. Việc đánh giá mức độ ảnh
hưởng và ý nghĩa thống kê của các tham số
cũng được thực hiện nhằm làm rõ vai trò
của từng yếu tố trong mô hình. Đặc biệt,
nghiên cứu chú trọng đến việc kiểm tra
mối quan hệ không gian trong phần dư của
mô hình hồi quy tuyến tính. Nếu phát hiện
hiện tượng tự tương quan không gian, việc
mở rộng mô hình sang hồi quy không gian
là cần thiết để cải thiện độ chính xác, tăng
hiệu lực mô hình và hạn chế sai lệch ước
lượng do bỏ qua sự tương tác không gian
giữa các quan sát.
3.1. Dữ liệu
Dữ liệu ước lượng cho các mô hình hồi quy
hedonic trong nghiên cứu được thu thập từ
khu vực đô thị Thành phố Thủ Đức. Mẫu
hộ gia đình trong nghiên cứu được lấy từ
các nền tảng bất động sản trực tuyến phổ
biến (Batdongsan.com.vn; Alonhadat.com.
vn; Muaban.net; và Nhatot.com) vào tháng
12/2022, bao gồm thông tin về giá chào
bán và các đặc điểm cấu trúc như diện tích,
số phòng và tình trạng xây dựng của 730
bất động sản đô thị. Đặc biệt, địa chỉ của
từng quan sát cũng được mã hóa bằng hệ
thống thông tin địa lý (GIS), giúp định vị
không gian chính xác.
Về loại hình bất động sản, dữ liệu mẫu bao
gồm đa dạng các loại: biệt thự, nhà liền kề,
căn hộ chung cư, nhà phố thổ cư và đất ở,
phản ánh tương đối đầy đủ cơ cấu giao dịch
thực tế trên thị trường bất động sản tại Thủ
Đức trong giai đoạn khảo sát. Điều này
giúp đảm bảo mức độ bao quát nhất định
cho phân tích mô hình.
Tuy nhiên, mẫu dữ liệu này vẫn tồn tại
một số giới hạn nhất định. Thứ nhất, dữ
liệu được thu thập tại một thời điểm cụ
thể (tháng 12/2022), nên chỉ phản ánh tình
hình thị trường ngắn hạn và không bao quát
các biến động theo mùa hay thay đổi chính
sách. Thứ hai, giá được sử dụng là giá chào
bán, không phải giá giao dịch thực tế. Mặc
dù theo các nghiên cứu như Hometrack
(2005), giá chào bán thường có tương
quan cao (~90%) với giá giao dịch, nhưng
vẫn có thể dẫn đến sai lệch nhỏ trong ước
lượng. Thứ ba, do dữ liệu được thu thập từ
nền tảng trực tuyến, nên có khả năng thiên
lệch về mặt không gian, khi các khu vực
sôi động hơn như Thảo Điền, Linh Tây,
hay Khu Công nghệ cao có thể được đại
diện nhiều hơn so với các khu vực ven hoặc
kém phát triển hơn.
Để giảm thiểu các giới hạn trên, nghiên
cứu đã sử dụng kỹ thuật mã hóa không gian
GIS và áp dụng các mô hình kinh tế lượng
không gian (SAR, SEM, SDM) nhằm kiểm
soát các đặc điểm địa lý và ảnh hưởng
không gian, góp phần nâng cao tính tin cậy
và khả năng suy rộng của kết quả.
Giá trị bất động sản tại Thủ Đức được định
hình bởi vị trí, môi trường sống và hệ thống
tiện ích. Khu vực Thảo Điền có mức giá
cao nhất nhờ môi trường sống cao cấp,
trong khi các khu vực có giá thấp nhất như
Bình Chiểu, Linh Đông, Tam Phú và Hiệp
Bình Phước dù có kết nối thuận tiện với
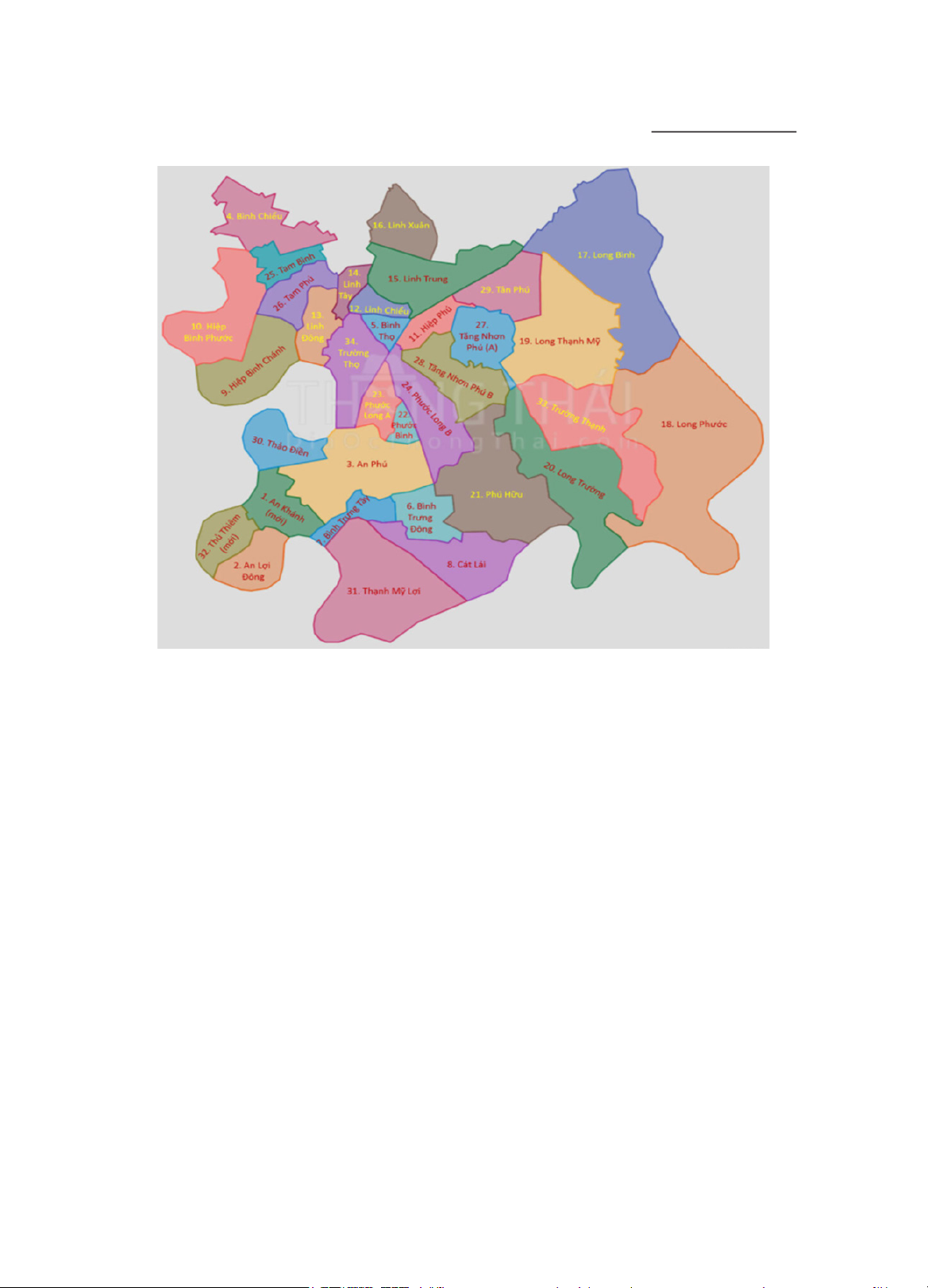
NGUYỄN MINH HẢI
17
Số 276- Năm thứ 27 (4)- Tháng 4. 2025- Tạp chí Kinh tế - Luật & Ngân hàng
trung tâm và khu công nghiệp nhưng lại
thiếu các tiện ích cao cấp và môi trường
sống hấp dẫn. Các khu vực gần khu công
nghiệp hoặc cảng sông như Hiệp Bình
Chánh, Tam Bình và Linh Xuân cũng bị
ảnh hưởng tiêu cực từ mật độ giao thông
cao, ô nhiễm không khí và tiếng ồn, làm
giảm sức hút. Vì vậy, việc dự đoán giá nhà
không thể chỉ dựa trên khoảng cách tới
trung tâm mà cần xem xét tổng thể các yếu
tố như môi trường sống, hạ tầng giao thông
và nhu cầu thị trường để đảm bảo mô hình
phản ánh chính xác giá trị bất động sản.
Nghiên cứu gặp hạn chế khi dữ liệu chỉ
phản ánh giá chào bán, không phải giá giao
dịch thực tế, nhưng theo Hometrack (2005),
giá chào bán thường tương quan cao với
giá thực tế (khoảng 90% giá thị trường cân
bằng) nên không ảnh hưởng đáng kể đến độ
tin cậy của các tham số ước lượng; dữ liệu
được thu thập trong giai đoạn bất động sản
tăng trưởng mạnh (13-15% mỗi năm) nhờ
quy hoạch chiến lược và đầu tư hạ tầng,
song số lượng biến đặc trưng còn hạn chế
do chưa có nguồn dữ liệu chính thức về đặc
điểm và giá giao dịch cuối cùng; dữ liệu
được thu thập từ các nền tảng bất động sản
trực tuyến uy tín trong năm 2022 tại thành
phố Thủ Đức, xử lý bằng phần mềm Stata
16 với các bước làm sạch, kiểm tra tính hợp
lệ và loại bỏ các quan sát ngoại lệ, chi tiết
biến số được trình bày trong Bảng 1.
Biến phụ thuộc trong mô hình nghiên cứu
là giá chào bán bất động sản, được chuyển
đổi sang dạng logarithm theo phương pháp
của Malpezzi (2008). Cách làm này cho
phép diễn giải tham số ước lượng dưới
dạng phần trăm thay đổi giá khi biến độc
Nguồn: Bản Đồ Việt Nam, 2025
Hình 1. Phân chia địa giới hành chính tổng thể của các phường thuộc
thành phố Thủ Đức











![Mức lương tối thiểu và mức sống tối thiểu cho người lao động tại các doanh nghiệp ở Việt Nam [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260129/hoaphuong0906/135x160/43101769669594.jpg)














