
Phân lớp dữ liệu
ThS. Dương Phi Long – Email: longdp@uit.edu.vn
Chương 6:
TRƯỜNG ÐẠI HỌC CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN
KHOA HỆ THỐNG THÔNG TIN
Tài liệu bài giảng:
KHAI THÁC DỮ LIỆU – IS252

2
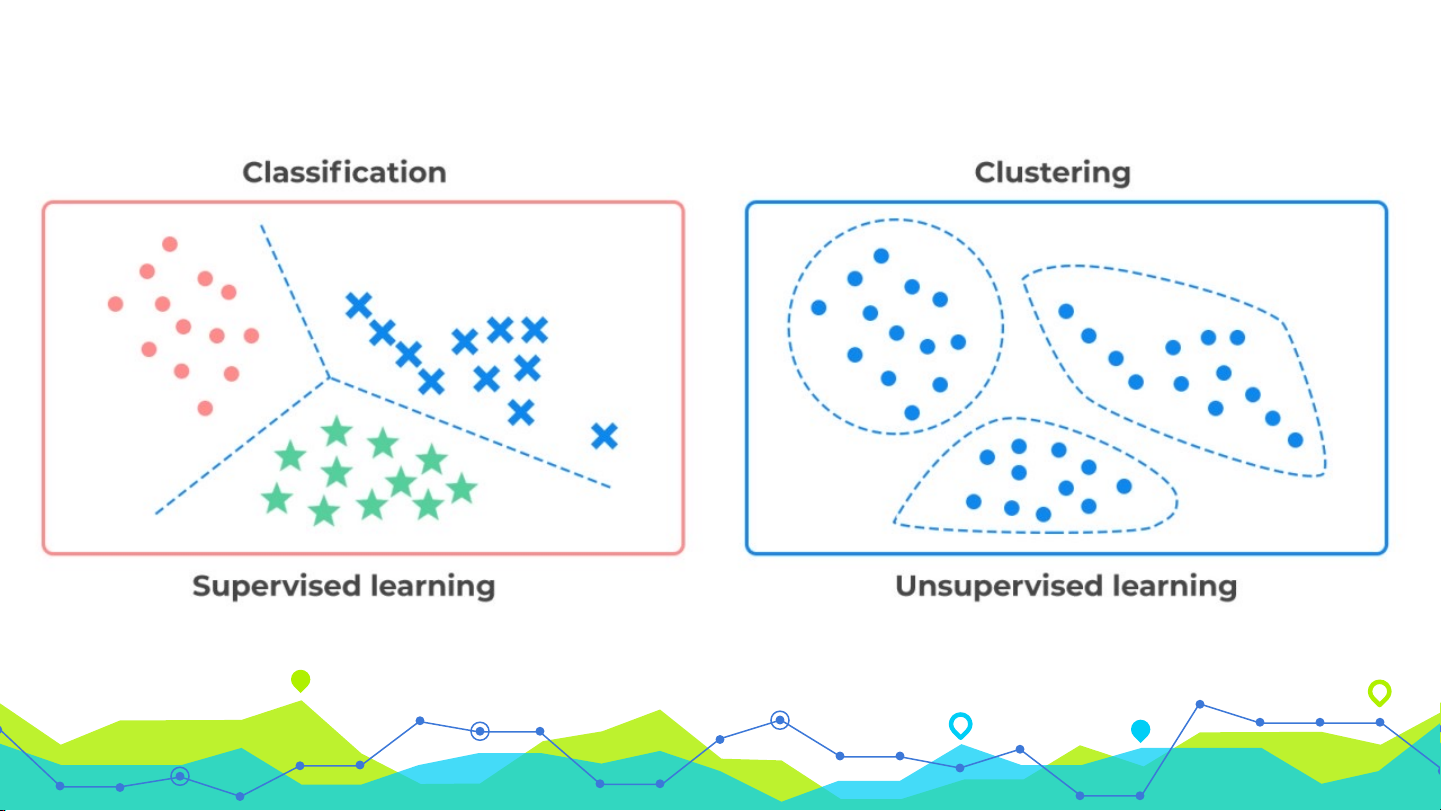
Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning
-Supervised Learning
•Supervision: Dữliệuhuấn luyện(quan sát, đo lường, …) được
kèm theo nhãn lớp
•Dữliệu mớiđượcphân lớp dựatrên tậphuấn luyện
(classification)
-Unsupervised Learning
•Nhãn lớp của dữliệuhuấn luyệnkhông xácđịnh
•Đưara một tập hợp cácphépđo, quan sát, ... với mụcđích
thiết lập sựtồn tại của các lớphoặc cụmtrong dữliệu
(clustering)
3
Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning
4
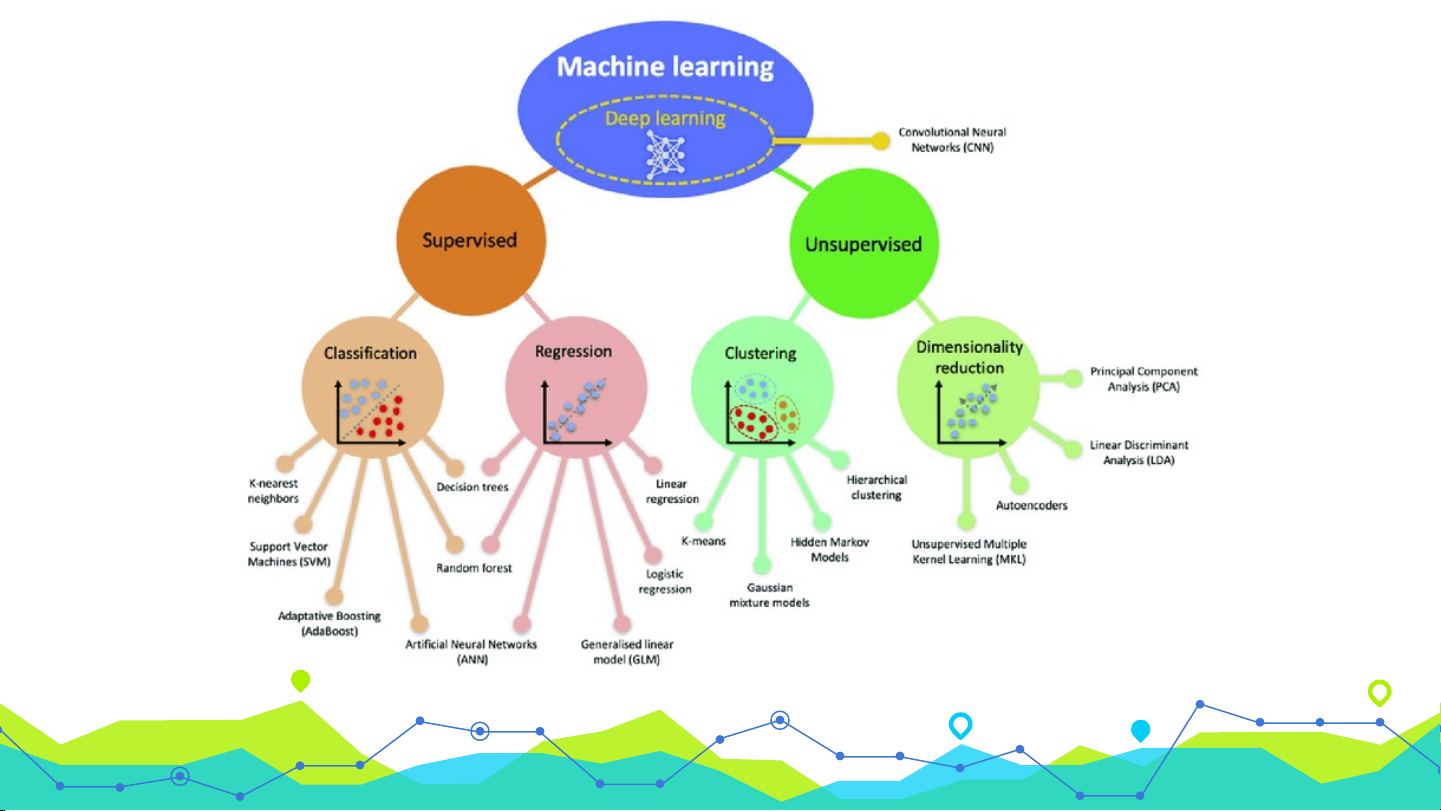
Supervised vs Unsupervised vs Semi-Supervised learning
Supervised
learning
Majority of algorithms.
Machine is trained using
well-labeled data; inputs
and outputs are matched.
Mapping function takes
inputs and matches to
outputs, creating a
target function
Classification
Regression
Decision tree, Random
forest, SVM, K-NN,
Neural network,
Linear regression,
Logistic regression, …
Unsupervised
learning
Unlabeled data (inputs
only) is analyzed.
Learning happens without
supervision
Inputs are used to
create a model of the
data
Clustering
Association
K-Means, C-Means,
Hierarchy, Gaussian
Mixture
Apriori, FP-Growth
PCA, LDA,…
Dimensionality
reduction
Semi-
Supervised
learning
Some data is labeled,
some not.
Goal: better results than
labeled data alone.
Good for real world data.
Combination of above
processes All the above
Self-training, Mixture
models, Semi-supervised
SVM,…
Overview Process Subtypes Examples
5


























