SINH HỌC TẾ BÀO
Huỳnh Duy Thảo
Bm Mô –Phôi – Di truyền
thao_huynhduy@pnt.edu.vn

MUÏC TIEÂU
◼Hiểu được định nghĩa về tế bào.
◼Liệt kê được các phương pháp nghiên cứu tế bào.
◼Giải thích được các học thuyết về tế bào.
◼Giải thích được các thuộc tính của tế bào.
◼Phân tích được mục tiêu của môn học.
◼Phân tích được mục tiêu của môn học
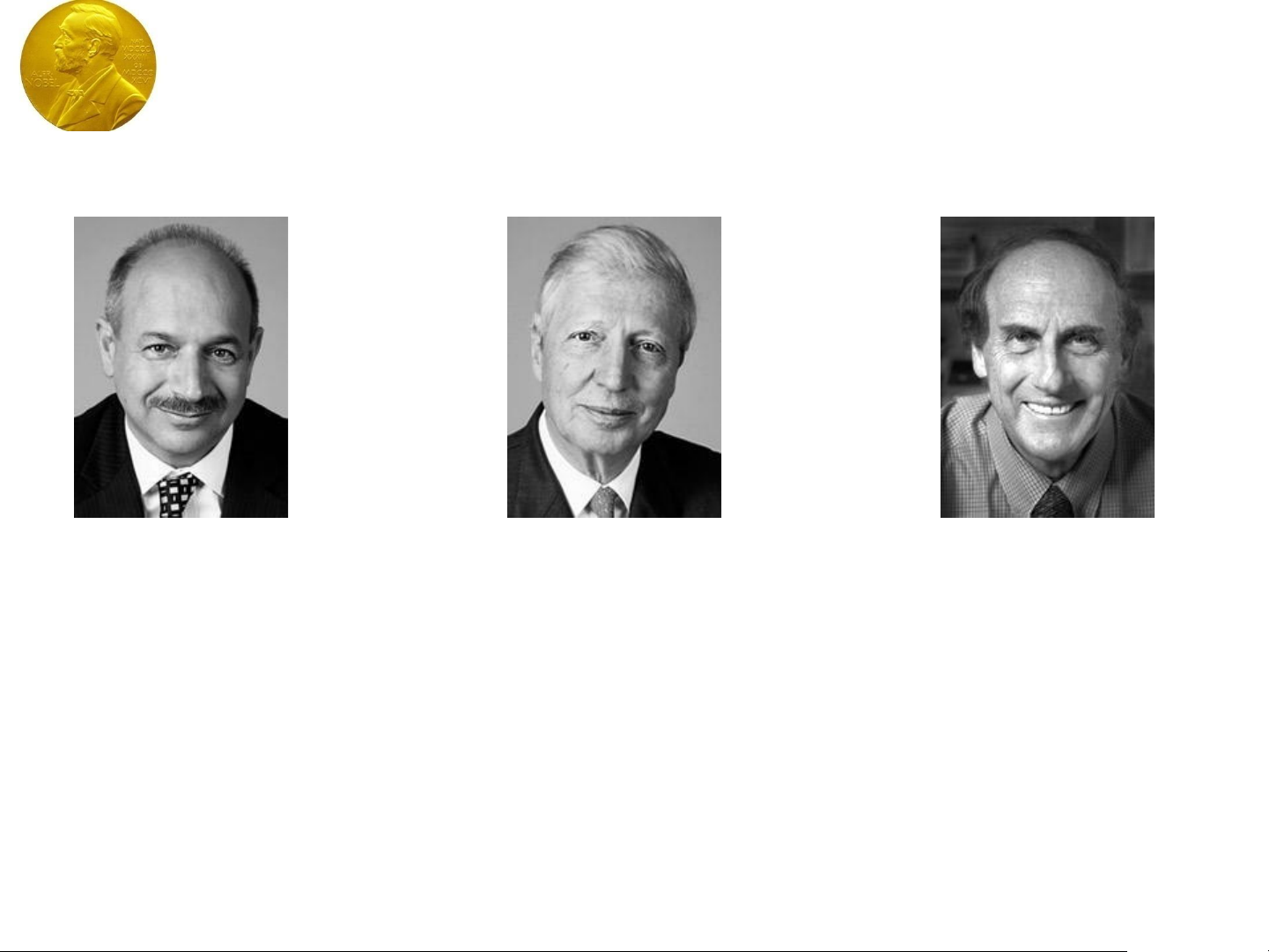

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or
Medicine 2011
Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffmann Ralph M. Steinman
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2011 was divided, one
half jointly to Bruce A. Beutler and Jules A. Hoffmann "for their
discoveries concerning the activation of innate immunity" and the
other half to Ralph M. Steinman "for his discovery of the dendritic cell
and its role in adaptive immunity".
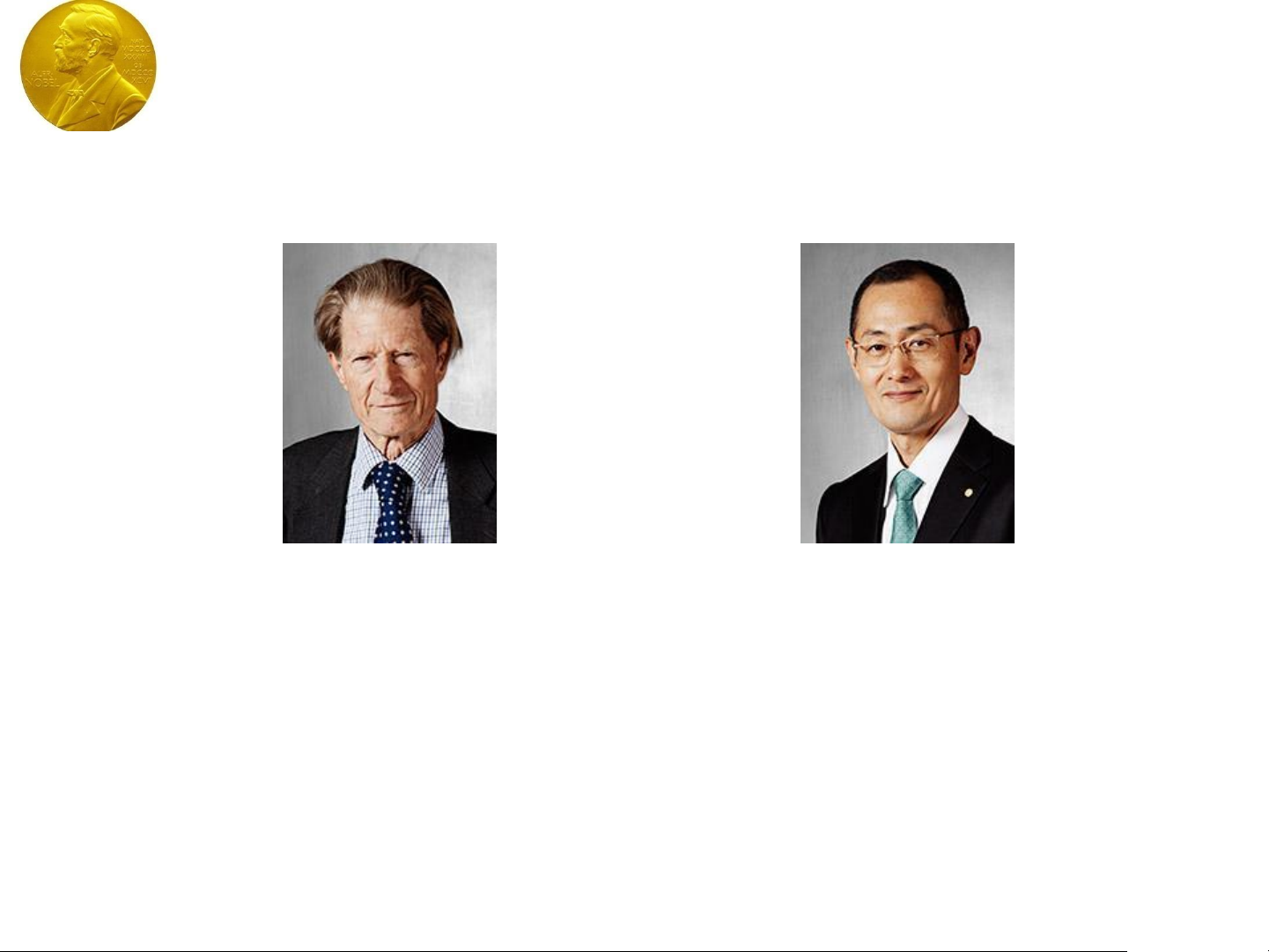

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or
Medicine 2012
Sir John B. Gurdon Shinya
Yamanaka
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 was awarded
jointly to Sir John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka "for the
discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become
pluripotent"
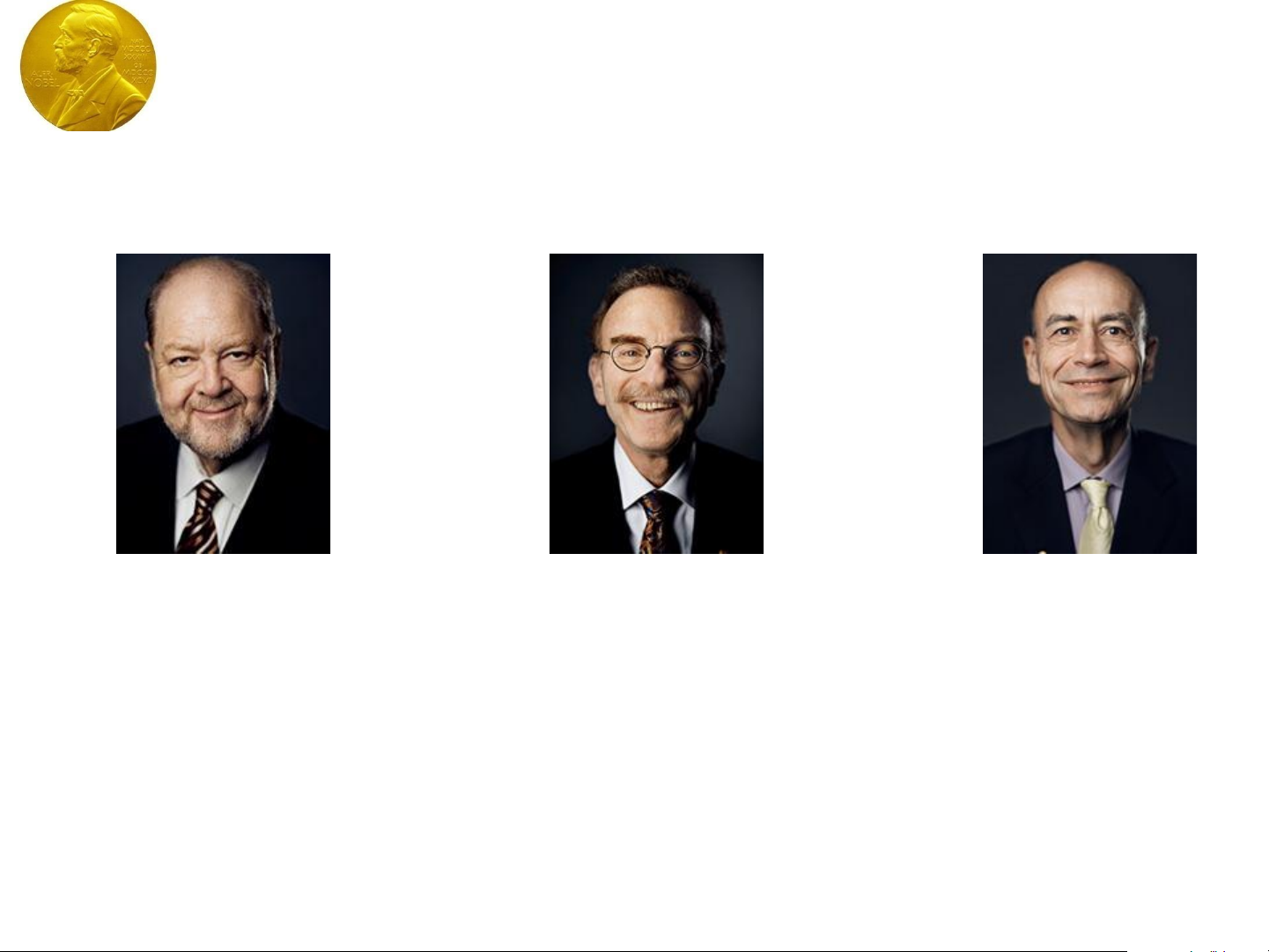

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or
Medicine 2013
James E.
Rothman
Randy W.
Schekman
Thomas C.
Südhof
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2013 was
awarded jointly to James E. Rothman, Randy W. Schekman
and Thomas C. Südhof
"for their discoveries of machinery
regulating vesicle traffic, a major transport system in our
cells"
.





![Câu hỏi ôn tập Sinh học tế bào [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250709/kimphuong1001/135x160/771752031316.jpg)









![Bài giảng Giáp xác chân mái chèo [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250927/lethihongthuy2402@gmail.com/135x160/92891759114976.jpg)



![Tài liệu học tập Chuyên đề tế bào [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250906/huutuan0/135x160/56151757299182.jpg)






