
TRƯỜNG TRUNG HỌC PHỔ THÔNG LÊ TRUNG KIÊN
TỔ NGOẠI NGỮ
---------- ---------
CÁC CHUYÊN ĐỀ NGỮ PHÁP
ÔN THI THPT
Giáo viên: Nguyễn Phước Diệu Hằng
CHUYÊN ĐỀ 1: THÌ VÀ SỰ PHỐI HỢP CÁC THÌ
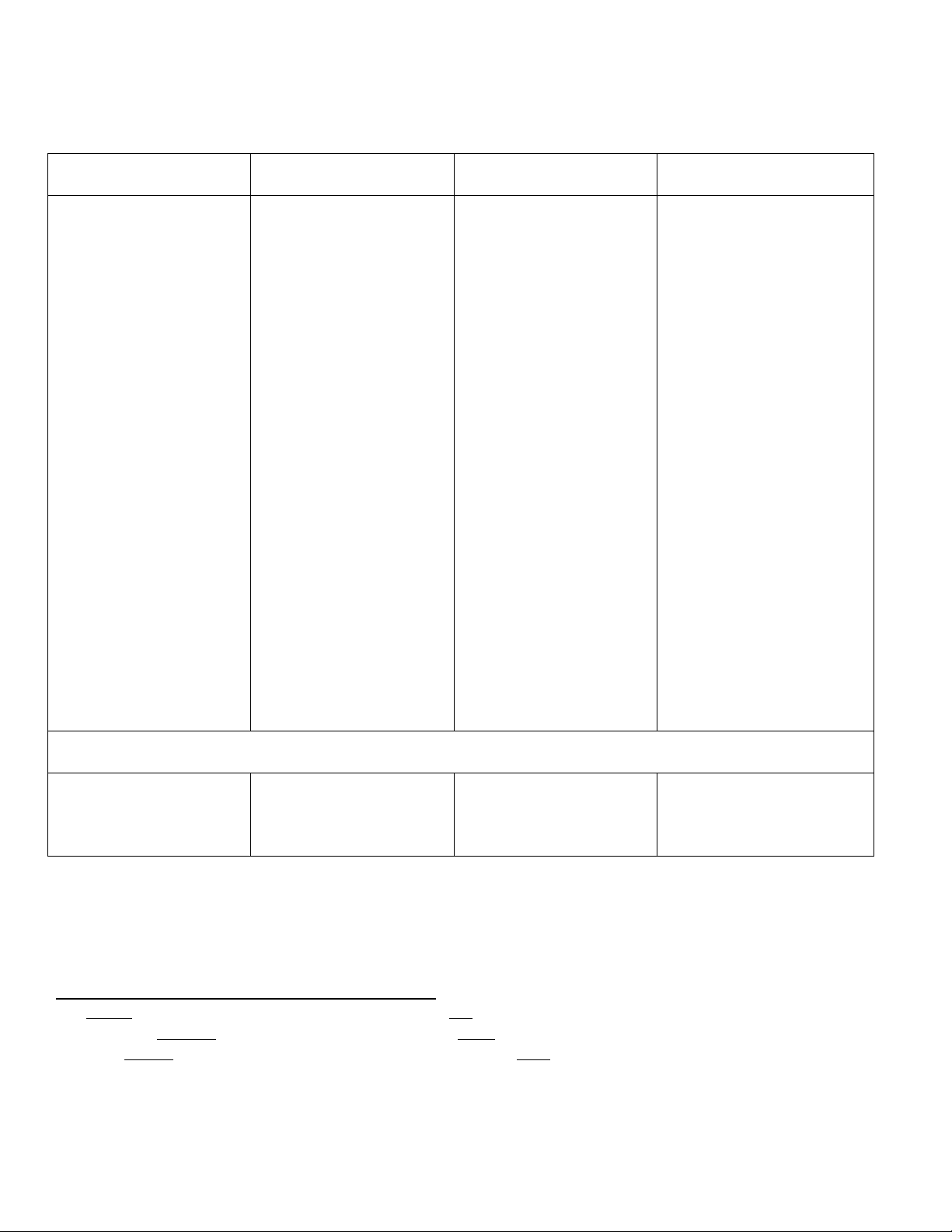
A. CÁC THÌ HIỆN TẠI
Present simple
Present continuous
Present perfect
Present perfect
continuous
1. Thói quen, trạng thái
lâu dài
Ex: Peter works for ACB
bank.
2. Hành động định sẵn
cho tương lai (thời gian
biểu, chương trình, …)
Ex: The train leaves at
4:30 so we need to hurry
up.
3. Quy luật tự nhiên, sự
thật, chỉ dẫn mang tính
khoa học
Ex: Water boils 212oF.
4. Văn phong mô tả / kể
chuyện / tường thuật sự
việc xảy ra trong sách
hoặc phim ảnh / tiêu đề
báo chí
Ex1: The lights go out
and the figure tears out of
the villa.
Ex2: At the end of the
film, the father and the
son forgive each other.
1. Hành động lặp đi lặp
lại (gây phiền) đặc biệt sử
dụng các trạng từ:
always, forever,
constantly
Ex: You’re always
leaving the cap off the
toothpaste.
2. Hành động đang diễn
ra tại lúc nói, khoảng thời
gian hiện thời
Ex: They’re hunting for a
flat.
3. Kế hoạch xác định
trong tương lai gần
Ex: They’re going on an
excursion tomorrow.
4. Xu hướng phát triển
đương thời
Ex: Oil prices are rising
at present.
5. Hành động khác với
thói quen thường ngày
Ex: He usually wears
black shoes but today
he’s wearing brown ones.
1. Hành động vừa mới
hoàn tất
Ex: She has just painted
her room.
2. Hành động bắt đầu
trong quá khứ, diễn ra
đến hiện tại, để lại kết
quả ở hiện tại.
Exq: He has written 3
books.
Ex2: She has lost the key,
so she has to stay
outdoors.
3. Hành động, trải
nghiệm trong quá khứ
không rõ thời gian
Ex: I have been to Berlin
twice.
4. Hành động lặp đi lặp
lại và vẫn còn tiếp diễn
Ex: He has worked as a
teacher for 4 years. (He
is still a teacher.)
1. Hành động xảy ra trong
quá khứ, để lại kết quả rõ
ràng ở hiện tại
Ex1: She has been painting
her room. (It smells of
paint)
Ex2: I feel tired. I have
been running for nearly
three hours.
2. Hành động xảy ra trong
quá khứ, kéo dài đến hiện
tại (nhấn mạnh tính liên tục
/ kéo dài của hành động)
Ex: She’s been waiting for
two hours but there’s still
no sign of him.
3. Hành động gây phiền hà
hoặc ngạc nhiên
Ex: What have you been
doing to my computer?
Time expressions
Always, usually, often,
sometimes, every day, in
the morning, on Mondays
…
Now, at present, at the
moment, these days, still,
today, tonight, always,
continually, constantly …
Since, yet, for, already,
just, ever, so far, recently,
lately, still, how long …
since, for, how long, lately,
recently, …
Notes: Stative verbs (Tĩnh động từ): Chỉ trạng thái và không bao giờ được chia tiếp diễn.
- Senses: see, hear, smell, feel, taste
- Thinking / mental: think, agree, believe, consider, doubt, expect, feel (think) …
- Emotion and feeling: feel, forgive, hate, love, loathe, like, dislike, mind, wish …
- Others: appear / seem, have (possess), be, belong, keep (continue), matter, owe, possess, own …
Compare the form of words in the sentences below*
I’m seeing my doctor. Do you see those birds?
Be quiet! I’m thinking. I think you are wrong.
We were having a good time at the party. Now, we have an appartment at the riverside.
HAVE BEEN TO / HAVE BEEN IN / HAVE GONE TO
He has been to Berlin. (He has gone and come back)
He has gone to Berlin. (He hasn’t come back yet)
He has been in Berlin for a year. (He lives there)
B. CÁC THÌ TƯƠNG LAI
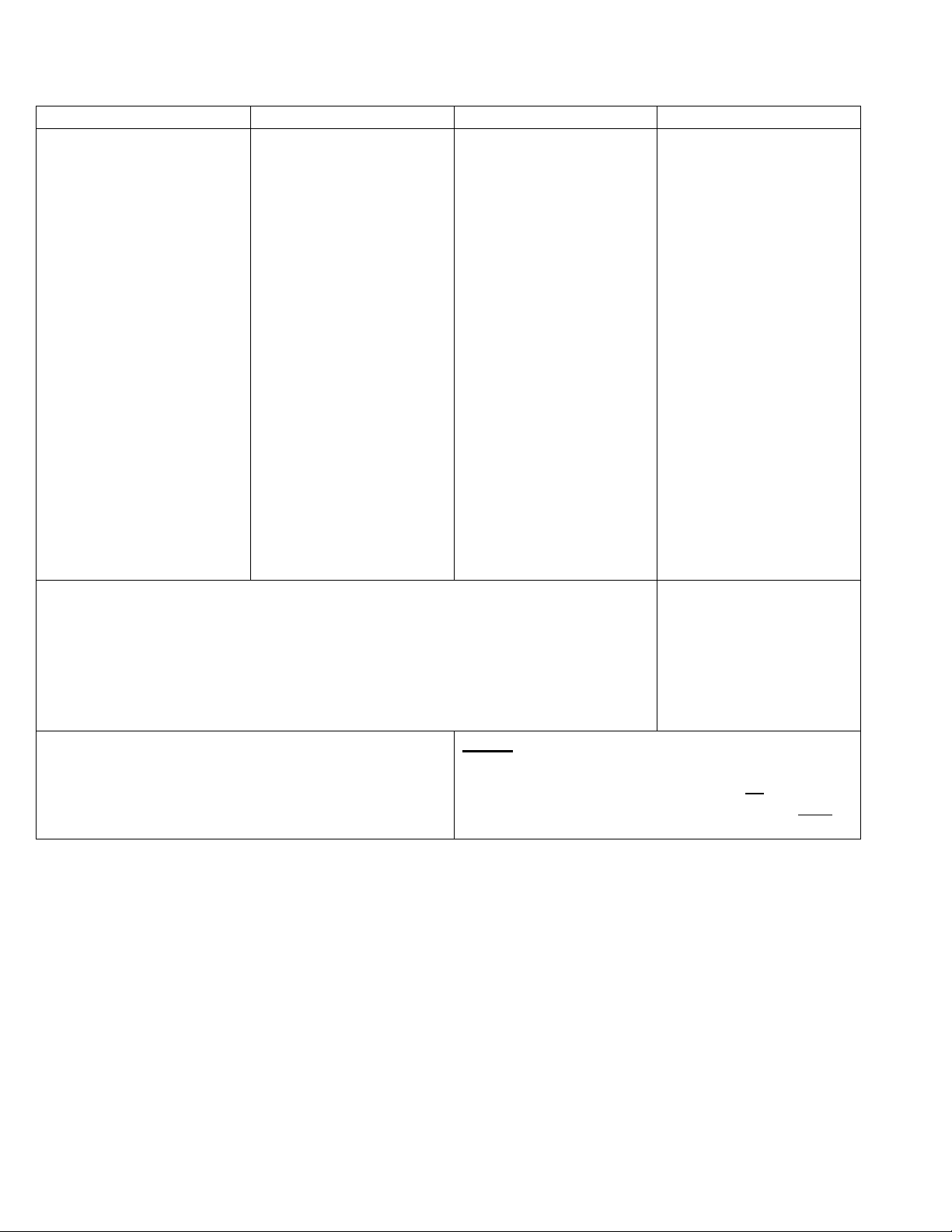
Will / shall
Be going to
Future continuous
Future perfect
1. dự đoán (không căn
cứ), đề nghị được giúp đỡ
ai đó, đề nghị lịch sự, lời
hứa, đề xuất
Ex1: Perhaps, it will rain.
Ex2: Will you help me
with the dishes?
2. quyết định tại chỗ (on-
the-spot)
Ex:
A: “Your clothes are
dirty.”
B: “Are they? I’ll wash
them.”
3. ý kiến, hy vọng, nỗi sợ,
đặc biệt sử dụng với
think, expect, fear, hope,
suppose …
Ex: I think he’ll pass the
test.
1. dự định
Ex: I know my clothes
are dirty. I’m going to
wash them tomorrow.
2. hành động có kế
hoạch trước
Ex: She’s going to take
her driving test next
month.
3. hành động tương lai
có thể tiên đoán trước
(kết quả của một điều
gì)
Ex: He doesn’t know
how to light a fire. He’s
going to burn himself.
4. sự việc xảy ra có căn
cứ
Ex: She’s going to have
baby (Her belly is
already big.)
1. hành động đang diễn
ra tại thời điểm xác định
trong tương lai
Ex: I’ll be flying to
Paris this time
tomorrow.
2. Suy luận logic về
hành động của ai đó ở
thời điểm hiện tại
Ex: He will be sleeping
now. (It’s midnight.)
3. Hành động có kế
hoạch từ trước (dùng
thay HTTD)
Ex: I’ll be seeing Sam
tonight. Would you like
me to tell him the news?
1. hành động hoàn tất
trước một thời điểm nhất
định trong tương lai,
thường dùng với before,
by, by then, by the time,
until / til
Ex: By the end of July,
he will have been in
Athens for two months.
2. suy luận logic về
hành động của ai đó
Ex: He will have gone to
sleep by now.
Future perfect
continuous
Hành động diễn ra đến
một thời điểm trong
tương lai (nhấn mạnh
tính liên tục), thường
dùng với by, for
Time expressions
Tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, tonight, soon,
next week/month/year, in a week/month/year…
Notes: by / before dùng với Future perfect trong
câu khẳng định, until trong câu phủ định
Ex1: She will have cleaned the house by 6 oclock.
Ex2: She won’t have cleaned the house until 6
oclock.
OTHER WAYS OF EXPRESSING THE FUTURE
Be + to infinitive: future plans, instructions
Ex1: The meeting is to take place on Wednesday.
Ex2: You are not to leave the premises until 17:00.
Be about + to infinitive / Be on the point of + gerund: immediate future (tương lai tức thì)
Ex1: They are about to leave. (The taxi is coming to pick them up.)
Ex2: We are on the point of finalizing the exam paper (in 5 minutes).
C. CÁC THÌ QUÁ KHỨ
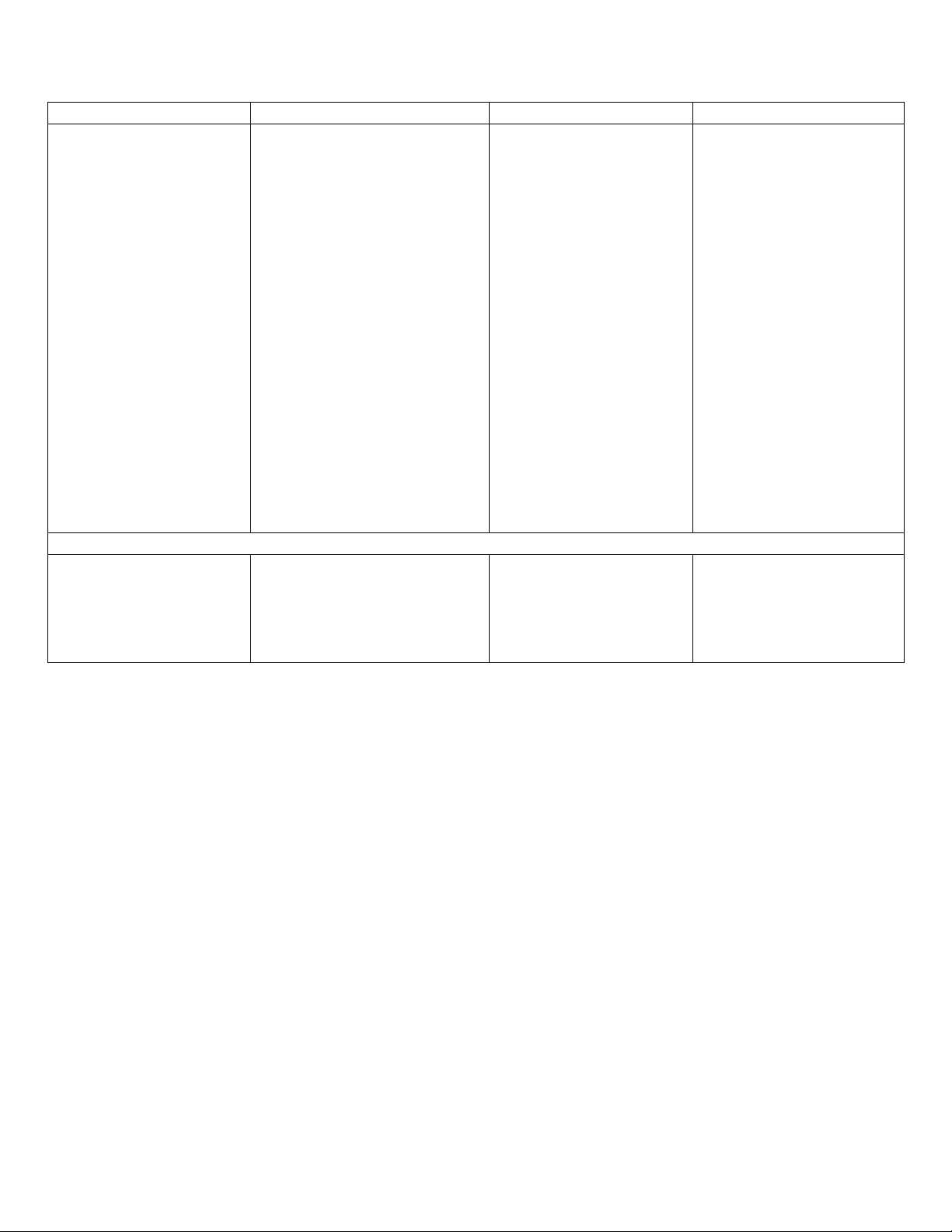
Past simple
Past continuous
Past perfect
Past perfect continuous
1. Hành động xảy ra và
kết thúc trong quá khứ
Ex: She left the room
one hour ago.
2. Thói quen trong quá
khứ
Ex: He traveled / used to
travel a lot when he was
young.
3. Chuỗi hành động
ngắn, liên tiếp
Ex: She stood up, picked
up her briefcase and left
the office.
4. Hành động trong quá
khứ sẽ không lặp lại
Ex: Marilyn Monroe
starred in “The Seven
Year Itch”.
1. Hành động đang tiếp diễn
tại một thời điểm xác định
trong quá khứ
Ex: She was still working at
8 oclock yesterday evening.
2. Hành động đang xảy ra thì
hành động khác chen ngang
Ex: She was leaving when
the phone rang.
3. Các hành động cùng diễn
ra song song
Ex: While Jane was getting
dressed, Tom was enjoying
his coffee.
4. Yêu cầu lịch sự
Ex: I was wondering if you
could help me.
1. Hành động xảy ra
trước hành động khác
trong quá khứ
Ex: She had already
typed all the letters
before her boss arrived.
2. Hành động xảy ra
trước một thời điểm xác
định trong quá khứ
Ex: Maria had gone to
sleep by 9 p.m last night.
1. Hành động kéo dài đến
khi diễn ra một hành
động khác trong quá khứ
Ex: She had been cooking
all day long when Tom
came home with some
fish and chips.
2. Hành động để lại kết
quả rõ ràng trong quá khứ
Ex: She was covered in
paint because she had
been painting her room.
Time expressions
Yesterday, then, ago
How long ago …?
Last
night/week/month...
While, when, as, all
morning/evening/day/night…
Before/by the time,
after, already, just, for
…
For, how long, before,
until…
USED TO / GET USED TO / WOULD
Used to + to inf: Thói quen trong quá khứ
He used to work till late at night.
This theatre used to be school.
Would + bare inf: hành động lặp đi lặp lại / lề thói trong quá khứ
When I was at my grandparents’ cottage, I used to get up early and go for a ride.
Be / get used to + gerund: thói quen hiện tại
She isn’t used to driving on the left.
I haven’t got used to living abroad yet.
LƯU Ý KHI LÀM BÀI TẬP PHẦN THÌ
(THE SEQUENCE OF TENSES)
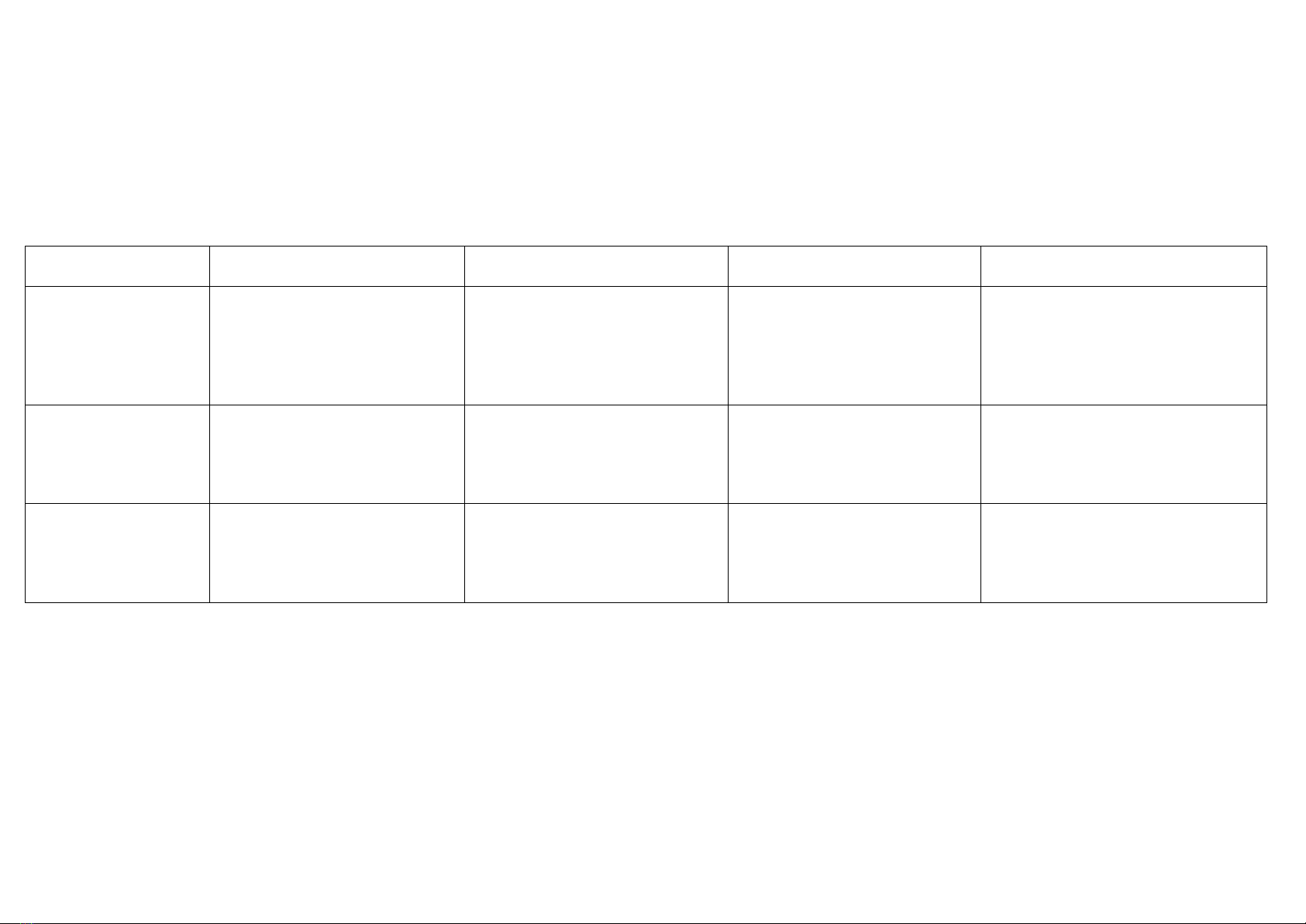
1. Các công thức cơ bản
Simple / Indefinite (đơn)
Continuous / Progressive
(tiếp diễn)
Perfect
(hoàn thành)
Perfect continuous
(hoàn thành tiếp diễn)
Present (hiện tại)
S + V (s/es)
I play.
She plays.
Lina brushes her hair.
S + am/is/are + V-ing
I am playing.
She is playing.
Lina is brushing her hair.
S + have/has + pp (ed/ cột 3)
I have played.
She has played.
Lina has brushed her hair.
S + have/has + been + V-ing
I have been playing.
She has been playing.
Lina has been brushing her hair.
Past (quá khứ)
S + V (ed / cột 2)
I played.
They played.
S + were / was + V-ing
I was playing.
They were playing.
S + had + pp (ed/ cột 3)
I had played.
They had played.
S + had been + V-ing
I had been playing.
They had been playing.
Future (tương lai)
S + will / shall + V (bare)
I will play.
Tom will write.
S + will/shall + be + V-ing
I will be playing.
Tom will be writing.
S + will/shall + have + pp
(ed/ cột 3)
I will have played.
Tom will have written.
S + will/shall + have been + V-ing
I will have been playing.
Tom will have been writing.
S+ SUGGEST/ PROPOSAL/ PROPOSE + that + S + V (bare inf)/ should + V(bare inf)
It is / was + essential/important/necessary … + that + S + V (bare inf)/ should + V(bare inf)
The first time / the last time + S1 + V2 + S2 + V2 / V (was / were + V-ing) # This is / It is the first/second… time + S + have / has + pp (ed/ cột 3)
This was / It was the first/second… time + S + had + pp (ed/ cột 3)


























