2
5. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Theoretical research and numerical simulation analysis are used.
6. NEW CONTRIBUTIONS OF THE DISSERTATION
(i) Established the nonlinear behavior model of the MIs and employed
this model to determine the seismic behavior of infilled RC frames;
(ii) Established the condition to control failure mechanisms of the RC
frames and proposed the method to design RC frames when considering
the interaction with the MIs based on the modern seismic design
conception;
(iii) Proposed a method to determine the interactive forces between
the frame and the MIs as well as a method to design RC frame columns
in shear considering these interactive forces.
7. LAYOUT OF DISSERTATION
The thesis consists of preface, four chapters, and conclusions,
presented in 116 pages with 29 tables, 55 figures, 149 references
(Vietnamese: 10, English, Romanian: 139). The appendix has 21 pages.
CHAPTER 1
INTERACTION BETWEEN FRAMES AND MASONRY INFILLS AND
DETERMINATION OF RESPONSES OF THE MASONRY INFILLED RC
FRAMES UNDER LATERAL IMPACT
1.1. INTRODUCTION
Contrary to the previous conception that considers MIs as non-
structural elements, the field observation results showed that MIs are the
cause of failures: columns, beam-column joints, and the collapse of
buildings, etc. under seismic action. This issue has attracted many studies
worldwide.
1.2. INTERACTION BETWEEN FRAMES AND MASONRY INFILLS AND
BEHAVIOR OF MASONRY INFILLED RC FRAMES UNDER LATERAL
IMPACT
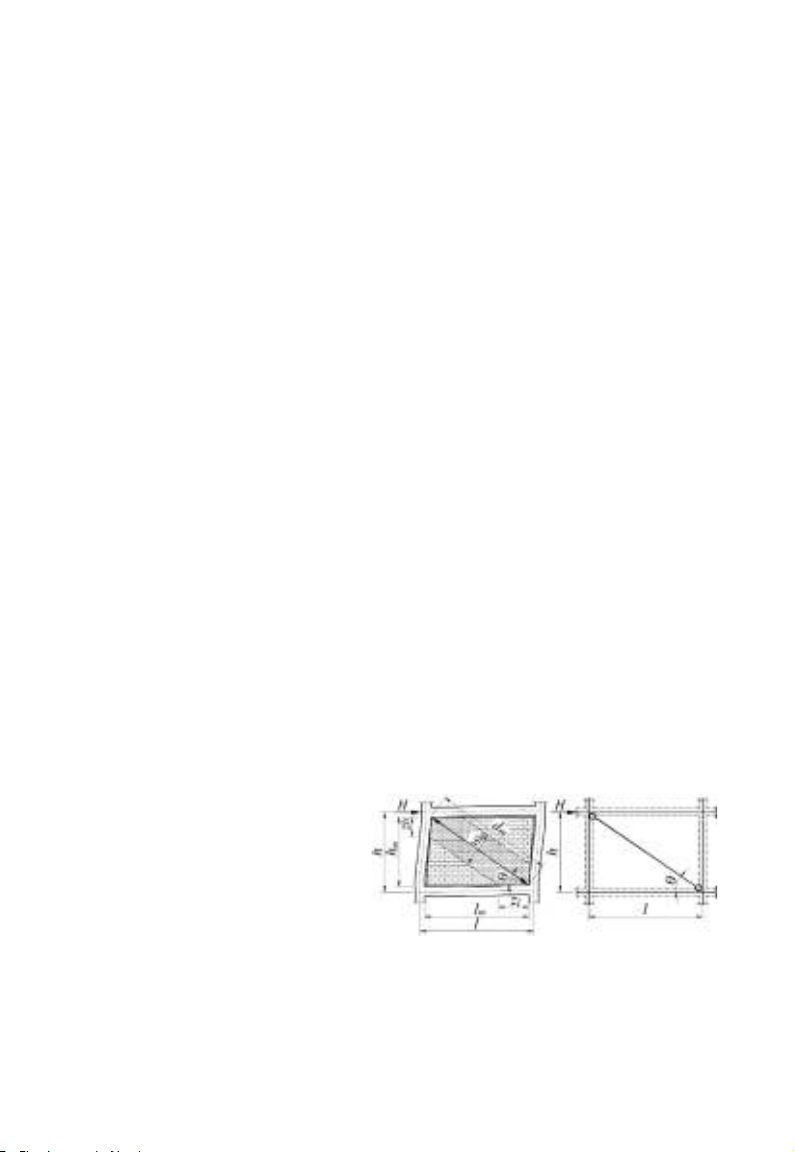
1.2.1. Interaction between frames and MIs under lateral impact
The behavior of MIs in the frames
under lateral impact can be divided
into two stages. At the first stage,
before the frame-MI contact surfaces
are cracked, the structure behaves like
a monolithic vertical cantilever; and at
the second stage after the contact
surfaces are cracked at the unloaded
corners (Figure 1.3a). In the remaining
contact regions, interactive forces appear (Figure 1.3b).
a) b)
Figure 1.3. The behavior of MI RC
frames and interactive forces in the
contact regions