TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 490 - THÁNG 5 - SỐ 1 - 2020
207
protein A in pregnancyrelated gynaecologic
emergency. Human Reproduction. 2(7): p. 615-616.
4. Kaplan Beth C, Dart Robert G, Moskos Margo,
et al.,(1996). Ectopic pregnancy: prospective study
with improved diagnostic accuracy. Annals of
emergency medicine. 28(1): p. 10-17.
5. Phạm Thị Thanh Hiền,(2007). Nghiên cứu giá
trị nồng độ progesteron huyết thanh kết hợp với
một số thăm dò phụ khoa trong chẩn đoán chửa
ngoài tử cung chưa vỡ, in Luận án tiến sỹ y học,
Đại học y Hà Nội: Hà Nội.
6. Bischof P, Reyes H, Herrmann WL, et
al.,(1983). Circulating levels of
pregnancy‐associated plasma protein‐A (PAPP‐A)
and human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in
intrauterine and extrauterine pregnancies. BJOG:
An International Journal of Obstetrics &
Gynaecology. 90(4): p. 323-325.
7. Dumps Patrick, Meisser Arielle, Pons
Dominique, et al.,(2002). Accuracy of single
measurements of pregnancy-associated plasma
protein-A, human chorionic gonadotropin and
progesterone in the diagnosis of early pregnancy
failure. European Journal of Obstetrics &
Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 100(2): p.
174-180.
8. Mueller Michael D, Raio Luigi, Spoerri
Stephan, et al.,(2004). Novel placental and
nonplacental serum markers in ectopic versus
normal intrauterine pregnancy. Fertility and
sterility. 81(4): p. 1106-1111.
9. Ugurlu Evin Nil, Ozaksit Gulnur, Karaer
Abdullah, et al.,(2009). The value of vascular
endothelial growth factor, pregnancy-associated
plasma protein-A, and progesterone for early
differentiation of ectopic pregnancies, normal
intrauterine pregnancies, and spontaneous
miscarriages. Fertility and sterility. 91(5): p. 1657-1661.
10.Rausch Mary E, Sammel Mary D, Takacs
Peter, et al.,(2011). Development of a multiple
marker test for ectopic pregnancy. Obstetrics &
Gynecology. 117(3): p. 573-582.
NGHIÊN CỨU MỘT SỐ YẾU TỐ LIÊN QUAN ĐẾN KẾT QUẢ
ĐIỀU TRỊ VIÊM MÀNG NÃO DO PHẾ CẦU Ở TRẺ EM
TẠI BỆNH VIỆN NHI TRUNG ƯƠNG NĂM 2015 - 2017
Phạm Duy Hiền*, Trần Văn Toản*, Nguyễn Văn Lâm*
TÓM TẮT53
Mục tiêu: Nghiên cứu một số yếu tố liên quan
đến kết quả điều trị viêm màng não (VMN) do phế cầu
ở trẻ em. Đối tượng và phương pháp: Nghiên cứu
mô tả, hồi cứu toàn bộ bệnh nhi được chẩn đoán
VMN do phế cầu tại bệnh viện Nhi trung ương từ
tháng 1/2015 đến hết tháng 12/ 2017. Kết quả : có
94 bệnh nhân trong nghiên cứu với lứa tuổi mắc nhiều
nhất là 1–12 tháng (66%), nam nhiều hơn nữ
(1.85/1), hay gặp mùa Đông Xuân, chủ yếu ở vùng
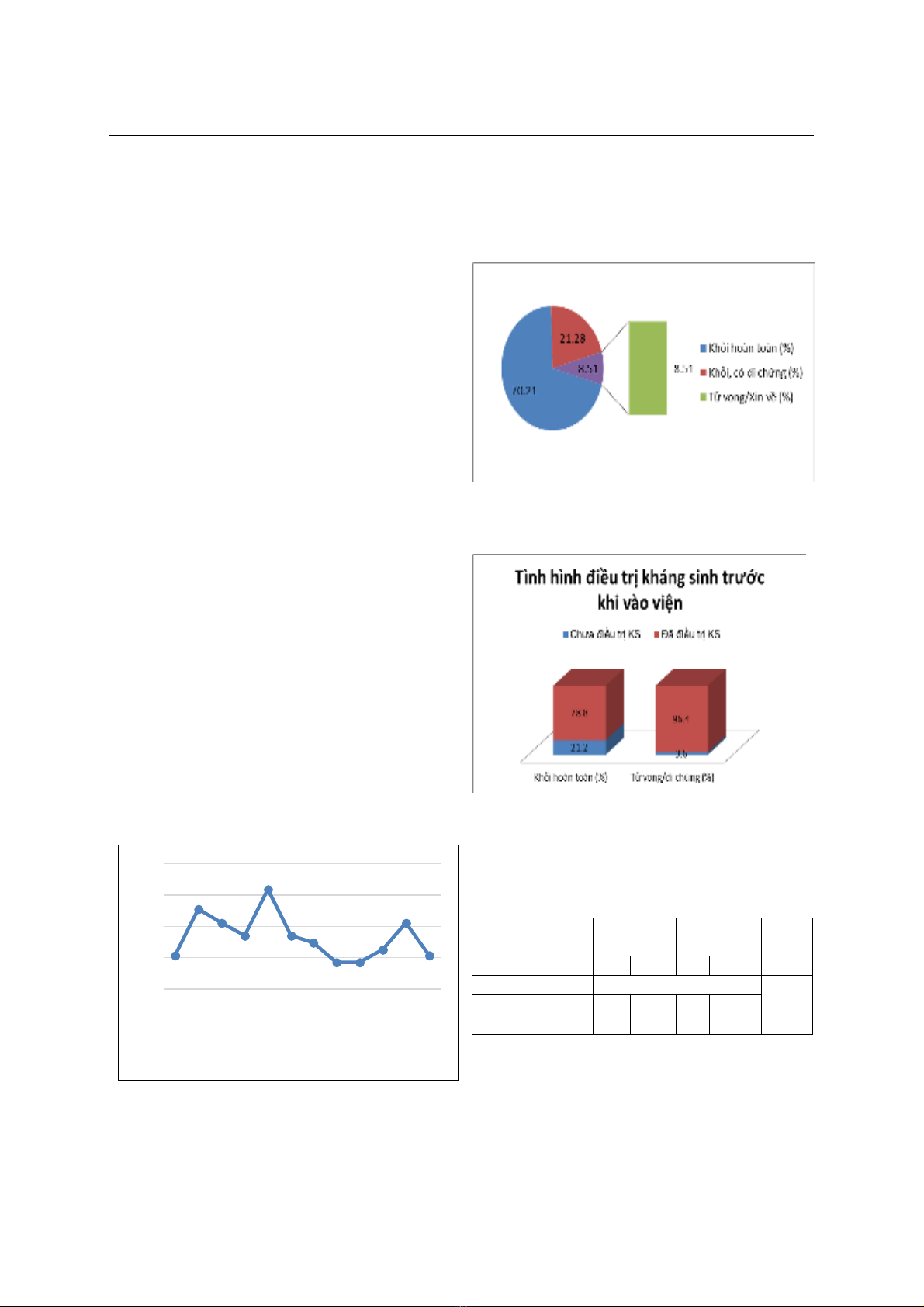
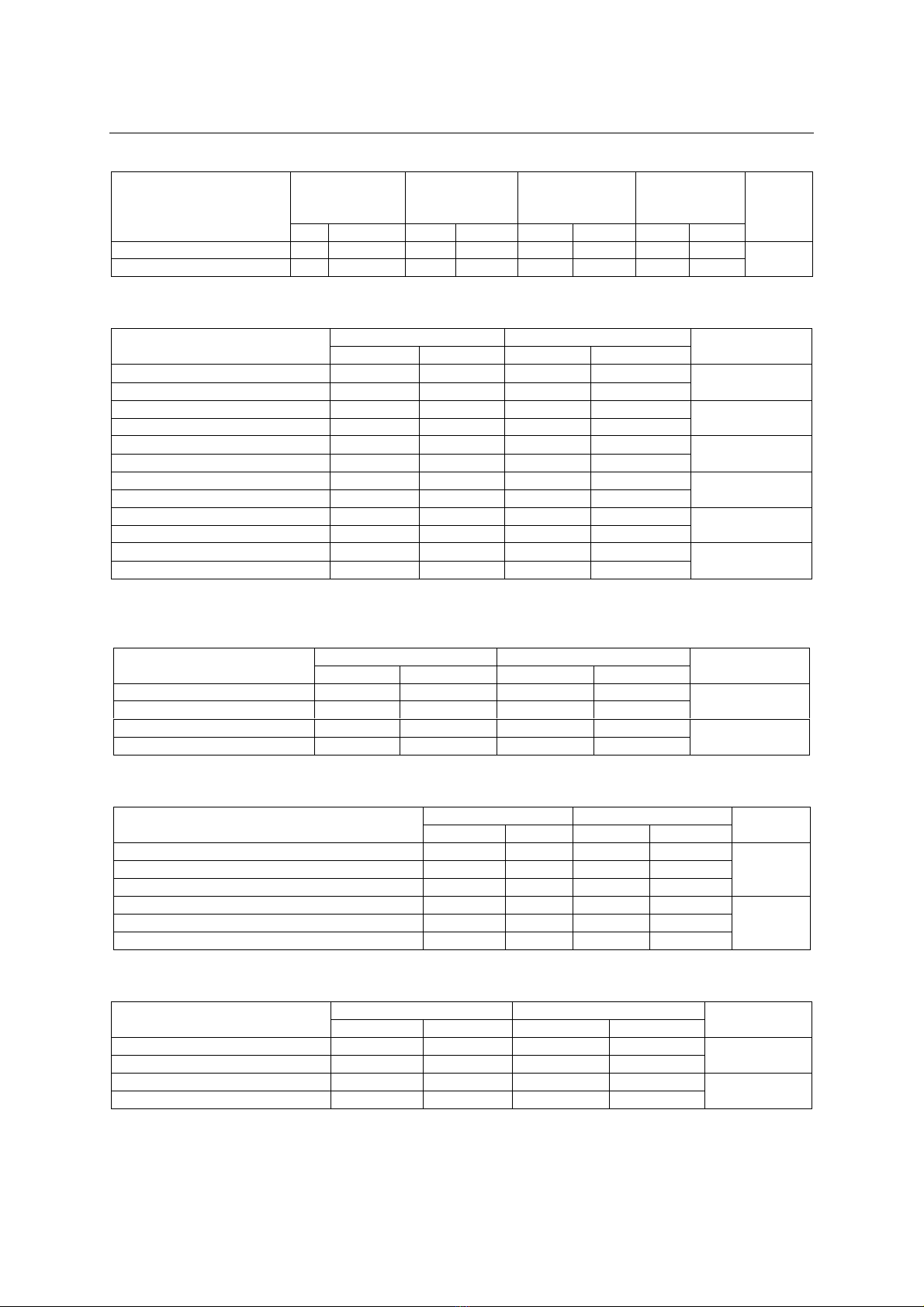
nông thôn (71,3%). Trẻ < 24 tháng: tỷ lệ tử vong, di
chứng cao (34.7%) (p = 0,04); thời gian bị bệnh đến
khi vào viện: tỷ lệ khỏi hoàn toàn: <2 ngày: 100%,
4-6 ngày: 57,1%, sau 7 ngày: 50% (p<0,01). Các
triệu chứng vào viện nặng: rối loạn ý thức, co giật, ran
phổi, suy hô hấp, hôn mê có tỷ lệ tử vong/di chứng
cao hơn (p <0,05). BC< 5G/L; TC< 150G/L; GOT,
GPT tăng cao; DNT: Cl- < 120 mmol/l, protein ≥1g có
tỷ lệ tử vong, di chứng cao (p<0,05). Kết luận: Viêm
màng não do phế cầu gặp nhiều ở trẻ từ 1- 12 tháng.
Một số yếu tố liên quan đến kết quả điều trị: trẻ < 24
tháng; vào viện muộn; triệu chứng vào viện nặng:
rốiloạn ý thức, co giật, suy hô hấp; protein DNT tăng,
Cl - DNT giảm; men gan tăng; BC, TC máu giảm.
Từ khóa:
viêm màng não do phế cầu, ở trẻ em
*Bệnh viện Nhi Trung ương
Chịu trách nhiệm chính: Phạm Duy Hiền
Email: duyhien1972@yahoo.com
Ngày nhận bài: 12.4.2020
Ngày phản biện khoa học: 13.4.2020
Ngày duyệt bài: 22.4.2020
SUMMARY
EVALUATION OF MANY RISK FACTORS OF
MENINGITIS DUE TO STREPTOCOCUS
PNEUMONIAE IN CHILDREN
Objective: to evaluate many risk factors of
meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae in chilren.
Methods: medical records of all the patients with
diagnosis of meningitis due to Streptococcus
pneumoniae in VN National Children Hospital from
1/2015 to 12/2017. Results: 94 patients were
identified. The most age range from 1month to 12
months (66%), male/female (1,8/1), more common in
Spring and rural area (71,3%). Patient < 24 months:
higher mortality and sequelae ( 34,7%) (p=0,04). Time
from occurence to admission: no sign: < 2 day: 100%,
4-6 day: 57,1 %, after 7 day: 50 % (p<0,01). Some
severe adimssion symptoms: mental disorder, paralysis,
respiratory failure,..: higher mortality and sequelae (p<
0,05): WBC< 5G/l, PLT: < 150 G/L, evalated GOT, GPT.
Cerebral fluid: Cl: Cl- < 120 mmol/l, protein ≥1g higher
mortality and sequelae (p<0,05)
Keywords:
Streptococal meningitis, children
I. ĐẶT VẤN ĐỀ
Viêm màng não do phế cầu chiếm tỷ lệ khá
cao trong các viêm màng não mủ nói chung.
Bệnh diễn biến phức tạp, điều trị khó khăn, tỷ lệ
tử vong cao, di chứng nặng nề về trí tuệ, tinh
thần, vận động và là gánh nặng cho gia đình và
xã hội[2]. Tỷ lệ tử vong của VMN do phế cầu nói
chung là cao hơn so với nhiều viêm màng não do
vi khuẩn khác. Nghiên cứu một số yếu tố liên