
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 70 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 7, Issue 7, November–December 2016, pp.70–81, Article ID: IJM_07_07_007
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
SUCCESSION PLANNING AND KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT WITH KNOWLEDGE SHARING
PERSPECTIVE IN BUSINESS FAMILIES
Antonette Asumptha J. and Mathan C.
National Institute of Technology, Trichy, India
ABSTRACT
Objective: Loss of knowledge is a critical factor for organizations. This paper approaches the
topic of a combined research of knowledge management and succession planning. Factors like
death and family partition and sudden loss of the key member is faced with succession planning.
This research has a glimpse of knowledge management and detailed study on succession planning
in particular family owned business.. The scarcest resource today is top management talent that
can handle anything negative that arises.
Methods: Here in this research we have tailored Structural Equation Modeling and Theory of
Planned Behavior.
Findings: From a managerial perspective, our results suggest that cultivating positive
normative beliefs of significant members motivation to comply as well as positive attitude for
sharing knowledge.
Novelty: A causal path from Attitude to Perceived Behavioral Control.
Key words: Family owned business, Succession Planning , knowledge management, knowledge
sharing..
Cite this Article: Antonette Asumptha J. and Mathan C., Succession Planning and Knowledge
Management with Knowledge Sharing Perspective in Business Families. International Journal of
Management, 7(7), 2016, pp. 70–81.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=7&IType=7
1. INTRODUCTION
Knowledge leads to successful competitive advantage. Hence we accentuate on strategic knowledge
management. Knowledge management is nothing other than collecting, using, disseminating and growing
knowledge in a concern. It involves the use of people, technology and processes (Awad and Ghaziri 2004,
2-3). One process that can be put in place is to enhance the capture of knowledge is succession
management.
Succession planning has been defined as “the process of ensuring that qualified persons are available to
assume key managerial positions once the positions are vacant” (Mondy and Noe 2005, 506).
Succession planning is an explicit plan for management succession to fill in key roles within the
company at all levels of the organization. Succession planning is a process whereby an organization

Succession Planning and Knowledge Management with Knowledge Sharing Perspective in Business Families
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 71 editor@iaeme.com
ensures that employees are recruited and developed for future purpose. Through the succession planning
process, organizations can recruit superior employees, develop the recruited person’s knowledge, skills,
and abilities, and prepare them for advancement or promotion for more challenging roles. (Kathy, PHD)
Some jobs are the lifeblood of the organization, hence it can’t be neglected or kept vacant for a
long time, thus succession planning came into being. Succession planning should be actively pursued
when the organization expands and loses the key role employees. The developmental needs of the
employee have to be fulfilled and ensured that all employees are developed to fill in their key roles which
are expected out of them.
1.1. Advantages of Succession Planning
To face sudden attrition the organization should be well prepared in advance and this is done by success
planning.
Key roles are maintained.
Identification of employee strengths, skills, abilities.
A motivating factor for the employees.
Advantage of recruiting internal employees who are aware about the organization reduces cost and
time.
The process of succession planning is as follows:
1. In order to ensure leadership continuity, creating a talent pool.
2. Building potential successors.
3. Scrutinizing candidates and obtaining the best candidature.
4. Yielding a greater return on investment by cotemplating resources.
Effective succession planning is required to recognize the lifeblood jobs of the organization essential to
be filled up and is critical.
2. GAP AND OBJECTIVES
The story of family succession has been there right from the 1950’s.Brazil has done a lot of studies in the
area of succession planning but Asia hasn’t touched this part. Hence we draw attention to succession
planning combined with knowledge management in family business. This paper is aimed to bring out the
concept of succession planning and knowledge management in family owned businesses.
3. COMMON PITFALLS INCLUDE
Full responsibility delegated to human resources
Succession Planning has to be updated regularly or else there would be adverse results. Friendships and
relationships cloud the judgment
Before getting into in depth understanding of succession planning let us consider what knowledge
management.
4. KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
“Systematic management of knowledge takes on new importance with the current economic reality where
knowledge is a differentiating competitive factor for individuals, corporations, and nations. This reality is
the driving force behind broad adoption.
Knowledge Management: A Working Definition Simply stated, in the opinion of this author, the
objectives of knowledge management (KM) are: (1) To make the enterprise act as intelligently as possible
to secure its viability and overall success and (2) To otherwise realize the best value of its knowledge
assets.” KARL M. WIIG (1997).
Antonette Asumptha J. and Mathan C.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 72 editor@iaeme.com
5. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SUCCESSION PLANNING AND
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
Eddleston and Kellermanns (2007) portray that family business may be stuck without a succession
strategic process. Succession planning is important when the present generation wants to grow and develop
the new generation. Hence transfer of knowledge from current generation to the new generation in family
owned business is crucial. Morris et al. (1997) and Tirsadari and Dhewanto (2012). Two types of
knowledge that is used in succession planning are implicit and explicit knowledge, explicit knowledge is
easily codified as a excel database while implicit knowledge is concerned with leadership,
entrepreneurship and risk taking. Factors that directly affect the succession process are: (1) tendency of the
holder to leave, (2) disposition of the successor to take over, (3) a deal among the family members to
maintain family involvement in the business, (4) acceptability of the individual roles, and (5) succession
planning (SHARMA;
CHRIMAN; CHUA, 2003).”W. Gibb Dyer (1989) has corroborated on the reason why should a family
business be professionalized.” One reason among them is acquiring or developing management expertise
to prepare for leadership succession. The founder or family leader may want to retire in the near future and
may feel that family members in the business need additional training before assuming the mantle of
leadership, or the founder may feel t9hat no one in the family is capable of running the business after he or
she is gone. A search is then made to find managers that can be trusted with the future leadership of the
firm.”
Succession planning, generally, in whatever industry it may be, is critical, especially when the business
is transferred to the next generation. Depending upon Coleman (2013) here one should appreciate the
entrepreneurship skills of the team leader as he has already set up the platforms, the new generation just
needs to build on. Here the team leader selects the new leader as he retires, here is way knowledge sharing
plays a role. the succession planning helps the leader to select the right one trained for taking up the
position.
6. RESEARCH MODEL
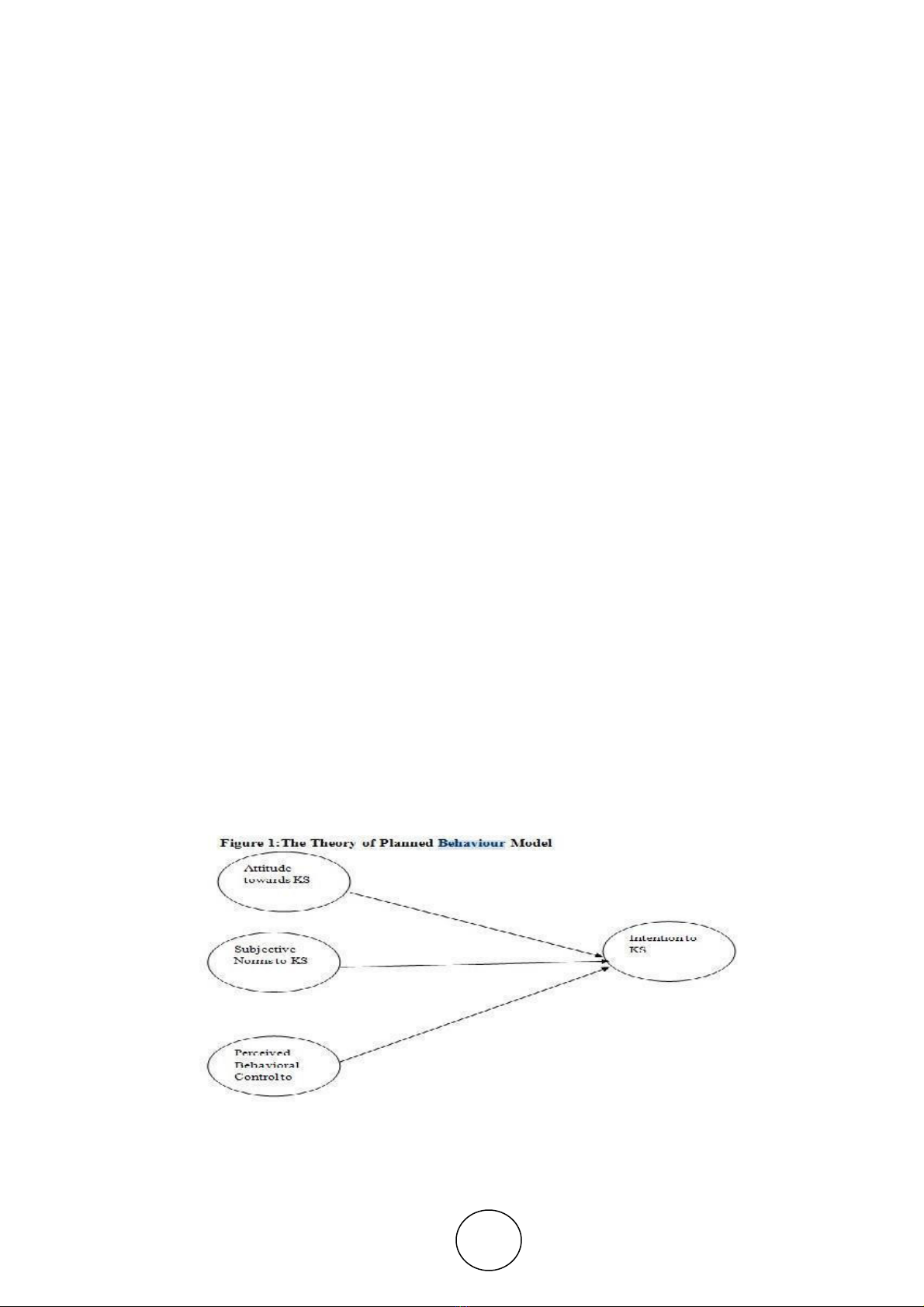
6.1. The Theory of Planned Behaviour Model
Ajzen (1992) proposed the TPB model an extension of TRA model. Attitude is the favorable or
unfavorable effect of performing a behaviour. Subjective Norms is the social pressure for performing the
behavior. Perceived Behavioral Control is the ease or difficulty in performing behaviour
Figure 1 The Theory of Planned Behaviour Model
Succession Planning and Knowledge Management with Knowledge Sharing Perspective in Business Families
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 73 editor@iaeme.com
6.2. Hypothesis
The proposed hypothesis are :
H1 Family members attitude has a positive effect on the intention to share knowledge
H2 Family members subjective norms has a positive effect on the intention to share knowledge.
H3 Family members perceived behavioral control has a positive effect on the intention to share
knowledge.
Figure 2 The THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOUR Model
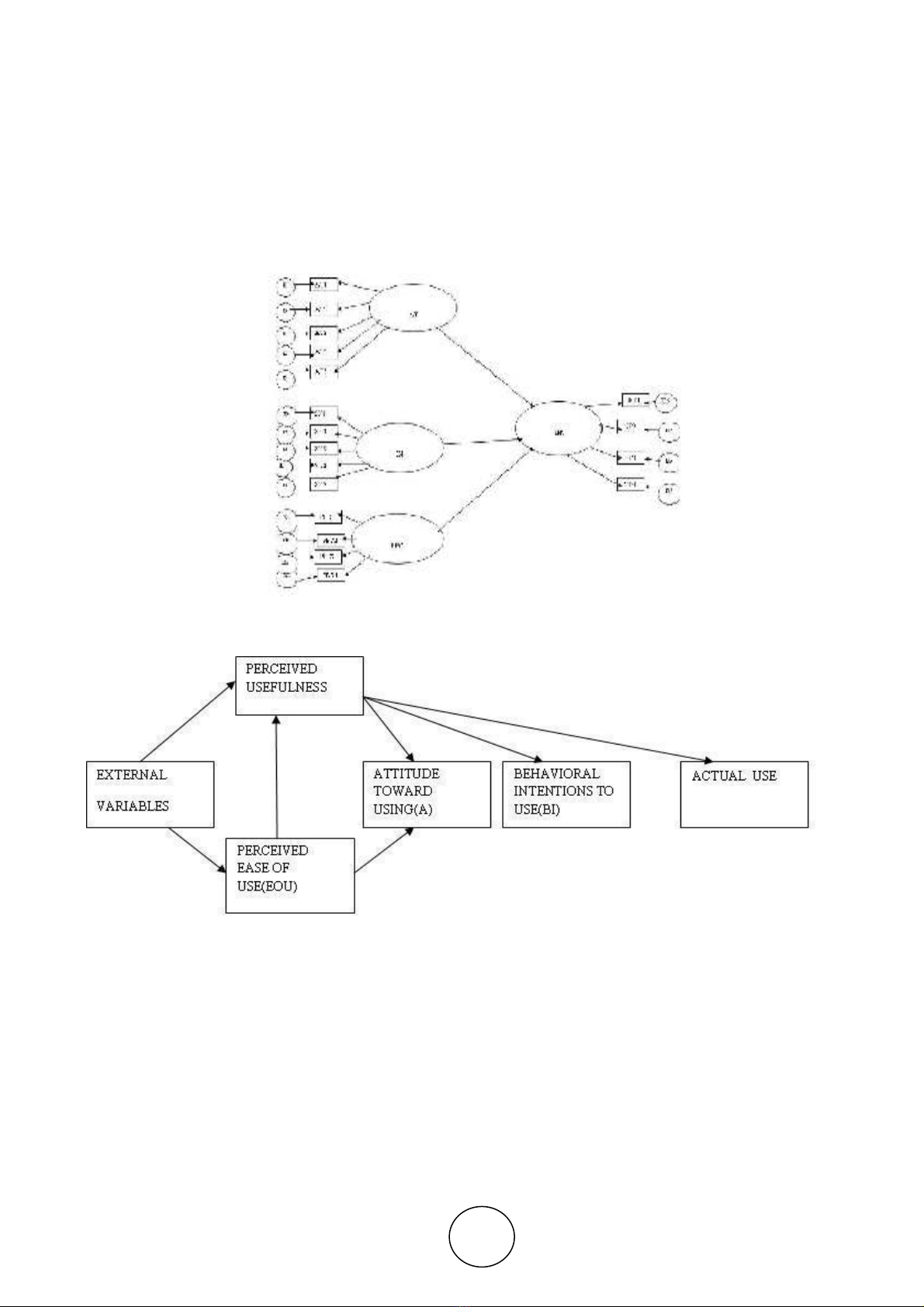
Figure 3 Technology Acceptance Model (Davis et al,1989)
PBC is the perceived ease or difficulty that the individual faces to perform the behaviour (Emma L.
Pelling and Katherine M. White,2009),2001a,b; Bock et al 2005; Ryu et al(2003) & Lin 2007c; Chang
1998, Chau & Hu 2001
Perceived ease of use (PU) – This was defined by Fred Davis as "the degree to which a person believes
that using a particular system would enhance his or her job performance"
Antonette Asumptha J. and Mathan C.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 74 editor@iaeme.com
Figure 4 Extended Model
The Extent to Which a Person Feels Able to Enact the Behaviour: has two Aspects Attitude Influences
Pbc: How much a Person has Control over The Behaviour and Attitude Influences Pbc: How Confident a
Person Feels about being Able to Perform the Behaviour
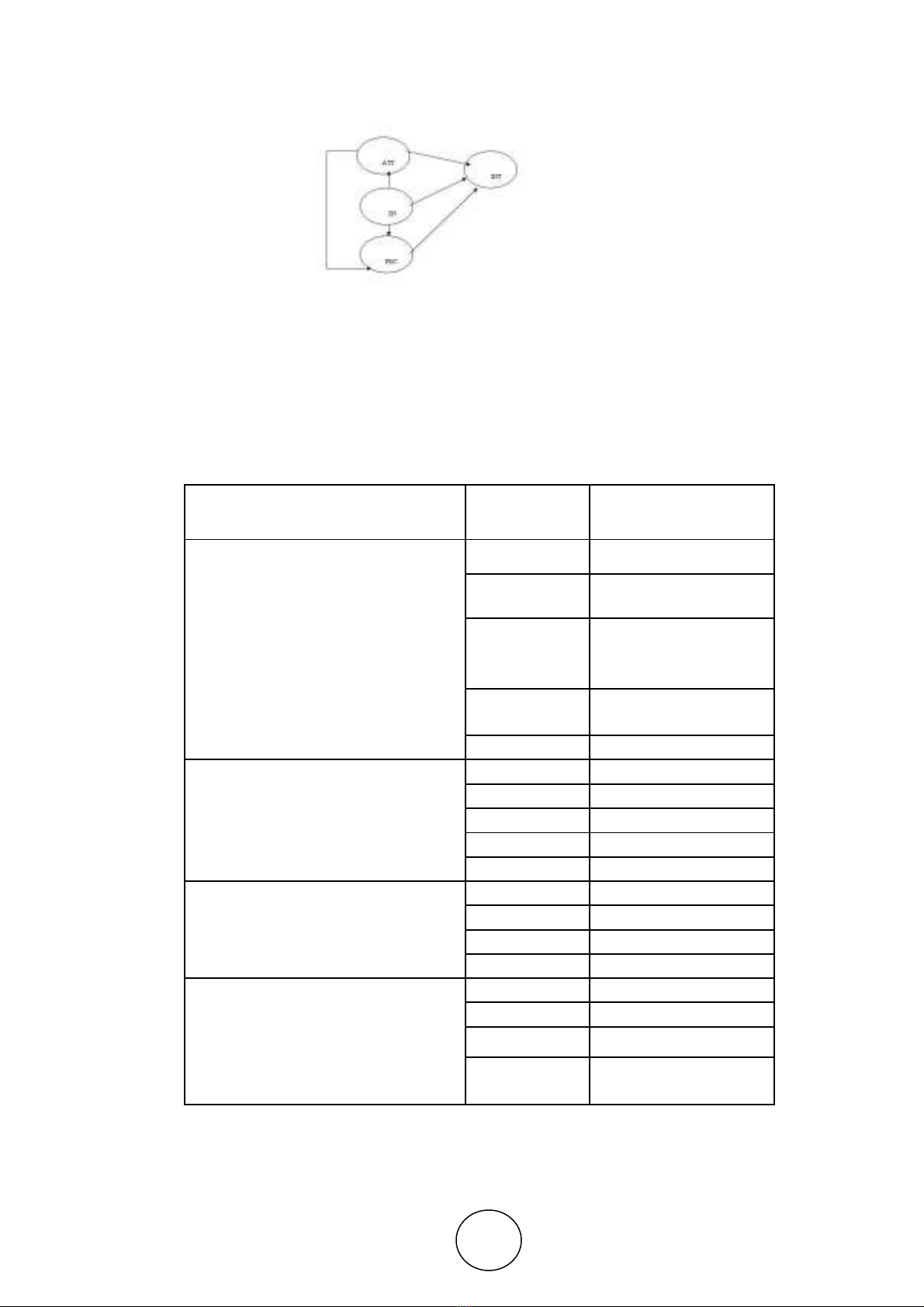
Table 1 Measurement Model Fit –Table1 Measurement Model Fit
Factor
Latent Constructs Item Loading
AT1 0.70
Attitude toward knowledge
AT2 0.65
AT3 0.72
sharing (AT)
AT4 0.75
AT5 0.83
SN1 0.66
SN2 0.79
Subjective Norm(SN) SN3 0.78
SN4 0.71
SN5 0.76
PBC1 0.47
Perceived Behavioral PBC2 0.73
Control(PBC) PBC3 0.63
PBC4 0.58
INT1 0.79
Intention to share knowledge INT2 0.59
(INT) INT3 0.73
INT4 0.62


![Tài liệu tập huấn bảng kiểm viên thuốc tránh thai cho giảng viên tuyến tỉnh [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250422/gaupanda088/135x160/3731745286813.jpg)










![Sổ tay Hướng dẫn truyền thông về lao động trẻ em [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251114/kimphuong1001/135x160/7201763091001.jpg)







![Cẩm nang Thanh niên hành động [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251017/kimphuong1001/135x160/1521760665202.jpg)




