
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 84 editor@iaeme.com
International Journal of Management (IJM)
Volume 9, Issue 1, Jan–Feb 2018, pp. 84–92, Article ID: IJM_09_01_014
Available online at
http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=1
Journal Impact Factor (2016): 8.1920 (Calculated by GISI) www.jifactor.com
ISSN Print: 0976-6502 and ISSN Online: 0976-6510
© IAEME Publication
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE
BEHAVIOR OF TRANSFORMATIONAL
LEADER AND JOB SATISFACTION OF
MEDICAL STAFF WORKING IN LABORATORY
AND BLOOD BANK DEPARTMENT- KING
FAHAD HOSPITAL, HOFUF, ALHASSA, K.S.A
Baqer Abbas Albeladi
MBA, School of Business, King Faisal University, Hofuf, K.S.A
Musaddag Elrayah
Assistant Professor, King Faisal University, School of Business, Hofuf, K.S.A
ABSTRACT
This study aims to investigate the interrelationship between behaviors of
transformational leader and satisfaction of medical staff in their jobs in laboratory
and blood bank department at King Fahad Hospital Hofuf (KFHH). A survey
questionnaire consists of forty five questions adopted from (Multi-Factor Leadership
Questionnaire (MLQ) short Form5X),Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (Short
form) , Researchers four questions regarding transformational leaders behaviors and
five demographic questions about: age, sex, experience and job title used in this
study. Thirty-six responses, which represent 32% response rate, found valid for
analysis. The Findings show the present of one behavior of transformational leader
behaviors, which is an idealized influence and overall job satisfaction. Moreover, the
study finds a positive correlation between the behavior of transformational leader and
medical staff job satisfaction. Furthermore, significant correlation between an
idealized influence, inspirational motivation and job satisfaction.
Key words: Healthcare industry, Laboratory, Blood Bank, Transformational leader,
Job satisfaction.
Cite this Article: Baqer Abbas Albeladi and Musaddag Elrayah, The Relationship
Between the Behavior of Transformational Leader and Job Satisfaction of Medical
Staff Working in Laboratory and Blood Bank Department- King Fahad Hospital,
Hofuf, Alhassa, K.S.A. International Journal of Management, 9 (1), 2018, pp. 84–92.
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/issues.asp?JType=IJM&VType=9&IType=1

The Relationship Between the Behavior of Transformational Leader and Job Satisfaction of Medical Staff
Working in Laboratory and Blood Bank Department- King Fahad Hospital, Hofuf, Alhassa, K.S.A
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 85 editor@iaeme.com
1. INTRODUCTION
"Medical Laboratory Science (also known as Clinical Laboratory Science) is one of the main
branches of modern medicine. It involves collection and analysis of patients' blood and body
fluid specimens, to provide data essential for diagnosing diseases and monitoring body
response to treatment. While accounting for only 5% of hospitals budgets, estimated that 60-
70% of diagnostic and therapeutic medical decisions influenced by laboratory results
(Forsman RW 1996) .Medical laboratories divided into small, medium and large volume
laboratories based on the volume of testing and the variety of services offered. Large volume
laboratories usually receive hundreds or even thousands of specimens daily and perform tests
with varying levels of complexity. Consequently, very strict regulations were put in place to
determine qualifications and skills of personnel involved in analyzing and interpreting these
tests"( Al Khamees, M. 2017)." Blood banking refers to the process of collecting, separating,
and storing blood. Today, blood banks collect blood and separate it into its various
components so they will be used most effectively according to the needs of the patient. Red
blood cells carry oxygen, platelets help the blood clot, and plasma has specific proteins that
allow proper regulation of coagulation and healing." Although research has yielded drugs that
help people's bone marrow produce new blood cells more rapidly, the body's response time
can still take weeks, thus donated blood remains an important and more immediate life-saving
resource. Blood is the vital connection to having a healthy body, and according to the
American Red Cross, nearly 5 million people receive blood transfusions each year ".
(American society of hematology).
Healthcare industry needs Leaders who are decision makers, visionary and knows how to
align resources and restructure the units in continuousness changeable industry. An effective
and efficient ways of management need to be used by leader to reserve and sustain resources.
The key to success of this industry depends on human resources who provide the services to
customers. Satisfied employee are more productive (Fischer & Sousa-Poza, 2007). Satisfied
employee definitely affects the healthcare services' quality and leads to customers'
satisfaction, and as a result community satisfaction of healthcare sector (Jimmy P. and Andy
D. 2009). Moreover, leader’s leadership style effects both organization performance and
employee job satisfaction. Employee job satisfaction reflects good leadership and will be used
as an indicator that good leadership leads employee to be more effective (Likhitwonnawut,
1996).
Satisfied employees are more productive (Fischer & Sousa-Poza, 2007). Job
dissatisfaction leads to burnout and, or turnover which both effects quality of work
performance (Fridrkin SX et al 1996). Employee's job satisfaction is not an easy task to
achieve (Albion and Gagliardi, 2007). There are many studies and researches tried to study
the effects of leadership behavior on employee's job satisfaction (Abualrub RF, Alghamdimg
MG.2012; Medley F.LA Rochelle D.1995; Furkan, B., Kara, E., Tascan. &Avsalli, H. 2010;
Rad, A.M. M., &Yarmohammadian, M. H. 2006; Hina Saleem.2014).
2. LITREATURE REVIEW
2.1. Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is one of the factor that positively affect productivity; this concept is widely
studied in researches (Weiss and Copranzano, 1996). The importance of these researches
came from the theory that satisfied employee work more productively (Lim, 2007). Job
satisfaction is "a pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s
job or job experiences " (Locke, 1975, p.1304)".(Spector, 1997) revel that what employee
feel and react with in their jobs or any aspect of their job is called employee job satisfaction.

Baqer Abbas Albeladi and Musaddag Elrayah
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 86 editor@iaeme.com
Furthermore, (Mosadragh, 2003) defined job satisfaction as" the interaction between
employee job, actual done job and environment in which job done". Job satisfaction is not an
easy task to be accomplished by decision makers. Many factors have their contributions to
reach such a task. Generally, these factors are classified into two main categories: overall job
satisfaction, which is most analyzed, and job satisfaction facet, which could be Extrinsic
factors, Intrinsic factors and environmental factors. Extrinsic factors such as wages, job
security. Intrinsic factors such as accomplishment, acknowledgment, independence, benefits,
job importance and motivation (Rad and Yarmohammadian 2006, Mueller & Kim, 2008).
Other factors such as working conditions, communication, coworkers, supervisor help,
workplace environment, organization climate, and reputation of the organization contribute on
employee job satisfaction. Any organization who seek improvement or looking for
understanding a trending phenomenon, like turnover should focus in job satisfaction facet
(Kerber & Campbell, 1987).
2.2. Transformational Leadership
In 1980s, a new leadership theory developed by (Burns, 1978) "transforming leader and
followed by (Bass, 1985) "transformational leadership". According to this theory, Leadership
styles classified into three styles: Transformational leadership style , Transactional
leadership, Passive/Avoidant Leadership Style. Transformational leadership style is “wherein
one or more persons engage with others in such a way that leaders and followers raise one
another to higher levels of motivation and morality (Burns, 1978).The transactional leadership
style "based on the hypothesis that followers are motivated through a system of rewards and
punishment." If the follower does something good, they will be rewarded. If the follower
does something wrong, they will be punished'. The laissez faire style "allows followers for
complete permissiveness, and the group often lacks direction because the leader does not help
in making decisions".
Since the 1990s, transformational and transactional leadership styles are widely used in
research (Burns, 1978). These studies emphasis on transformational leadership behaviors.
Transformational leadership style is “wherein one or more persons engage with others in such
a way that leaders and followers raise one another to higher levels of motivation and
morality". According to (Burns, 1978). (Northouse 2007) defined leadership, as "Leadership
is a process through which an individual influence a group of people to attain common goals".
In leadership research, the most widely used type of leadership style is transforming
leadership (Burns, 1978) which developed by (Bass ,1985) to transformational leadership.
According to (Krishnan, 2005) the valuable character of transformational leader is ability to
motivate employee to achieve more than what are needed.
2.3. Transformational Leadership Behaviors
2.3.1. Idealized Influence
Transformational leaders act as a model for their employee and has an ethical and moral
conduct. They give priority to employee needs when compared to their needs(Tales, 2010).
2.3.2. Inspirational Motivation
Transformational leaders has a vision and able to inspire followers with it by making them
think about future optimism. (Bass and Avolio, 1990; Tales2010).
2.3.3. Intellectual Stimulation
Transformational leaders encourage employee's thinking and motivate them for success,
innovation and creativity. (Burke RJ, Cooper CL. 2006).

The Relationship Between the Behavior of Transformational Leader and Job Satisfaction of Medical Staff
Working in Laboratory and Blood Bank Department- King Fahad Hospital, Hofuf, Alhassa, K.S.A
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 87 editor@iaeme.com
2.3.4. Individual Consideration
Transformational leaders take care of each employee needs and accomplishment by providing
different types of support such as emotional support and work like mentor or coach for every
employee to achieve their goals and objectives. (Bass and Avolio, 1990; Tales2010).
Theoretical framework: From the given literature, following research model and hypothesis
has been formulated.
3. HYPOTHESIS OF THE STUDY
The following hypotheses are taken for the study:.
H1: Transformational leader behavior idealized influence is positively effects subordinate job
satisfaction.
H2: Transformational leader behavior inspiration motivation behavior is positively effects
subordinate job satisfaction
H3: Transformational leader behavior intellectual stimulation behavior is positively effects
subordinate job satisfaction.
H4: Transformational leader behavior individual consideration is positively effects
subordinate job satisfaction.
4. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
This study aims to investigate the interrelationship between behaviors of transformational
leader and subordinates satisfaction. Specific objectives are:
To investigate the interrelationship between behavior of transformational leaders and job
satisfaction between medical staff working in laboratory and blood bank at (KFHH).
To assess the level of job satisfaction between laboratory and blood bank medical staff at
(KFHH).
To provide recommendations for KFHH management.
5. METHODOLOGY
This is study uses quantitative research design. The data collected via survey- based from
primary source (Medical staff working in laboratory and blood bank).It uses descriptive
analysis technique to describe the relationship between variables and Pearson correlation to
test the hypothesis. The population of this study is medical staff working in laboratory and
blood bank department at (KFHH). Al-Hassa, Eastern province, Saudi Arabia. They are
medical staff who are working in different units such: Blood Bank, Microbiology,
Hematology, Immunology, Biochemistry, and Histopathology ….etc. They are medical staff
Baqer Abbas Albeladi and Musaddag Elrayah
http://www.iaeme.com/IJM/index.asp 88 editor@iaeme.com
with at least one-year experience. The study uses simple random technique. All medical staff
that working at (KFHH) laboratory and blood bank consider as a respondents and ask to
identify the presence or absence of transformational leader behaviours in his direct boss where
in this study consider as a supervisor. Moreover, the respondents ask about his/her different
level of job satisfaction. The study use primary data sources through distributing survey. Pilot
study was done by establishing an online survey. A short explanation about the study, it is
practical and theoretical importance and the way to answer the survey provided and only little
responses received due to two reasons: difficulty of the survey English language and inability
to understand the questions. Researcher change the survey to be paper based and acted as a
translator in different groups of participants. Researcher mobile number and email provided
in the survey. To avoid any deviation, answering the survey was in an individual basis and
voluntary. 75 surveys distributed. After one month, 42 surveys received about 56%. Six of
them excluded due to missing answer of some questions. 36 surveys are valid and ready for
analysis. The response rate is 32%. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version
22.0 was used to analyze the data of this study.
6. RESEARCH FINDINGS
6.1. Demographic Analysis
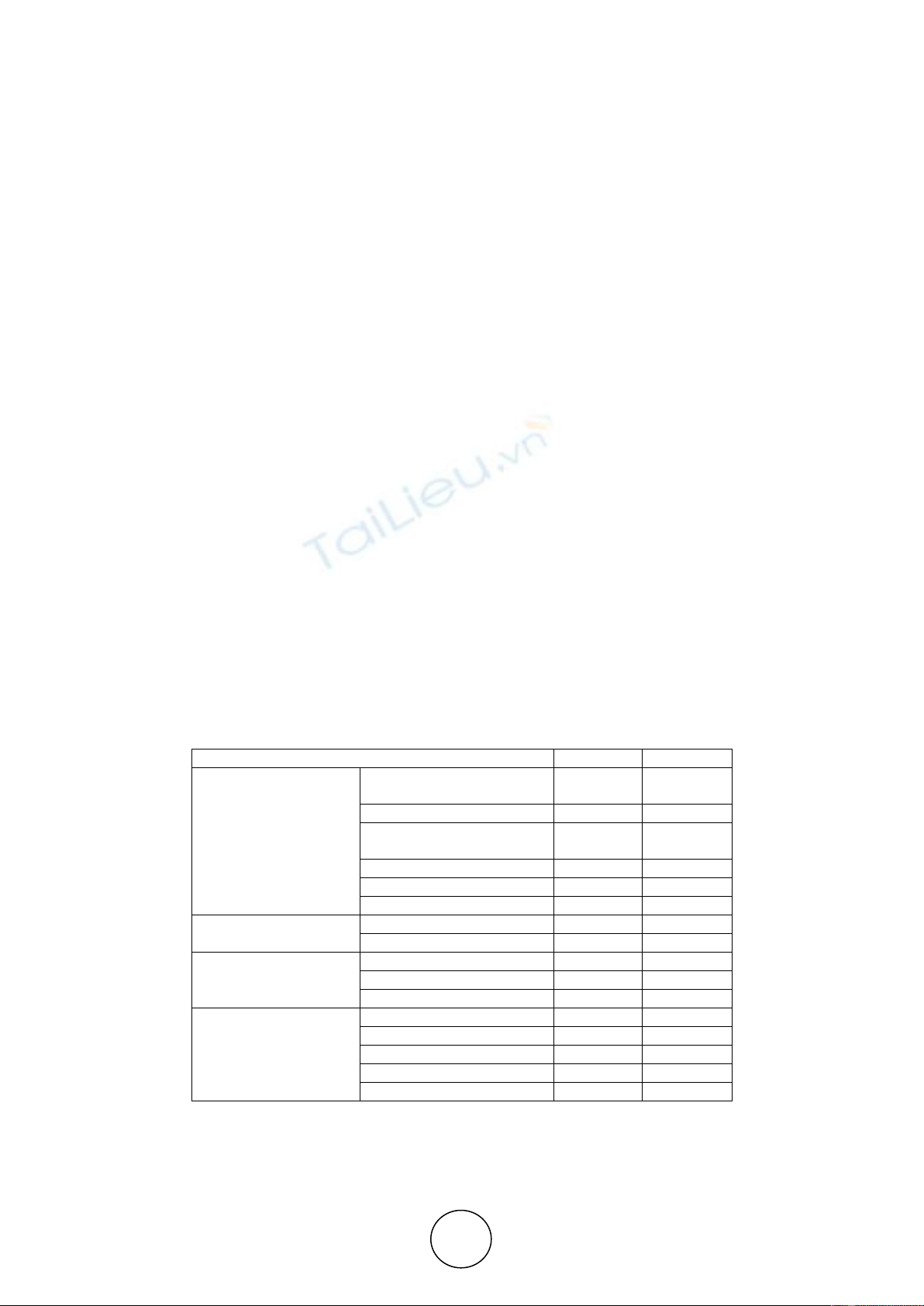
The table below shows the respondents of this study is 36 participants. 86.1% are male and
13.9% are female. The age of 47.2 percentage is between 35-44 years. Meanwhile,25%
between age 21-34. Meanwhile, 22.2% between age 45 to 54 and only 5.6% between age 55
or older. 69.4% has an experience more than ten years which. Meanwhile 19.4% has
experience between 5 to less than 10 years and 11.1% has an experience between two years
and less than 5 years. Technologist represent 36.1% , Technician 38.9%,Specialist physician
8.3% , Senior technologist 11.1% by 4 respondents which indicate one respondent not
included in the population ( see research limitation). Only 2.8% respondent for both
Consultant physician and Nurse. Full demographic data listed in the table below:
Table 1 Demographics data.
CHARCHTERISTICS
Frequency
Percentage
CONSULTANT-
PHYSICIAN
1
2.8
Job Title
SPECIALIST-PHYSCIAN
3
8.3
SENIOR
TECHNOLOGIST
4
11.1
TECHNOLOGIST
13
36.1
TECHNICIAN
14
38.9
NURSE
1
2.8
SEX
Male
31
86.1
Female
5
13.9
Experience
TWO TO LESS THAN 5
4
11.1
FIVE TO LESS THAN 10
7
19.4
TEN YEARS AND MORE
25
69.4
21-34
9
25
Age
35 TO 44
17
47.2
45 TO 54
8
22.2
55 OR OLDER
2
5.6
Total respondents
36
100%
6.2. Descriptive Statistics for Transformational Leader Behaviors
The table below shows: the aggregate mean for each of transformational leader's behavior and
aggregate mean for transformational leadership. As per the criteria mentioned earlier only one


























