
6/12/141 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
COLLECTIONs FRAMEWORK
Nguy n Xuân Vinhễ
nguyenxuanvinh@hcmuaf.edu.
vn
C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ
DATA STRUCTURES
[214441]

6/12/142 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
Introduction to Collections
•Acollection—sometimescalledacontainer—issimplyanobject
thatgroupsmultipleelementsintoasingleunit.
•Collectionsareusedtostore,retrieve,manipulate,and
communicateaggregatedata.
•Representdataitemsthatformanaturalgroup,suchas:
–Apokerhand(acollectionofcards)
–Amailfolder(acollectionofletters)
–Atelephonedirectory(amappingofnamestophonenumbers)

6/12/143 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
What is a Collections Framework
•Acollections frameworkisaunifiedarchitectureforrepresenting
andmanipulatingcollections.
•Allcollectionsframeworkscontainthefollowing:
–Interfaces:Theseareabstractdatatypesthatrepresent
collections
–Implementations:Thesearetheconcreteimplementationsof
thecollectioninterfaces.
–Algorithms:Thesearethemethodsthatperformuseful
computations,suchassearchingandsorting
6/12/144 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
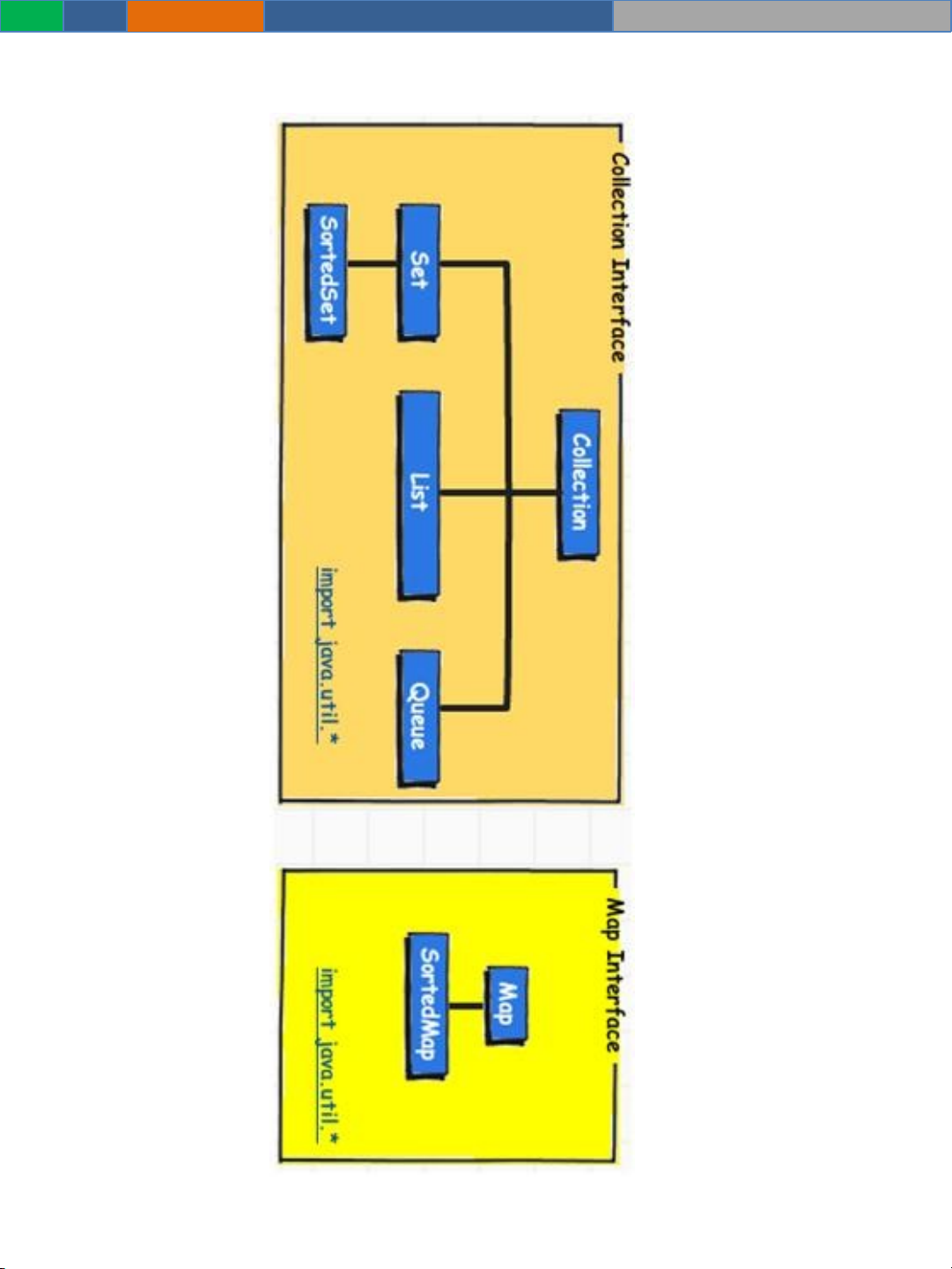
Collections Interface
6/12/145 /XX MÔN: C U TRÚC D LI UẤ Ữ Ệ GV: NGUY N XUÂN VINHỄ
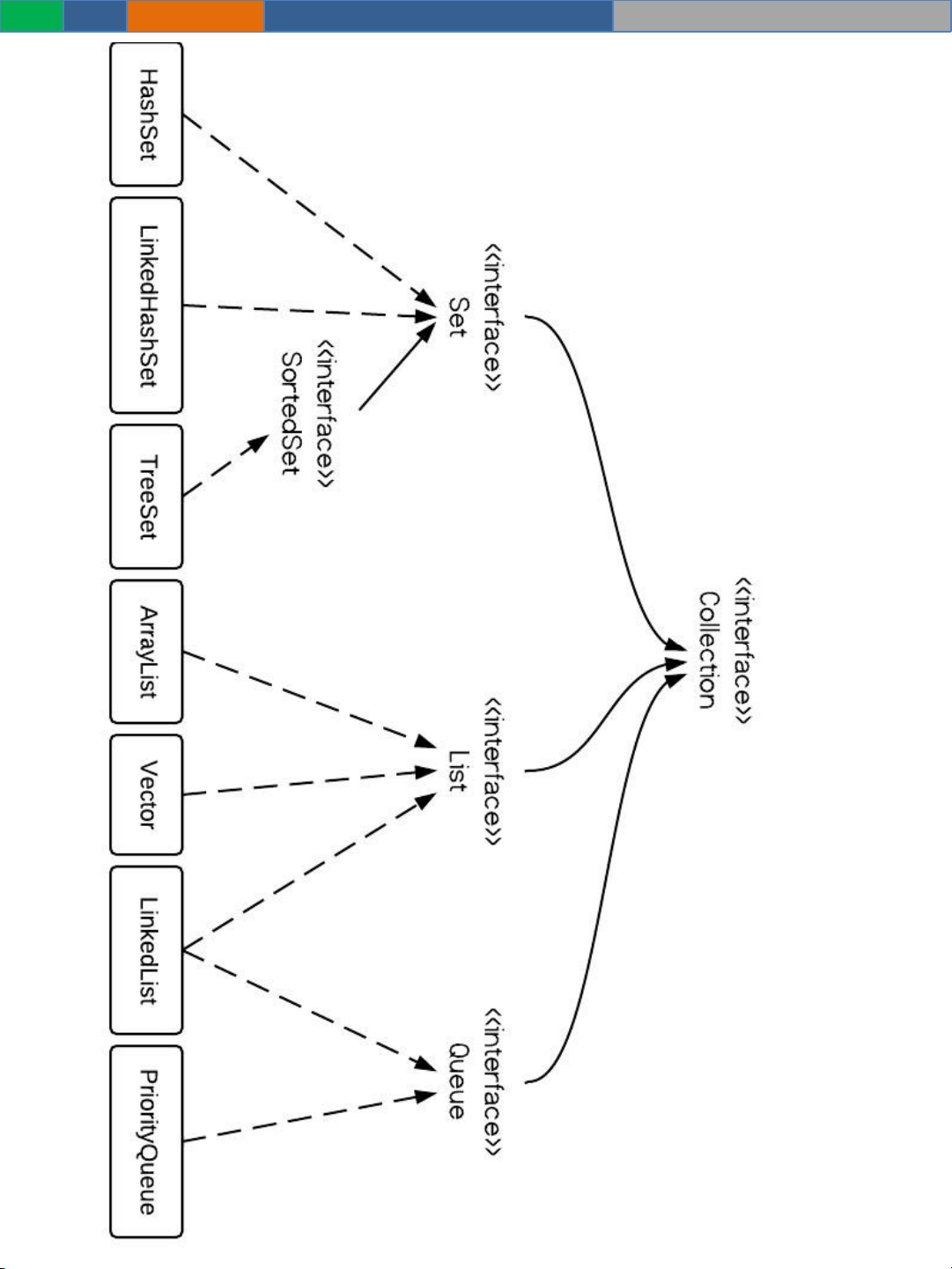
Collections Implementations

![Bài giảng Thực hành cơ sở dữ liệu Trường ĐH Công Nghệ [năm] mới nhất](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251120/oursky02/135x160/14661768233842.jpg)
























