
CHƯƠNG 3: UI & UX TRONG THIẾT KẾ WEBSITE
32
Download miễn phí gì cũng có tại ilook.asia
TRƯỜNG CAO ĐẲNG KỸ THUẬT CAO THẮNG
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

CHƯƠNG 3: UI và UX trong thiết kế website
!
Khái niệm về UI và UX
33
!
Thói quen trải nghiệm của người dùng
Học lập trình trực tuyến tại itclass.vn
!
Cách thiết kế giao diện tổng quan
!
Cách thiết kế bố cục trang
!
Cách thiết kế đồ hoạ
Download miễn phí gì cũng có tại ilook.asia
TRƯỜNG CAO ĐẲNG KỸ THUẬT CAO THẮNG
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Khái niệm về UI và UX (tt)
34
Học lập trình trực tuyến tại itclass.vn
!
UX (USER EXPERIENCE) là gì?
!
UI (USER INTERFACE) là gì?
Download miễn phí gì cũng có tại ilook.asia
TRƯỜNG CAO ĐẲNG KỸ THUẬT CAO THẮNG
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Thói quen trải nghiệm người dùng
35
Học lập trình trực tuyến tại itclass.vn
NOT THINKING
...and these
are today’s
special deals.
Memory,
Modems...
There it is:
Monitors.
Click
OK. This looks
like the product
categories...
THINKING
Hmm. Pretty
busy. Where
should I start?
Hmm. Why did
they call it
that?
Can I click on
that?
Is that the
navigation? Or
is that it over
there?
Why did they
put that there?
Those two links
seem like they’re
the same thing.
Are they really?
Download miễn phí gì cũng có tại ilook.asia
TRƯỜNG CAO ĐẲNG KỸ THUẬT CAO THẮNG
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thói quen trải nghiệm người dùng
36
Học lập trình trực tuyến tại itclass.vn
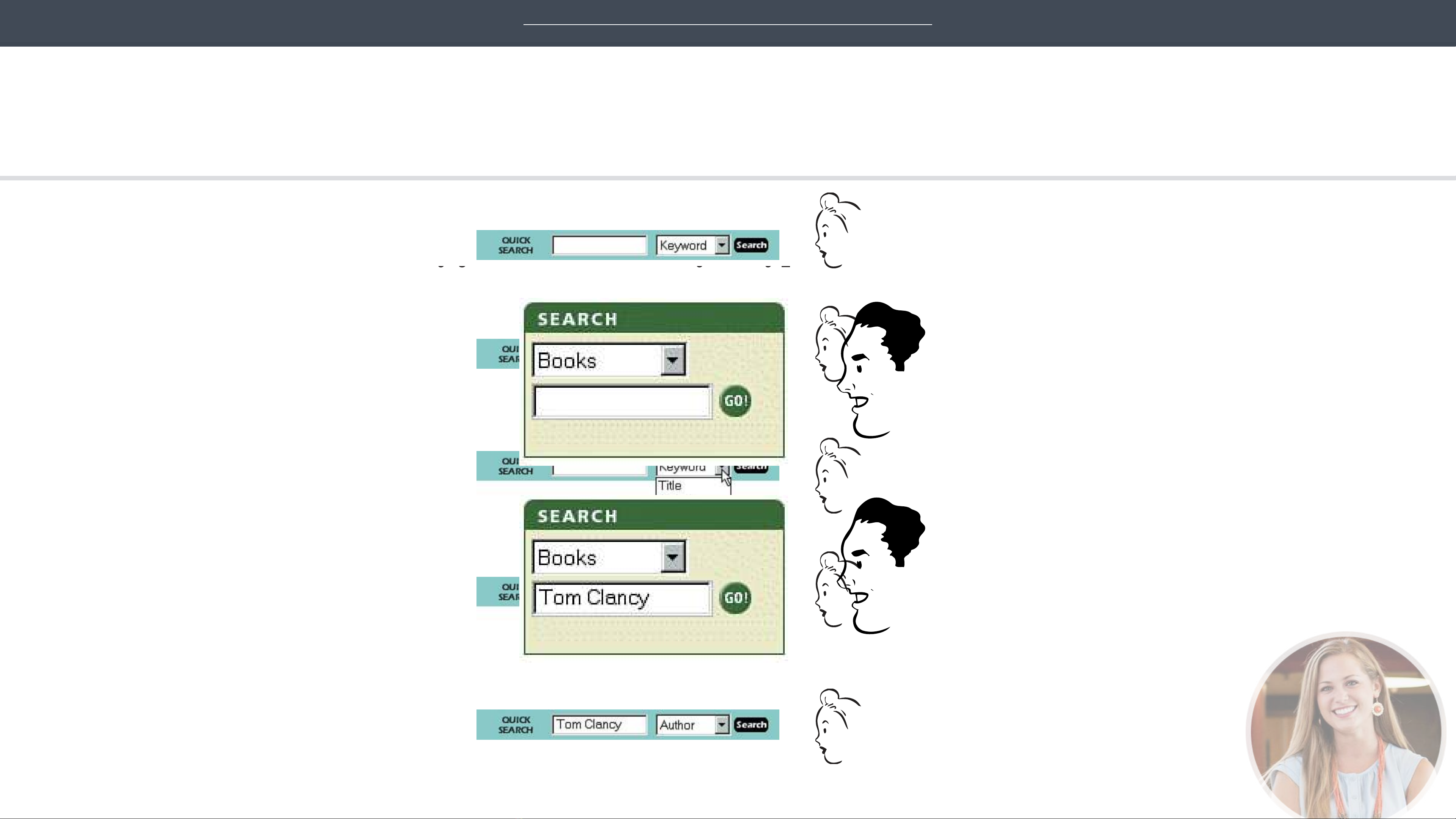
MOST BOOKSTORE SITES Let’s see. “Quick Search.”
That must be the same as
Search,” right?
Do I have to click on that drop-down
menu thing?
All I know about the book is that it’s
by Tom Clancy. Is Clancy a keyword?
(What is a keyword, anyway?)
I guess I have to use the menu.
Clicks on the arrow
Title. Author. Keyword.”
OK. I want “Author.”
Clicks “Author”
Types “Tom Clancy”
Clicks “Search”
“
“
distinction. They just look at what you type and do whatever makes the most sense
OK. “Search books
for
_____
.”
Types “Tom Clancy”
Clicks “Go”
AMAZON.COM
Download miễn phí gì cũng có tại ilook.asia
TRƯỜNG CAO ĐẲNG KỸ THUẬT CAO THẮNG
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



















![Hệ thống quản lý cửa hàng bán thức ăn nhanh: Bài tập lớn [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251112/nguyenhuan6724@gmail.com/135x160/54361762936114.jpg)
![Bộ câu hỏi trắc nghiệm Nhập môn Công nghệ phần mềm [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251111/nguyenhoangkhang07207@gmail.com/135x160/20831762916734.jpg)





