2/17/2014
1
Trường Đại học Bách Khoa Hà Nội
Viện Điện tử Viễn thông
Thông tin di động
Mobile Communications
TS. Đỗ Trọng Tuấn
Bộ môn Kỹ thuật thông tin
Hà Nội, 04-2011
2/17/2014
2
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ
trong mạng GSM

2/17/2014
3
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ GSM
Location Information-GSM Service Area Hierarchy
2/17/2014
4
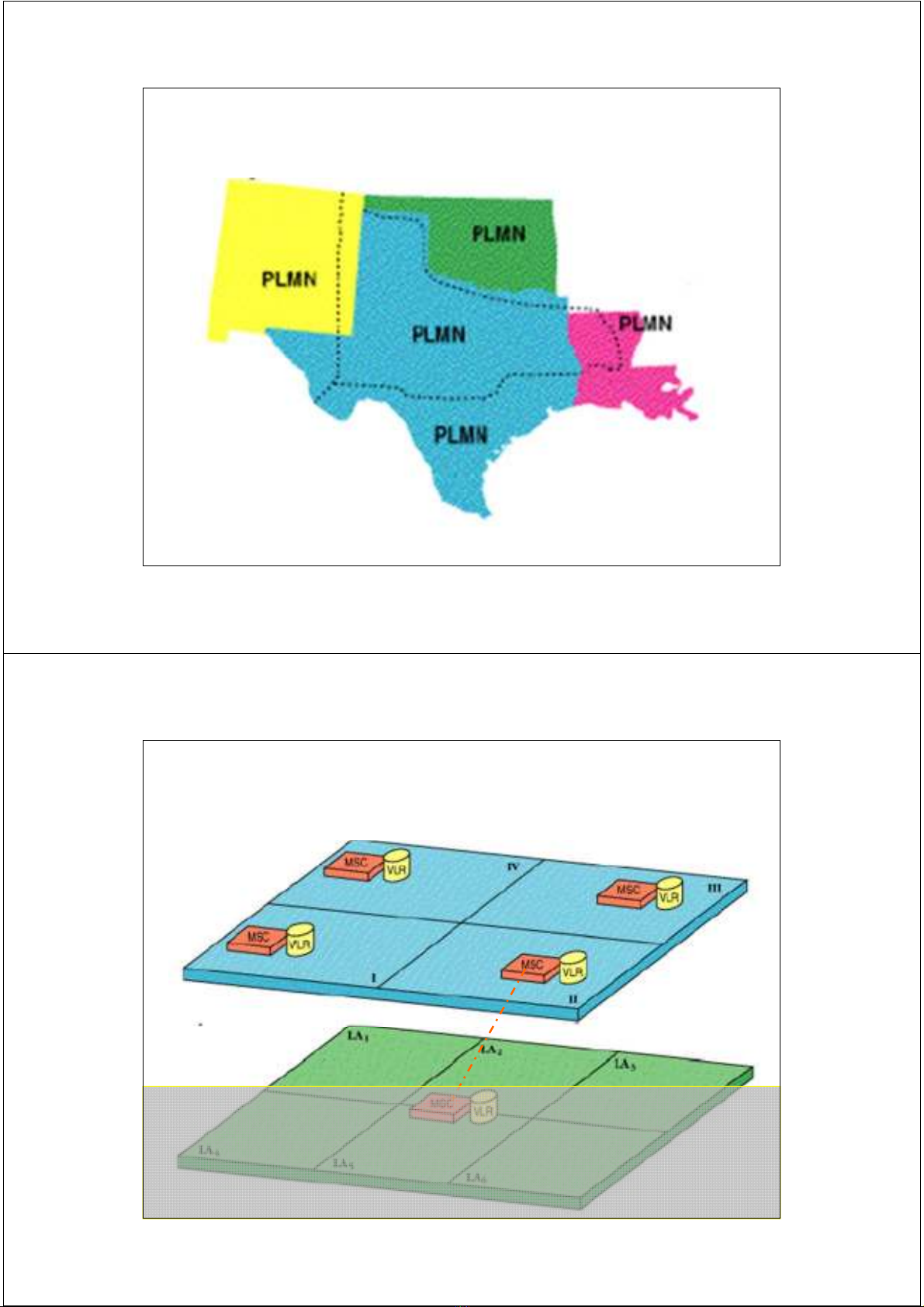
GSM Service Area
Service area = the area
in which a subscriber
an access the network.
Location Information-GSM Service Area Hierarchy
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ GSM
2/17/2014
5
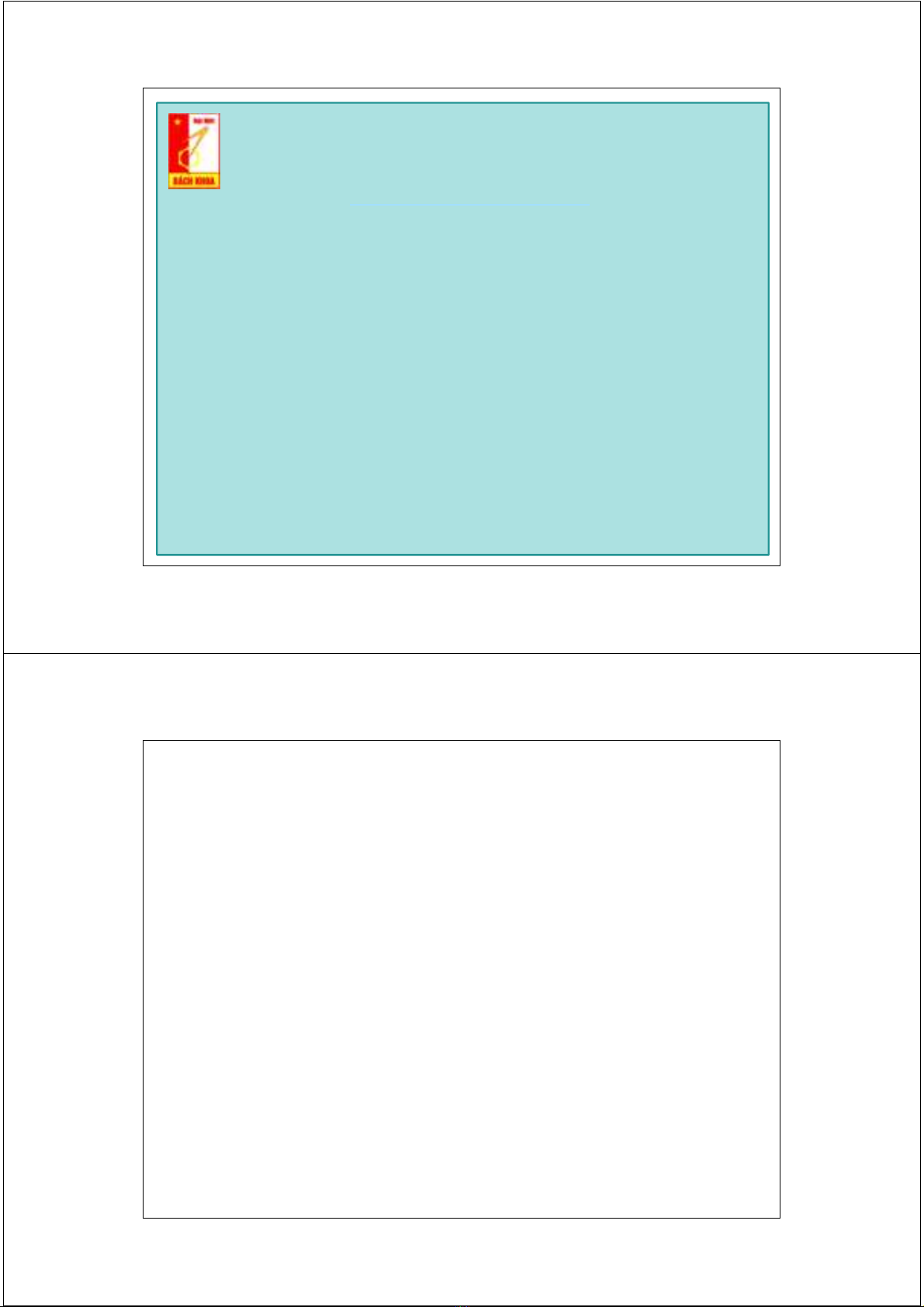
Vùng phục vụ PLMN
2/17/2014
6
Vùng định vị LAI và vùng phục vụ MSC/VLR
Vùng định vị LA là vùng gồm một số cell do nhà
quy hoạch ấn định tại đó MS có thể di chuyển tự
do mà không cần cập nhật lại vị trí.

2/17/2014
7
Số nhận dạng vùng định vị LAI
Location Area
Code (LAC)
Mobile country
Code (MCC)
3 digits 2 digits
Số LAI: Location Area Identity => Số nhận dạng vùng định vị
Location Area
Code (LAC)
Mobile country
Code (MCC)
3 digits 2 digits
Số nhận dạng ô toàn cầu GCI:
GCI = MCC + MNC + LAC + GCI = LAI + GCI
Global Cell
Identity (GCI)
2 Bytes 2 Bytes
2 Bytes
Mobile
Network Code
(MNC)
Mobile Network
Code (MNC)
2/17/2014
8
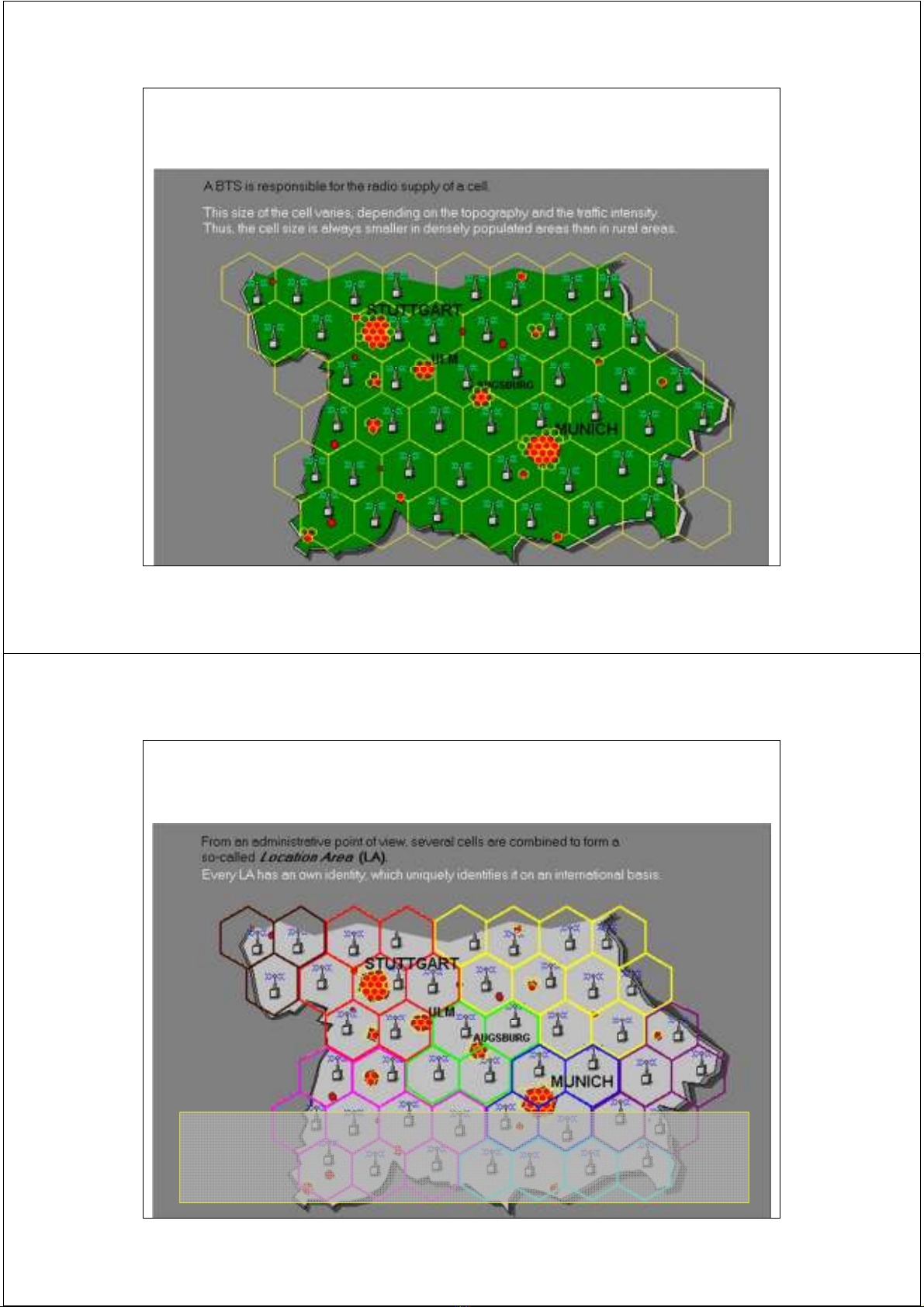
Location Information-GSM Service Area Hierarchy
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ GSM
2/17/2014
9
Location Information-GSM Service Area Hierarchy
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ GSM
2/17/2014
10
Số nhận dạng vùng định vị LAI được lưu giữ
ở đâu ?
Location Information-GSM Service Area Hierarchy
Phân cấp vùng phục vụ GSM